
Top 10 Trends in Phishing Attacks (2024)
Phishing continues to evolve in 2024, posing a significant threat to both individuals and organizations. This form of social engineering is designed to deceive victims into revealing sensitive information or performing unauthorized actions, often leading to fraud. The latest Phishing Trends reports from the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) shed light on the scale of phishing attacks in the year of 2024.
In the first quarter of 2024 alone, nearly 964,000 phishing attacks were recorded, with a notable rise in voice phishing, or “vishing.” In parallel, social media platforms remain the most targeted, making up over 1/3 of all attacks.

AI illustration for “Phishing Trends 2024” by DALL-E
As we explore the top phishing trends this year, it’s essential to stay ahead of these threats and understand how attackers continue to refine their tactics, including leveraging phone-based scams. This blog post will explore the evolving landscape, drawing from the APWG‘s findings and more, and focusing on the tactics you need to watch for in 2024.
1. Phishing Websites Are A Steady Threat in 2024
Phishing websites remain a significant vehicle for fraud and social engineering attacks in 2024.
In the first quarter of 2024, APWG reported 963,994 unique phishing websites, and this number further decreased to 877,536 in the second quarter. Interestingly, even with this decline, phishing remains a persistent issue. Interisle Consulting reported a slight year-over-year increase in phishing attacks globally, rising by 50,000 to just under 1.9 million between May 2023 and April 2024.
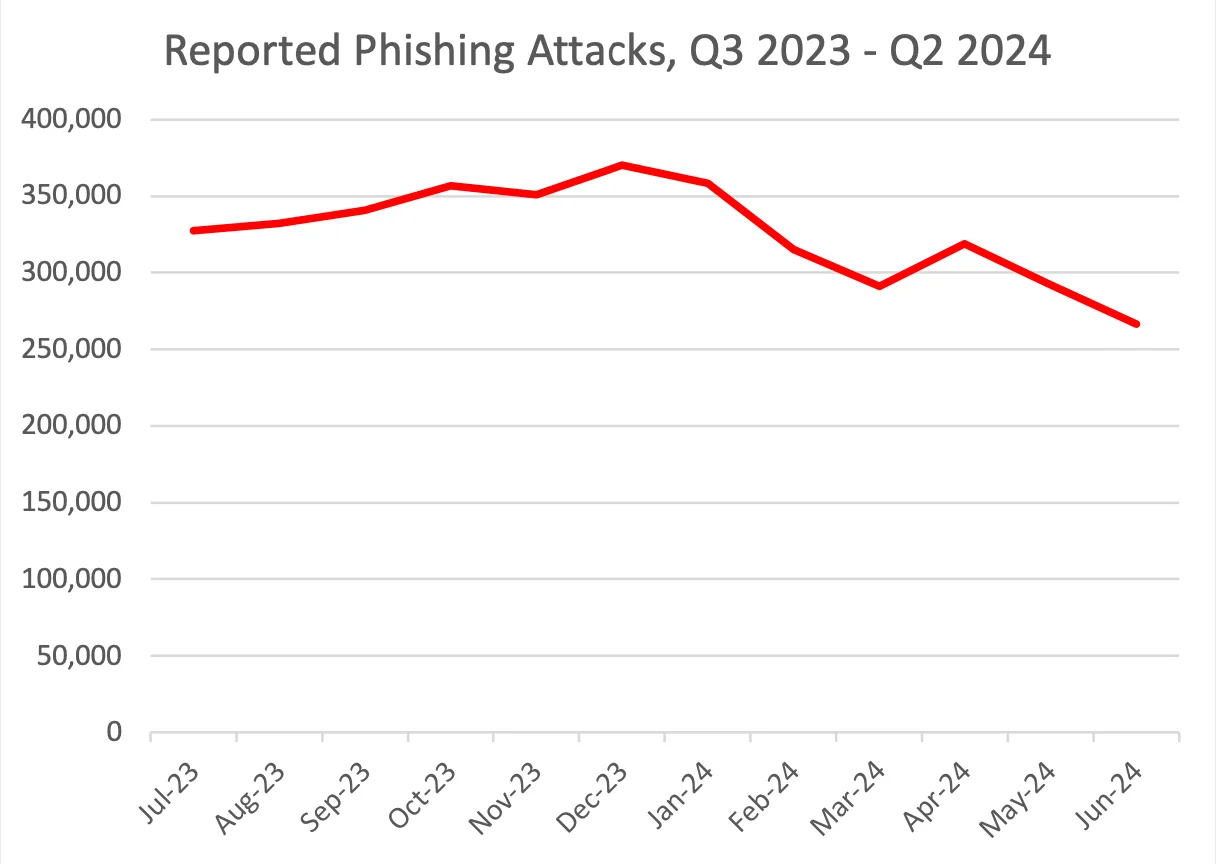
The decline in reported phishing attacks from Q3 2023 to Q2 2024 suggests fluctuations (APWG)
The reduced number of reported phishing websites could also indicate that threat actors are shifting towards more sophisticated, targeted attacks.
Some phishing websites go beyond mere deception, deploying stealer malware that captures user data. The data may end up in stealer logs, shared across the Dark Web, where it can be accessed by other malicious actors. This complicates the challenges faced by cybersecurity efforts, as these tactics require more advanced detection methods.
Additionally, many phishing sites are designed to mimic legitimate brands and services, making detection and prevention more challenging. As a result, URL-based fraud increased by 10% in Q2 2024 compared to Q1, highlighting the ongoing risk that phishing websites pose despite the apparent drop in overall attack numbers.
SOCRadar LABS provides free services such as Phishing Radar, which helps identify phishing attacks swiftly. Our AI-powered Digital Risk Protection platform scans millions of domain registrations to detect malicious domains and alerts on suspicious activity.
