The Dominant Role of Compromised Credentials in Data Breaches
Compromised credentials are at the heart of modern cyber threats, driving a significant portion of data breaches across industries. Approximately 77% of web application breaches involved stolen credentials, according to the Verizon DBIR 2024 Report, highlighting how these credentials have become a favored tool for cybercriminals.
Techniques such as credential stuffing, where attackers use automated tools to input stolen usernames and passwords across multiple sites, are particularly effective due to widespread password reuse. Additionally, methods like password spraying—where a few common passwords are tried against many accounts—further increase the risk of compromise. Whether obtained through phishing attacks, brute force tactics, or leaked on the dark web, compromised credentials offer attackers a straightforward path to infiltrate sensitive systems, escalate privileges, and access valuable data.
How Are Threat Actors Weaponizing Compromised Credentials?
Threat actors have perfected the art of weaponizing compromised credentials, turning them into powerful tools to bypass security defenses and achieve their malicious objectives. The process of weaponizing these credentials involves a series of sophisticated tactics and strategies that allow cybercriminals to exploit system weaknesses, gain unauthorized access, and carry out further attacks. Here’s how they’re doing it:
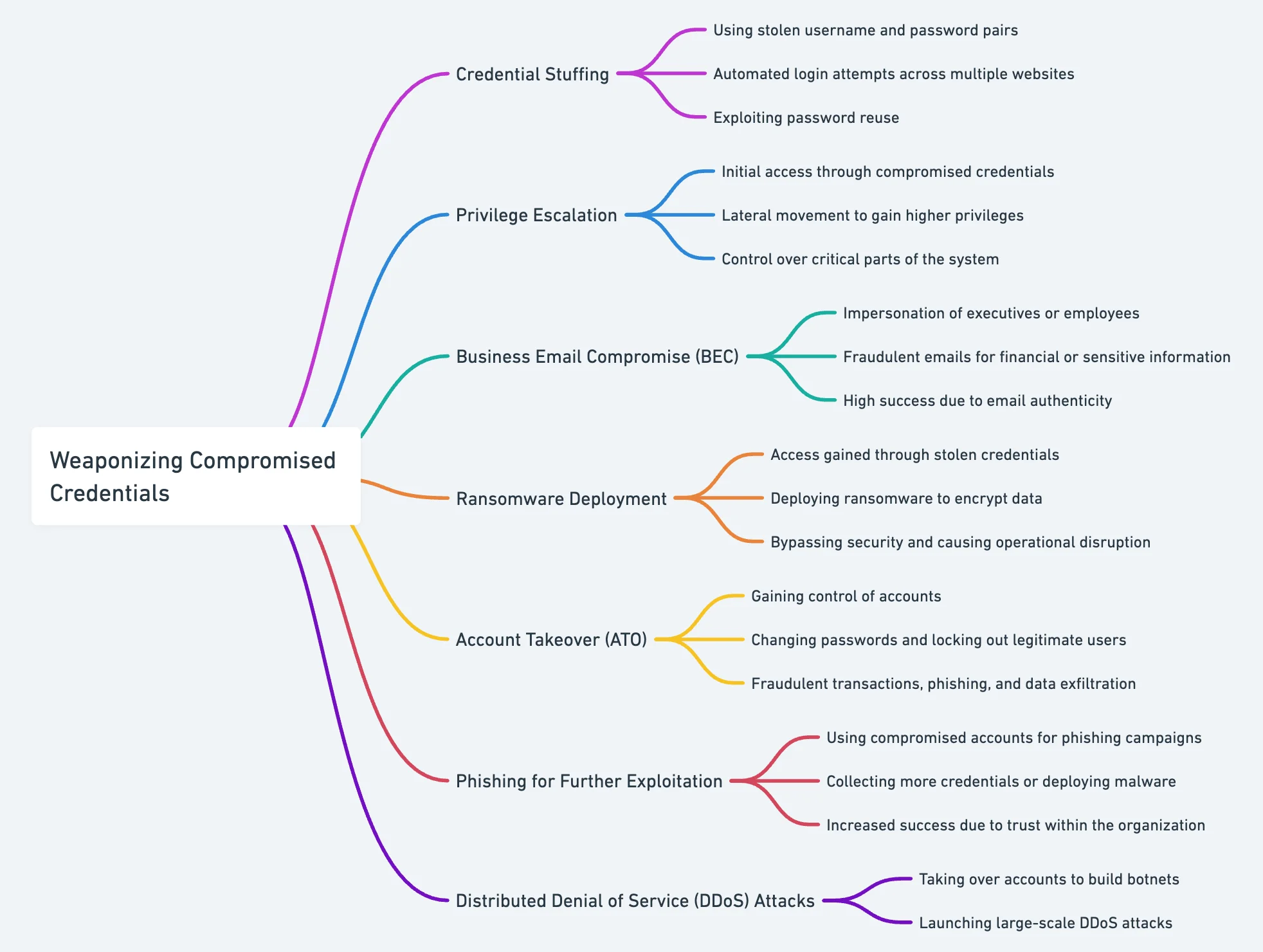
Weaponizing compromised credentials mindmap
- Credential Stuffing
Credential stuffing is a technique where attackers take large volumes of stolen username and password pairs—often obtained from previous data breaches—and use automated tools to attempt logins across multiple websites and services. This method takes advantage of the common practice of password reuse. Once a valid combination is found, attackers can access user accounts, which may contain sensitive personal information, financial data, or even administrative privileges.
