Major Cyberattacks in Review: August 2022
Threat actors did not stay idle in August, and as always, they continued their attacks on small or large companies, government organizations, and critical infrastructures that could disrupt daily life.
While ransomware attacks remained popular, data breaches and leaks were also on the agenda. Here are the most important cyber events of August at a glance.
Ransomware Attack Targets Semiconductor Firm Semikron

Semikron, a German manufacturer of power electronics, has revealed that its network was partially encrypted due to a ransomware attack.
With over 3,000 workers and locations in 24 countries, including Germany, Brazil, China, France, India, Italy, Slovakia, and the USA, Semikron is expected to generate over $461 million in revenue in 2020.
Semikron published a statement about the incident. The attackers have claimed that they stole data from their system. Several of Semikron’s IT systems and files have been encrypted as a result of the attack. Forensic analysis and adjustments are now being made on the entire network.
Although Semikron declined to provide details about the incident, a ransom note posted on one of the encrypted Semikron systems and obtained by BleepingComputer reveals it was an LV Ransomware attack and claims the hackers stole 2 TB worth of information.
A Cyberattack Resulted in the Closure of 7-Eleven Stores in Denmark

A cyberattack that affected the payment and checkout systems at 7-Eleven stores in Denmark resulted in the closure of 175 stores in the country.
“Working at the 7-eleven at Strøget and our checkout system does not work, all the country’s 7-eleven run with the same system, so all 7-eleven in Denmark are “closed” right now,” the 7-Eleven worker posted on Reddit.
The company confirmed that threat actors broke into its network and encrypted systems; it gave no further details about the group responsible.
Hackers Responsible for the Twilio Attack Also Target Cloudflare Employees

According to Cloudflare, a similar SMS phishing attempt to the one that compromised Twilio’s network also resulted in the theft of some of its employees’ login information.
76 employees and their families were the recipients of phishing emails that led them to a Cloudflare Okta login page copy located on the cloudflare-okta[.]com domain.
Even though the attackers gained access to the accounts of Cloudflare employees, they could not compromise the company’s systems since their efforts to log in using those accounts were rejected because they lacked the victims’ company-issued FIDO2-compliant security keys.
Network Breach Confirmed by Cisco Through Hack of Employee’s Google Account
The Lapsus$ extortion organization’s affiliate Yanluowang ransomware group announced on Tuesday night, August 10, that it had attacked Cisco and would release its files. Cisco posted a thorough comment about the incident on its official blog two hours following this allegation.
According to the published blog post, threat actors attempted to access the systems by using the password for the company network after gaining control of a Cisco employee’s personal Google account, most likely through a stealer log. The computers were then accessible remotely over VPN using this account information.
IoCs and other information about the incident can be found here.
3 Ransomware Groups Attacked an Automotive Supplier in Two Weeks
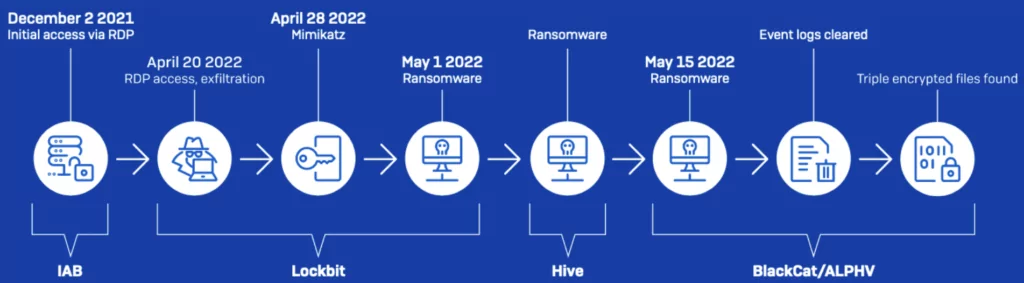
Over two weeks in May, three different ransomware gangs compromised the systems and encrypted the files of an automotive supplier, with two of the attacks taking place in the space of only two hours.
The attacks came after an initial intrusion into the company’s systems by a suspected initial access broker (IAB) in December 2021, who took advantage of a firewall misconfiguration to access the domain controller server via a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connection.
Following the initial intrusion, the victim’s network was also accessed on April 20, May 1, and May 15 by LockBit, Hive, and ALPHV/BlackCat affiliates.
On May 1, legal PsExec and PDQ Deploy tools were used to spread LockBit and Hive ransomware payloads over the network within two hours of each attack, encrypting more than a dozen systems.
The same management server hijacked by LockBit and Hive was also used by a BlackCat threat actor two weeks later, on May 15, when the automotive supplier’s IT team was still working to restore systems. They obtained persistence on the network and exfiltrated stolen information after setting the legitimate Atera Agent remote access solution.
The BlackCat affiliate moved laterally through the network using compromised credentials within 30 minutes, delivering its own ransomware payloads on the network using PsExec to encrypt six workstations.
Zimbra Auth Bypass Issue Used to Compromise More than 1,000 Servers