Phishing Radar service on SOCRadar LABS
2. Which Sector and Country Are the Most Targeted by Phishing Attacks in 2024?
Phishing attackers are constantly evolving their strategies to target specific sectors and countries. Based on APWG’s reports for Q1 and Q2 2024, another interesting phishing trend is that social media platforms continue to be the most frequently targeted sector, accounting for 37.6% of such cyberattacks in Q1 and 32.9% in Q2.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and webmail services also consistently attract phishing campaigns, making up 21% of attacks in Q1 and rising to 25.6% by Q2.
Other notable sectors include financial institutions and payment services, which combined, made up over 17% of phishing targets throughout the first half of 2024.
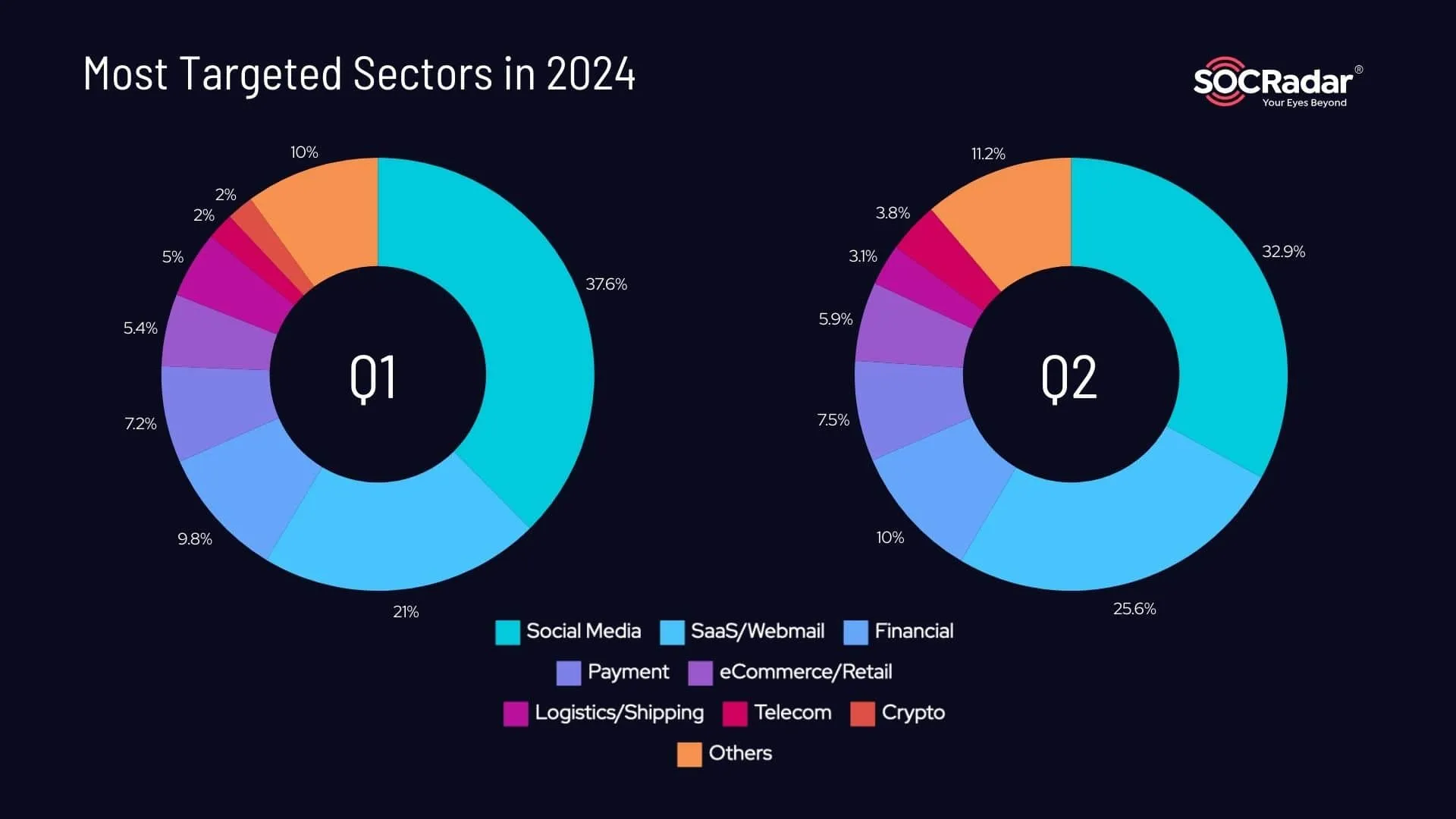
What sectors had more phishing attacks in 2024?
When it comes to countries, the United States remains the most targeted by phishing attacks, with a significant lead over other nations.
Other countries highly targeted in phishing campaigns include the UK, Brazil, Turkey, and Russia, as shown in the heat map from our Phishing Radar. These regions represent key areas where attackers focus their efforts.
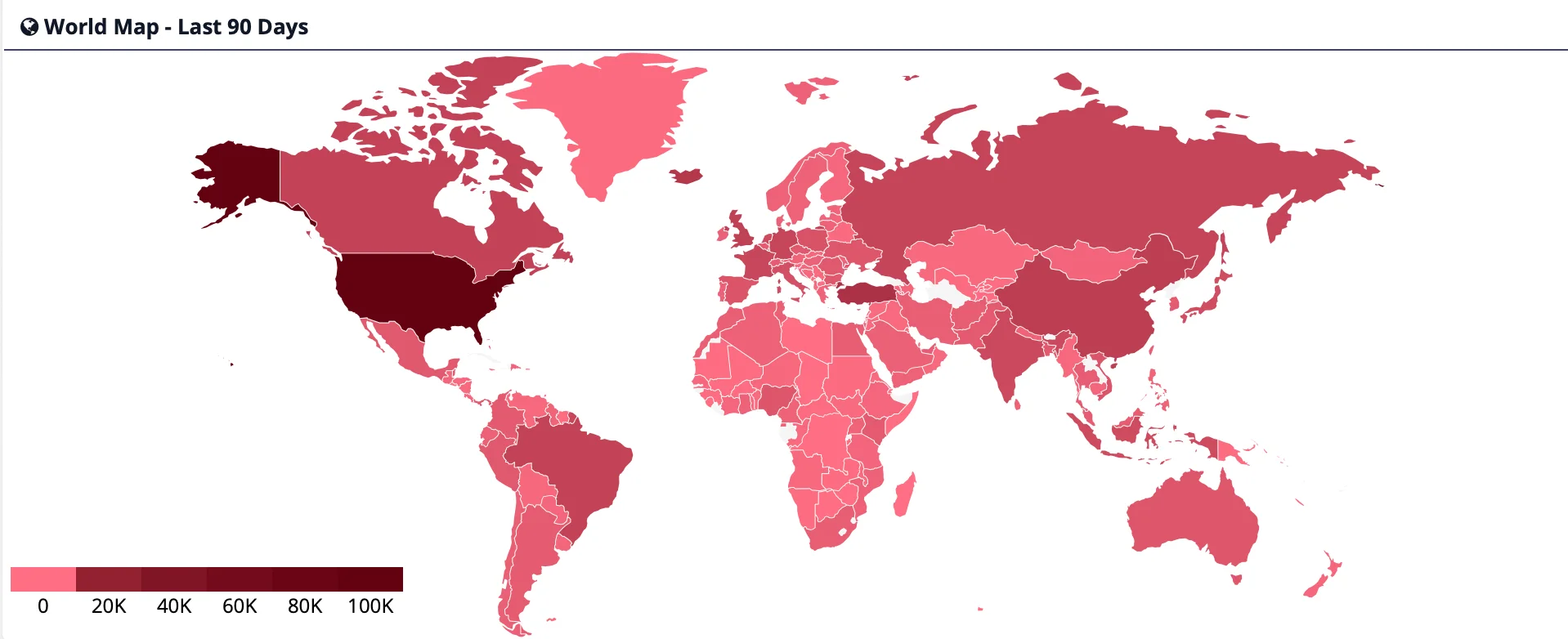
Phishing Attacks by Country (Last 90 Days)
For more detailed insights into the latest threat landscape across industries and countries, you can access free, instant Industry and Country Threat Landscape Reports via SOCRadar LABS.
3. Phishing Email Campaigns
According to reports, the number of unique phishing email campaigns fluctuated significantly throughout the first half of the year.
In January 2024 alone, 50,837 unique phishing email campaigns were detected, though this number fell dramatically to 24,086 in February before rebounding to 41,550 by March. By Q2 2024, the number of unique phishing campaigns had again risen, with May seeing the highest number at 33,874 campaigns.
Attackers are increasingly using sophisticated techniques, often varying the subject lines and content of their emails to avoid detection. The changing frequency of these attacks, with still high numbers, shows that phishing operators are actively diversifying their strategies.
| Q1 2024 | January | 50,837 |
| February | 24,086 | |
| March | 41,550 | |
| Q2 2024 | April | 31,005 |
| May | 33,874 | |
| June | 31,173 |
Number of unique phishing email campaigns detected from January to June 2024
As these campaigns grow more targeted and frequent, organizations must adopt more advanced phishing detection strategies to keep pace with the evolving threat landscape.
To stay informed on the latest phishing and cyberattack trends, you can explore SOCRadar’s Campaigns page on the platform. It provides comprehensive insights into various cyberattack campaigns, including phishing schemes, malware delivery tactics, and more.
SOCRadar Campaigns page. View its free version on SOCRadar LABS.
4. Hijacking Trusted Names for Phishing: Top Impersonated Companies in 2024
Phishers are increasingly targeting well-known brands, leveraging their reputation to lure unsuspecting users into clicking on malicious links.
Over the years, the number of legitimate entities affected by phishing attacks has fluctuated significantly, peaking during specific periods. According to data from Statista, as of March 2024, the number of affected brands has seen a notable decline after a period of heightened activity.