It was discovered that the Zimbra Collaboration Suite (ZCS) included an active authentication bypass vulnerability. The flaw is identified as CVE-2022-37042 and is rated as high severity.
Along with CVE-2022-27925, the vulnerability has recently been added to CISA’s list of Known Exploited Vulnerabilities. RCE vulnerability CVE-2022-27925 requires authentication, which could be bypassed when CVE-2022-37042 is exploited.
The attackers can set up web shells and gain persistence if the exploit is successful.
Although over a thousand compromised and backdoored ZCS instances have been discovered, the actual number is probably higher. These ZCS instances are a part of a wide range of multinational organizations, such as political organizations, military divisions, multibillion-dollar enterprises, etc.
With Okta Phishing Campaign, Twilio and MailChimp Attackers Target 130 Organizations

The hackers responsible for some recent attacks, including those on Twilio, MailChimp, and Cloudflare, have been linked to a broader phishing campaign that targeted 136 firms and resulted in the theft of 9,931 account login credentials.
This login information was taken using the phishing tool known as 0ktapus.
The attacks’ initial goal was to obtain users’ two-factor authentication (2FA) codes and Okta identity credentials from the targeted organizations.
You can read our blog post to find out how the attack happened and which businesses were affected.
LockBit’s Leaksite Went Offline in a DoS Attack Involving Security Giant Entrust
IT security company Entrust suffered a cyberattack on June 18, in which attackers gained unauthorized access to the company’s network and reached internal data. Entrust’s workflow was unaffected, yet some files were stolen. LockBit ransomware group later claimed the attack on their leak site. Just when LockBit started leaking the stolen data, their site was brought offline in retaliation by a DoS attack.
Google Was Targeted in the Largest DDoS Attack Ever Recorded
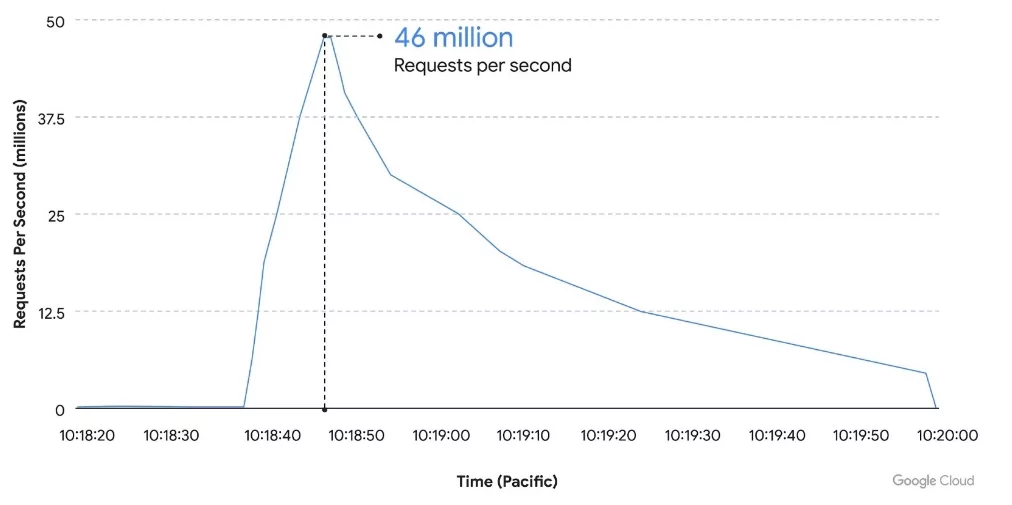
A Google Cloud Armor customer experienced the largest DDoS attack in records. The DDoS attack lasted 69 minutes and peaked at 46 million requests per second.
According to Google researchers, the attack traffic used HTTPS and originated from a total of 5,256 IP addresses from 132 countries, suggesting the attackers had relatively powerful resources.
Although the malicious software responsible for the attack has not yet been identified, the geographic distribution of the services leads to Mēris as the best prediction.
Critical Vulnerability Affects Over 80,000 Hikvision Cameras