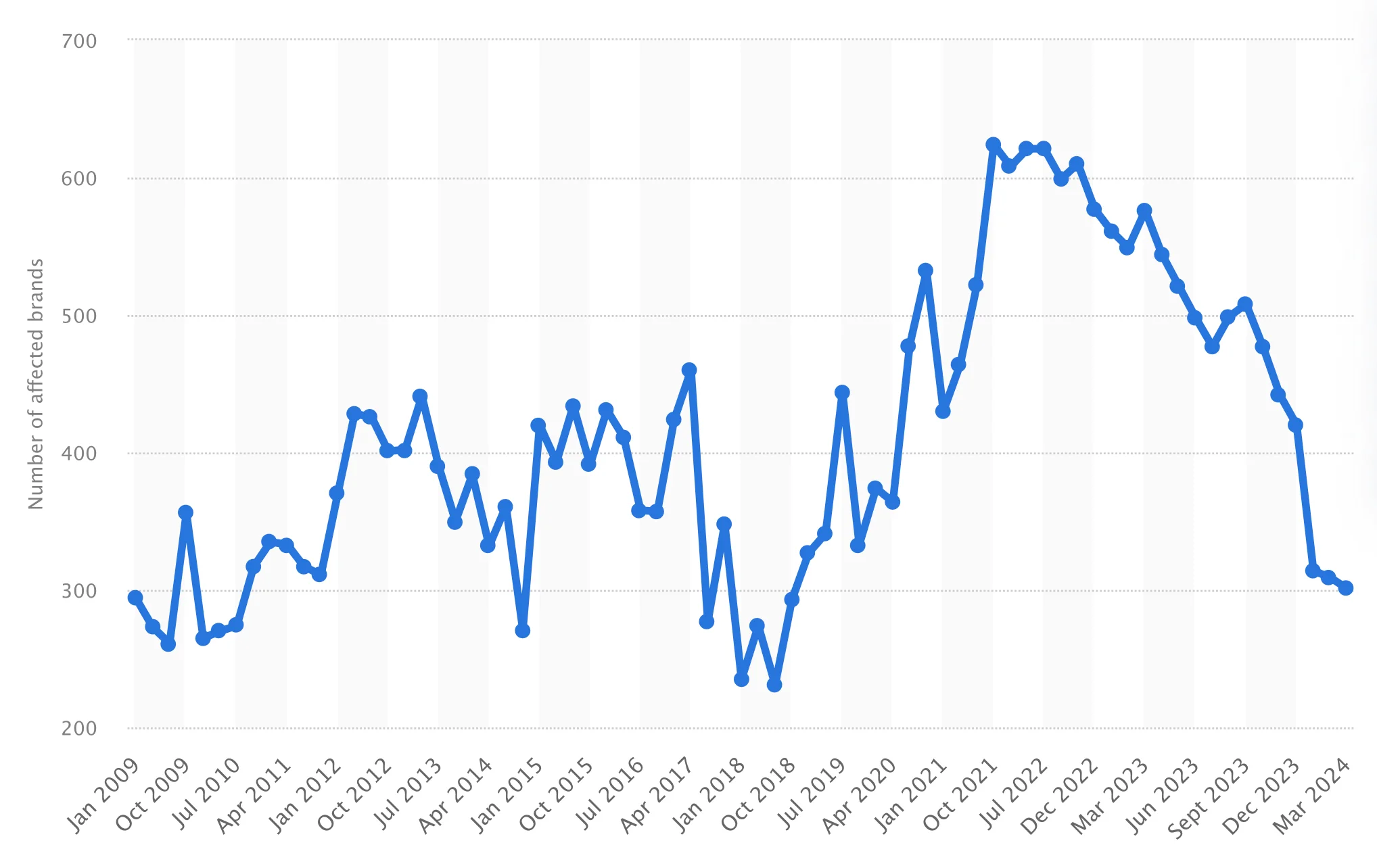
Number of brands hijacked by phishing attacks, 2009-2024 (Statista)
This decline could suggest improved security measures from some organizations, although the overall threat remains prevalent.
Moreover, according to a report from Zscaler, Microsoft was the most frequently impersonated brand in phishing schemes, accounting for 43.1% of all attempts. OneDrive followed at 11.6%, with Okta, Adobe, and SharePoint rounding out the top five most targeted brands.
Attackers often exploit the familiarity of these brands to create a false sense of security, tricking users into providing sensitive information or downloading malicious content.
5. BEC Attacks Are A Persistent Threat in the Phishing Landscape
Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks remain a major trend in phishing, exploiting trust within organizations to steal financial or sensitive information. Attackers often impersonate high-level executives, requesting urgent fund transfers or gift card purchases. They also target supply chains, posing as vendors to manipulate payment details.
A BEC attack typically relies on credentials stolen through phishing scams, which are frequently sold or traded on Dark Web forums, enabling attackers to impersonate high-level executives more convincingly.
In Q1 2024, the average amount requested in BEC wire transfer attacks was $84,059, rising to $89,520 in Q2, according to the reports. While the volume of attacks slightly decreased, their financial impact continues to grow. For example, BEC attacks were responsible for $2.9 billion in losses in the U.S. during 2023, according to the FBI’s IC3.
APWG also reports that gift card scams, advance fee fraud, and payroll diversion remain common in BEC-related phishing.
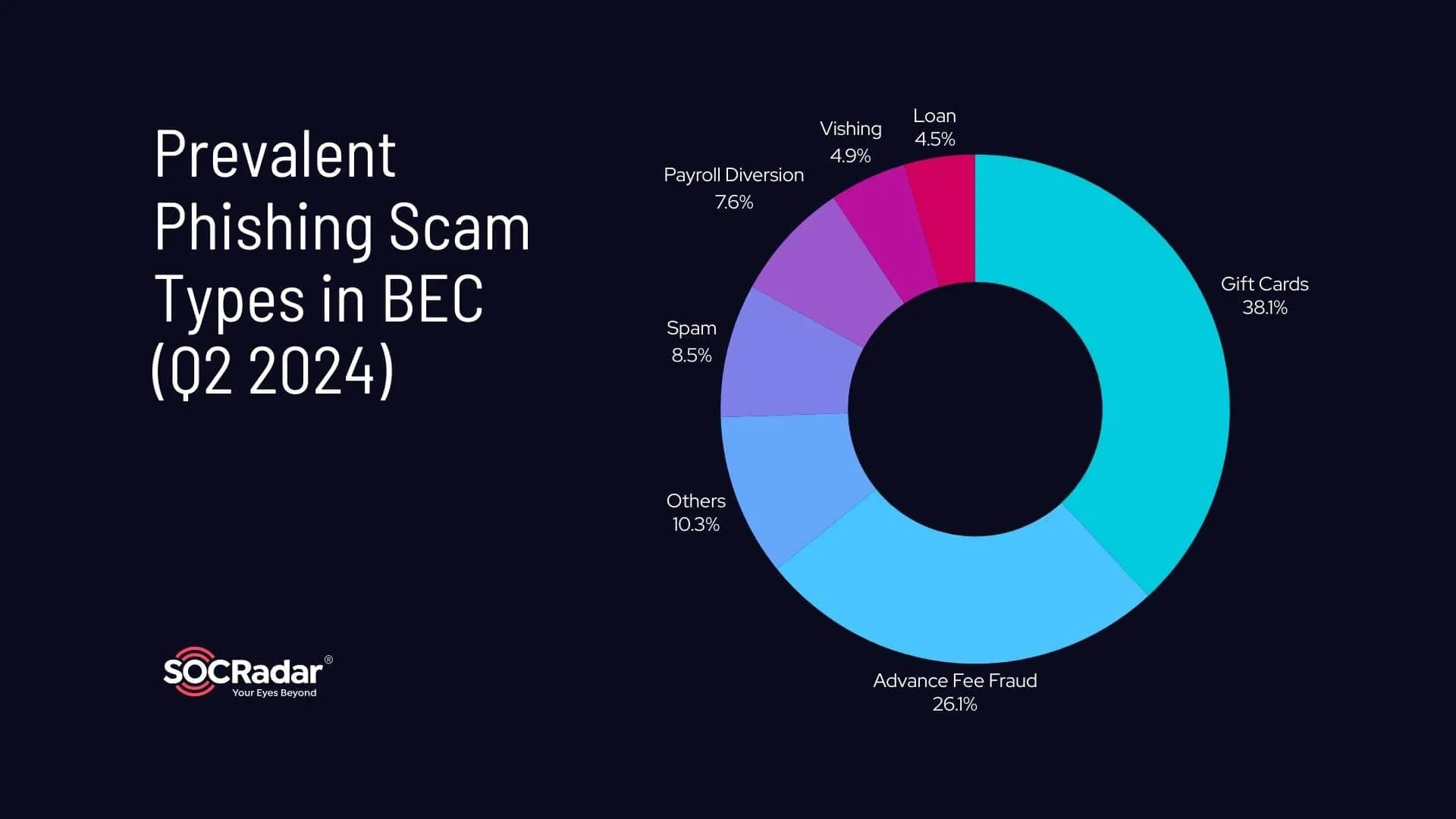
Most common BEC phishing scams in 2024
For further protection, SOCRadar’s Brand Protection module offers organizations comprehensive monitoring to detect and respond to potential impersonation threats.
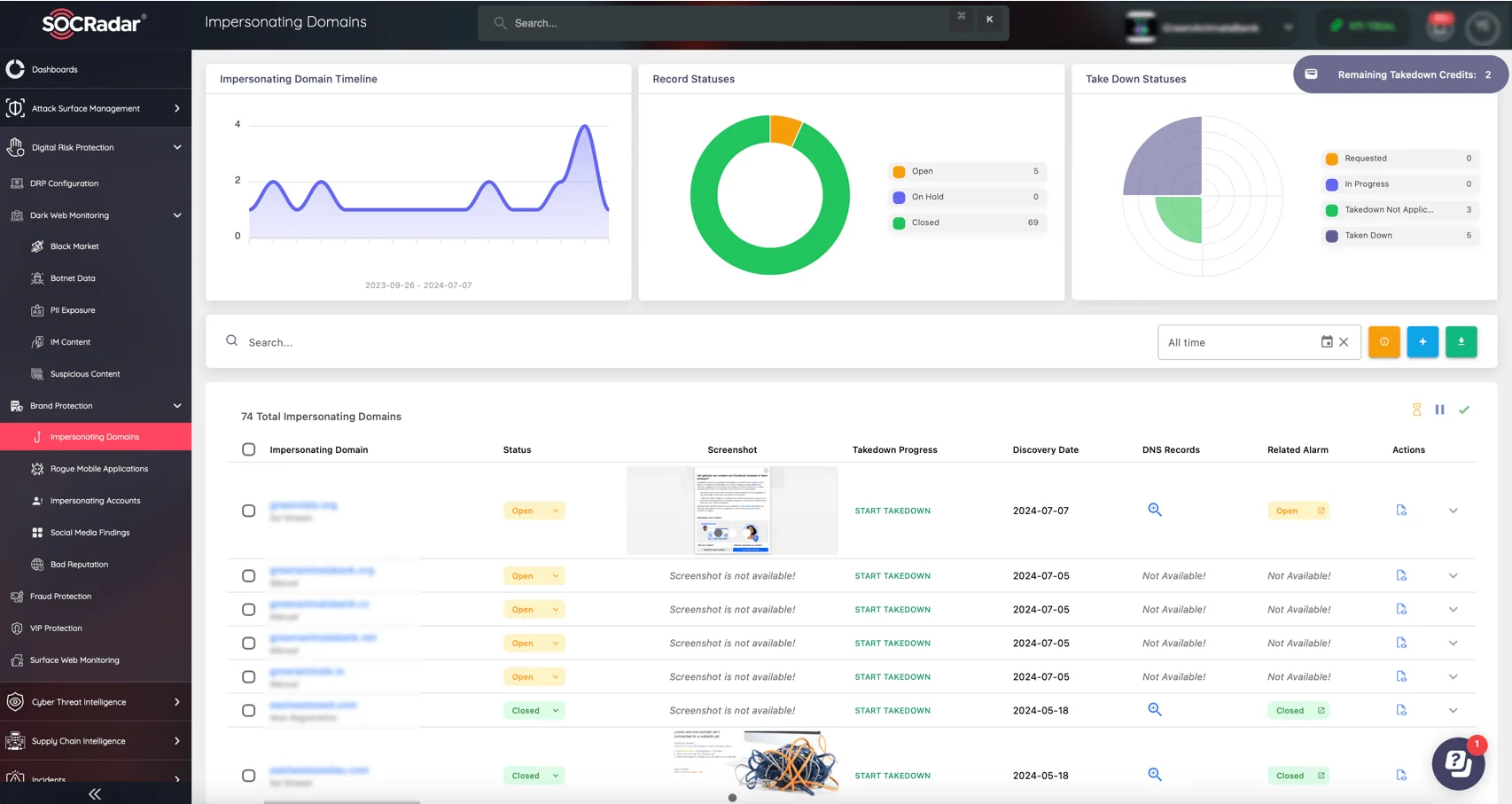
Impersonating Domains, SOCRadar’s Brand Protection
From spoofed domains, social media accounts, to rogue mobile apps, organizations can quickly act to takedown these threats and safeguard their operations with the Brand Protection module.