More than 80,000 Hikvision cameras have a critical command injection flaw (CVE-2021-36260). CISA warned that the vulnerability is actively exploited and could result in device takeover.
According to research, approximately 80,000 of 285,000 servers accessible by the internet are still at risk of exploitation, the root cause being out-of-date firmware. Hikvision camera entry vectors were for sale on hacker forums and frequently used in botnets.
Over 1.3M Records of Health Information Breached Due to Misconfigured Meta Pixel

A data breach occurred at Novant Health, a US healthcare provider, that exposed the private health information of 1,362,296 people. The data was unintentionally gathered by the Meta Pixel ad tracking script.
It started in May 2020 when Novant used Facebook advertisements in their COVID-19 vaccination campaigns. To track their advertisements, the healthcare provider added a misconfigured Meta Pixel code to their website. The data was sent to Meta and its advertising partners.
Novant claims that despite their efforts to get in touch with Meta to have the data deleted, they have not received a response.
Patients are Sent Elsewhere After $10M Ransomware Attack on French Hospital

Due to a cyberattack, the Center Hospitalier Sud Francilien (CHSF) has had to refer patients to other facilities and postpone surgery.
The CHSF release states that the hospital’s commercial software, storage systems (particularly for medical imaging), and information system related to patient admissions are temporarily unreachable due to this attack on the computer network.
The doctors at CHSF will assess those who require emergency care, and if medical imaging is necessary for their condition’s treatment, they will send them to another facility.
The ransomware attackers that targeted CHSF requested a $10,000,000 ransom in exchange for a decryption key, according to Le Monde, which has information from the nation’s law enforcement agencies.
Malicious Chrome Extensions May Impact Over 1.4 Million Users

Researchers from McAfee found many dangerous Google Chrome extensions. Over 1.4 million downloads of the extensions have been made in total. The extensions can monitor and steal browsing data.
Following is a list of the malicious extensions:
- Netflix Party
- Netflix Party 2
- Full Page Screenshot Capture – Screenshotting
- FlipShope – Price Tracker Extension
- AutoBuy Flash Sales
Although the user-facing features of these extensions vary, their harmful behavior is remarkably similar. They keep track of user activity on e-commerce websites.
Nelnet Servicing Breach Exposes 2.5M Student Loan Accounts’ Data

Over 2.5 million persons with student loans from the Oklahoma Student Loan Authority (OSLA) and EdFinancial had their information exposed after threat actors gained access to the systems of technology services provider Nelnet Servicing.
OSLA, EdFinancial, and Nelnet Servicing use technology services, such as a web portal, to give online access to student loans.
The following information was made public:
- Full name
- Social Security Number
- Physical address
- Phone number
- Email address
To inform their clients about an example notification letter to the affected parties, Nelnet Servicing has informed OSLA and EdFinancial. According to the notes, neither financial account numbers nor other payment-related information was disclosed in the incident.
Data Breach Affecting 7.5M Users Is Announced by a Streaming Service

The Russian media streaming service “START” (start.ru) has disclosed a data breach affecting millions of customers. The platform’s operators disclosed that intruders gained access to their network and stole a database for 2021, which they then utilized to disseminate samples online.
The following details can be found in the stolen database:
- Usernames
- Email addresses
- Phone numbers
Because they were not kept in the database, financial data, bank card information, surfing history, and user passwords were unaffected.
The stolen dump and START’s release are different. The latter contains data that has not been made available in the platform’s official statement, including md5crypt-hashed passwords, IP addresses, login logs, and subscription information.



