Learn more about how to stop BEC attacks with SOCRadar.
6. Phone-Based Phishing Attacks Surge
Phishing via phone calls, or vishing, has seen a sharp increase, with scammers using this tactic to directly engage victims. As of 2024, over 20% of fraud-related assets now involve phone numbers, according to the Q1 report, and the number of these assets increase each quarter.
Vishing often involves fraudsters impersonating trusted entities to trick individuals into revealing personal information or making financial transfers.
One common approach is hybrid phishing, where victims receive a fake email receipt and are urged to call a support number. Once on the phone, scammers extract sensitive data or convince victims to send money. Vishing’s rise is partly due to its ability to bypass advanced email filters, making it easier for attackers to reach victims directly through phone calls.
Unlike email, phone calls are harder to block, providing scammers with a more personal method to manipulate victims, whether through building trust or creating panic.
7. Top Domain Registrars in Phishing Schemes
Domain registrars play a critical role in the execution of phishing campaigns, as attackers often register fake domains to impersonate legitimate entities. These domains are used in phishing websites to deceive victims into providing sensitive information, making fraudulent payments, or to distribute malware.
According to APWG’s reports from Q1 and Q2 2024, certain domain registrars are more commonly exploited by attackers to register Business Email Compromise (BEC) domains. In Q1 2024, NameCheap was the most frequently used registrar for BEC domains, accounting for 36% of registrations. Other popular registrars included Squarespace (15%), Hostinger (11%), and TUCOWS (8%).
By Q2 2024, NameCheap‘s share increased further to 40.7%, while other registrars like Hostinger UAB (7.2%), TUCOWS (7.9%), and GoDaddy (4.1%) also played notable roles.
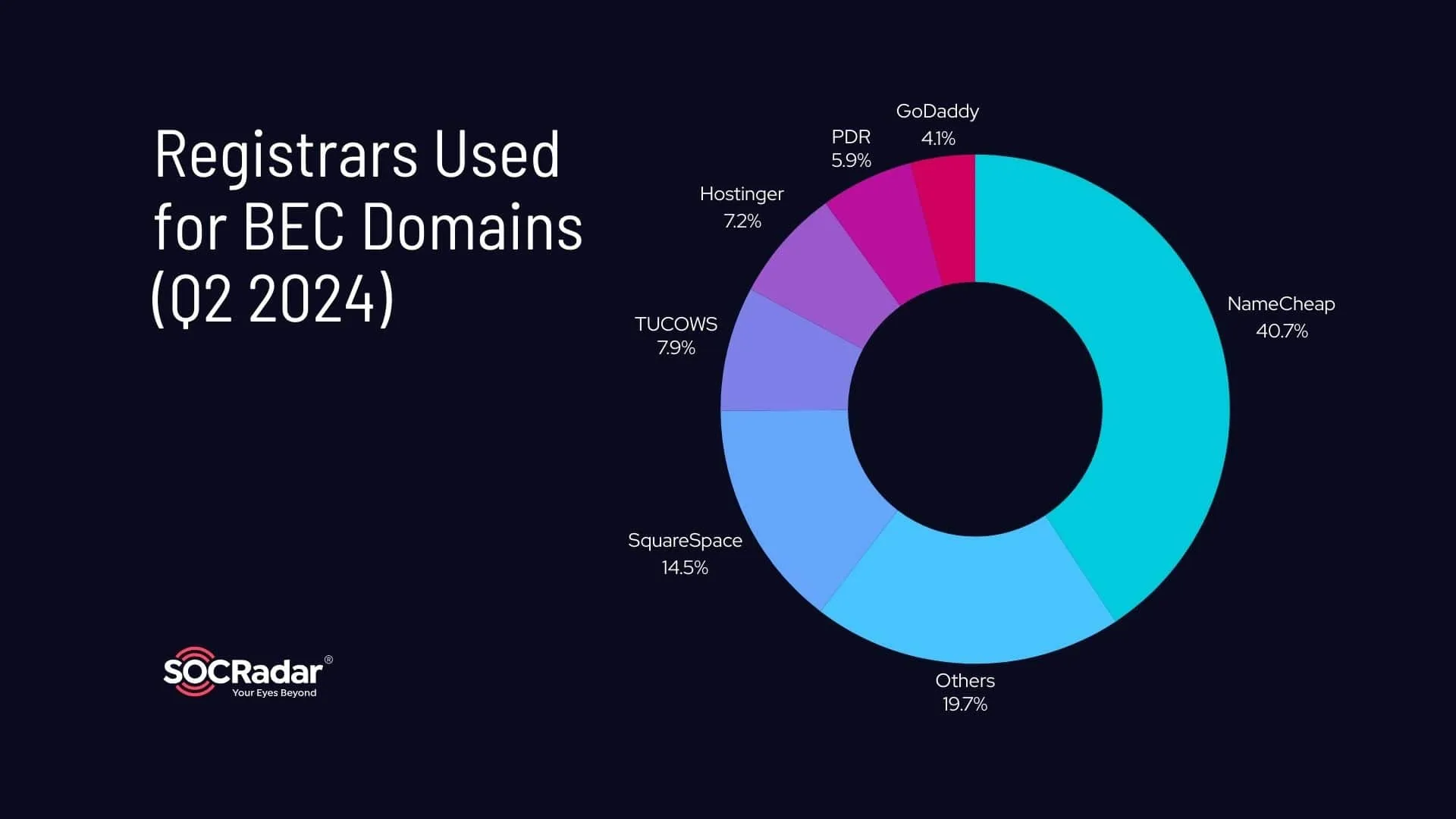
Top domain registrars used in BEC phishing attacks
8. Top TLDs in Phishing Attacks in 2024
A Top-Level Domain (TLD) is the last segment of a domain name, such as .com, .net, or .org. In phishing attacks, the choice of TLD can significantly impact the success of a campaign.
While free domains offer a cost-effective way for attackers to set up phishing websites, more well-known TLDs, like .com or .org, often bring higher credibility and success rates for phishing schemes.
Data from the Phishing Radar reveals that .com remains the most commonly used TLD in phishing attacks, followed by other TLDs like .org, .top, and .xyz. Threat actors often choose these TLDs to appear more legitimate, increasing the likelihood that victims will trust and engage with malicious content.
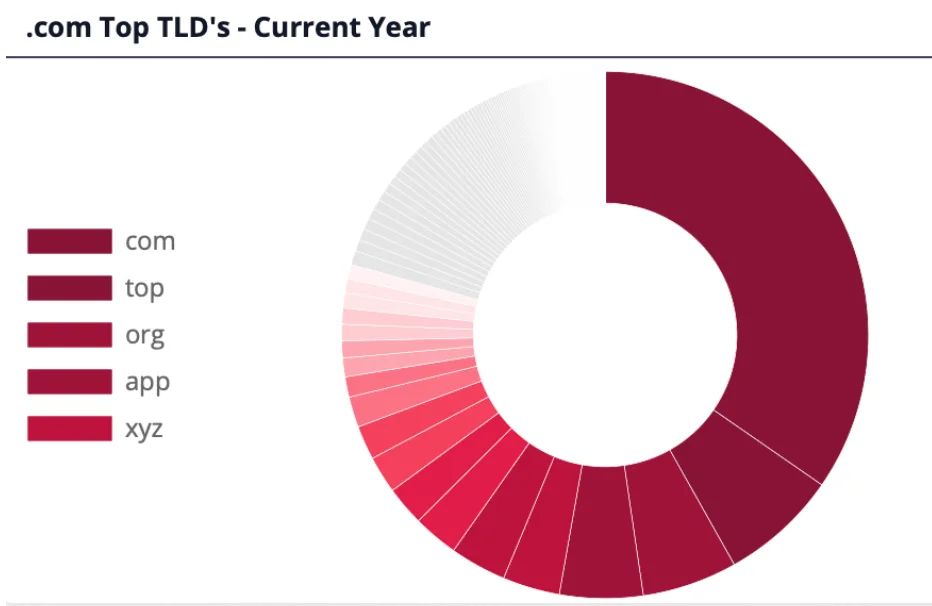
Top TLDs used in phishing in 2024
By recognizing the most commonly exploited TLDs, organizations can strengthen their phishing detection strategies, keeping a closer watch on suspicious domains.
For more information on the commonly targeted TLDs, check out SOCRadar’s analysis on the top 10 TLDs used in phishing.
9. Webmail Providers Used in Phishing Attacks
In Q2 2024, 72% of BEC attacks were launched using free email domains. The remaining 28% of attacks used a mix of maliciously registered domains and compromised email accounts.
Among the webmail providers, Google’s Gmail was the top choice for scammers, being used in 72.4% of BEC-related attacks.
Microsoft‘s webmail services came second, contributing to 16.3% of webmail-based BEC attacks. The widespread use of these platforms highlights the ease with which attackers can set up and exploit free webmail accounts to carry out phishing schemes.

Top webmail providers in 2024 BEC attacks
To protect your organization against these threats, you can leverage SOCRadar Labs’ Email Grader, a free tool that allows you to assess your email server’s security.
10. Phishing Attacks Exploiting Major Events
Phishing attacks often capitalize on major events, such as sports tournaments, Black Friday sales, concerts, or even officials in elections, to trick victims. These high-profile events provide an opportunity for attackers to impersonate some vendors or officials, offering fake products or services.
One common method involves scammers setting up websites to sell fraudulent event tickets, leveraging the urgency and popularity of these occasions. For example, during Black Friday, phishing emails offering too-good-to-be-true deals flood inboxes, while major sports events like the Olympics are prime targets for ticketing scams.
![Phishing Radar results for the paris2024[.]org domain](https://socradar.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/paris2024-phishing-radar.png.webp)
Phishing Radar results for the paris2024[.]org domain
A recent large-scale phishing campaign, dubbed “Ticket Heist,” targeted Russian-speaking individuals looking to purchase tickets for the 2024 Summer Olympics in Paris. The operation used over 700 fake domain names to lure victims into buying fake tickets. Additionally, the scammers expanded their efforts by offering fraudulent tickets for the UEFA European Championship and major music concerts. The entire operation was highly organized, with new domains being registered monthly.
Such phishing schemes continue to evolve, using official events as bait to target unaware victims.
Bonus: Rise of GenAI Is of the Latest Phishing Trends
The emergence of Generative AI tools has significantly accelerated the rise of phishing attacks. Cybercriminals now have the ability to craft highly convincing phishing emails and even generate malicious code at an unprecedented speed. These tools, particularly platforms like ChatGPT, allow attackers to refine their tactics and increase the scale of their operations.
Since the launch of ChatGPT in late 2022, phishing campaigns have surged. Researchers have reported a staggering 4,151% increase in malicious emails linked to the use of AI-driven tools. In 2024, the situation continues to escalate, with organizations facing an 856% rise in phishing emails compared to previous years. The capabilities provided by generative AI have transformed phishing from simple, clumsy scams into sophisticated campaigns that are much harder to detect.
As phishing becomes more advanced, it’s essential for organizations to strengthen their defenses and stay vigilant against these evolving threats.
Conclusion; Safeguard Against the Advancing Phishing Trends
Phishing remains one of the most pervasive cybersecurity threats in 2024. From the rise in BEC attacks and the exploitation of major events to the increasing use of vishing and the role of generative AI in phishing schemes, attackers continue to evolve their methods.
Key sectors like social media, finance, and retail remain prime targets, while webmail providers such as Gmail and Microsoft are frequently abused by cybercriminals. As phishing campaigns grow more sophisticated, organizations must stay proactive in their defenses.
Here are some recommendations to protect against phishing attacks:
- Be cautious with unsolicited communications – Verify the sender before clicking on links or downloading attachments.
- Regularly update software and email filters – Ensure your defenses are equipped to block the latest phishing tactics.
- Educate employees – Raise awareness about phishing scams and the latest techniques used by attackers. Be on the lookout for common red flags that signal a phishing attempt.
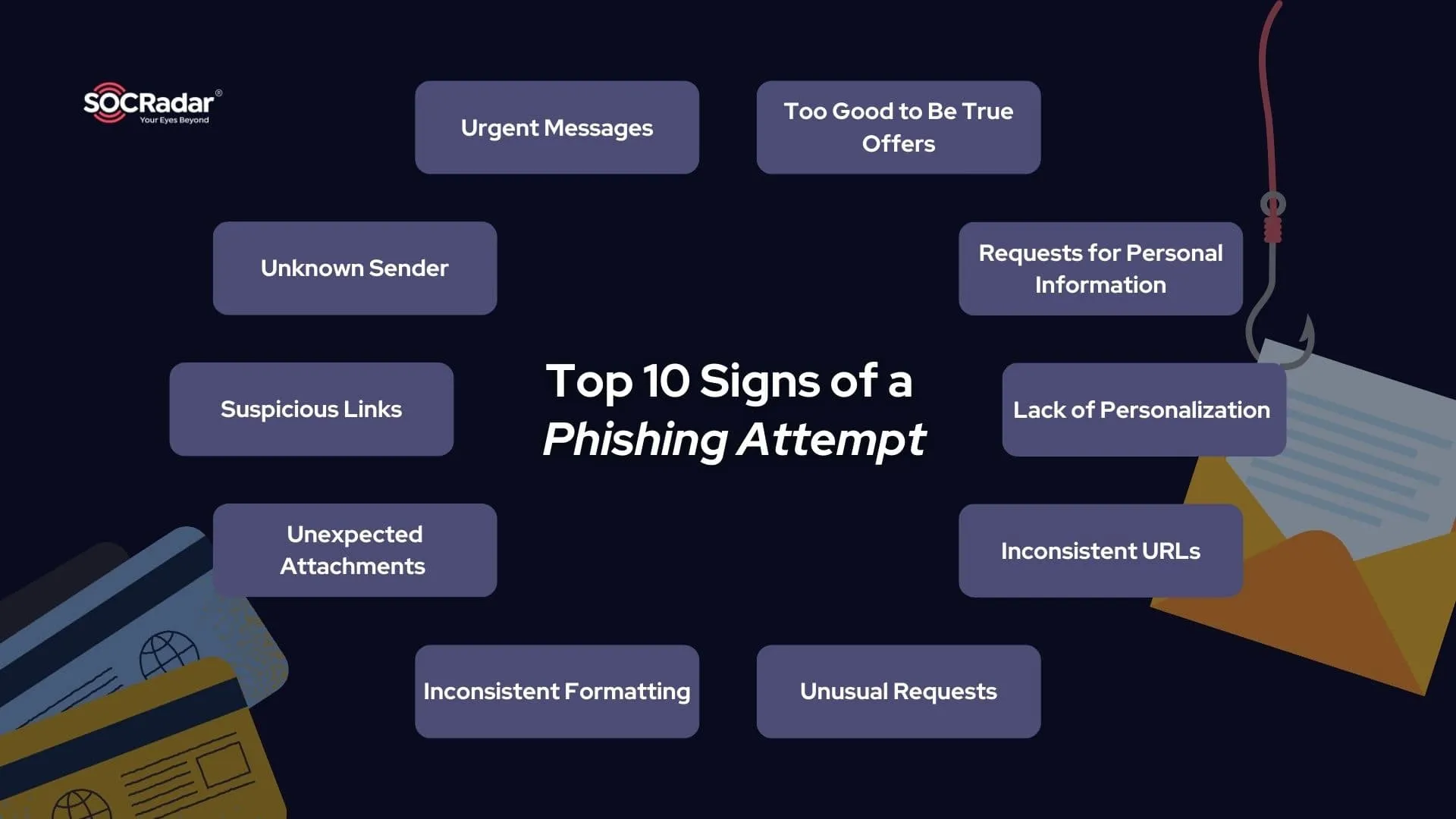
Top 10 signs of a phishing attempt
- Monitor domain registrations – Keep an eye on suspicious domains that may be used for phishing attacks.
- Leverage Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Adding an extra layer of security can help protect accounts from unauthorized access.
- Monitor Dark Web channels and forums – Stolen credentials may surface on Dark Web forums. Using SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring, you can easily monitor these channels and receive early warnings that can help prevent broader security breaches.





