- Privilege Escalation
Once inside a network, attackers often seek to escalate their privileges. With initial access granted through compromised credentials, they may use lateral movement tactics to gain control over more critical parts of the system. By leveraging administrator accounts or other high-privilege credentials, attackers can move from one compromised account to another, increasing their control and ability to cause damage.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC)
In a Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack, compromised credentials for corporate email accounts are used to impersonate executives or employees. Attackers send fraudulent emails from these accounts, often instructing recipients to transfer funds, disclose sensitive information, or approve invoices. The authenticity of the email—sent from a legitimate account—makes the deception more convincing and successful.
- Ransomware Deployment
Compromised credentials can also be a precursor to more devastating attacks like ransomware. Attackers gain access to a network using stolen credentials and then deploy ransomware to encrypt critical data. The ability to bypass security measures with legitimate credentials allows the ransomware to spread more quickly and effectively, often leading to significant operational disruptions and financial losses.
- Account Takeover (ATO)
Account Takeover (ATO) is another common use of compromised credentials. Once attackers gain control of an account, they can change passwords, lock out the legitimate user, and use the account for various malicious purposes—such as making fraudulent transactions, sending phishing emails, or exfiltrating data. This can be particularly damaging for organizations that rely on cloud services or remote access systems.
- Phishing for Further Exploitation
With initial access gained through compromised credentials, attackers may conduct phishing campaigns within the compromised environment to collect more credentials or deploy malware. By using the compromised account to send phishing emails, attackers increase the likelihood of success, as the email comes from a trusted source within the organization.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
In some cases, threat actors use compromised credentials to take over accounts and utilize them to build botnets for large-scale DDoS attacks.
How to Detect Compromised Credentials
Detecting compromised credentials before they are weaponized by cybercriminals is critical to preventing data breaches and safeguarding your organization’s assets. With the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, organizations must employ proactive detection strategies to identify compromised credentials swiftly. Here’s how you can effectively detect compromised credentials:
- Dark Web Monitoring: The dark web is a hotspot for selling and trading stolen credentials. Utilizing tools that continuously monitor dark web forums, marketplaces, and other hidden online spaces can provide early warnings if your organization’s credentials are exposed. SOCRadar Extended Threat Intelligence excels in this area by continuously scanning the surface, deep, and dark web for mentions of your organization’s credentials, providing you with immediate alerts and actionable intelligence to prevent unauthorized access.
SOCRadar XTI Dark Web Monitoring
- Credential Stuffing Detection: Credential stuffing attacks are rampant, and detecting these attacks is crucial. Implementing systems that monitor for unusual login attempts, such as repeated failed logins from different IP addresses or locations, can help identify credential stuffing attempts. SOCRadar XTI integrates advanced analytics to detect and analyze suspicious login patterns in real time, helping to prevent credential stuffing attacks before they can cause significant damage. For further information on how to detect and prevent credential-stuffing attacks with SOCRadar XTI, you can check out our detailedblog post.
- Identity and Access Intelligence: Identity and Access Intelligence tools play a pivotal role in detecting compromised credentials. By analyzing login patterns, device fingerprints, and user behavior, these tools can flag unusual access attempts that may indicate credential compromise. SOCRadar XTI’s Identity & Access Intelligence Module provides deep insights into compromised credentials and helps identify the root cause of the breach, enabling organizations to respond swiftly and effectively.
SOCRadar XTI Identity & Access Intelligence
- Phishing Detection and Prevention: Phishing remains a leading method for stealing credentials. Training employees to recognize phishing attempts and implementing robust email security solutions can significantly reduce the risk. SOCRadar Extended Threat Intelligence offers comprehensive phishing detection services that analyze and identify phishing attempts before they reach your employees, helping to protect your organization from credential theft.
- Behavioral Analytics: Behavioral analytics is essential for identifying compromised credentials based on how users interact with systems. By establishing baseline behavior patterns for each user, any deviation from the norm—such as unusual login times, access from unfamiliar devices, or abnormal activity within accounts—can trigger alerts for potential credential compromise.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Alerts: Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security, but it’s also a valuable detection tool. If an MFA request is triggered unexpectedly or from an unusual location, it could indicate that credentials have been compromised. Monitoring and analyzing these alerts can help identify potential breaches early.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regularly conducting security audits and penetration testing can help identify vulnerabilities that could lead to credential compromise. These practices allow you to simulate attacks and discover weak points in your system before an actual breach occurs. It’s also a way to ensure that your detection systems are functioning correctly and efficiently.
- Leveraging Compromised Credential Databases: There are several databases of known compromised credentials that can be used to cross-reference your organization’s credentials. SOCRadar XTI provides access to extensive databases of compromised credentials, enabling you to cross-check and identify if any of your employees’ or customers’ credentials have been exposed, allowing you to take preemptive action.
SOCRadar XTI Threat Hunting
Conclusion
Detecting compromised credentials requires combining advanced technology, proactive monitoring, and human intelligence. SOCRadar XTI offers a comprehensive suite of tools designed to help organizations detect, respond to, and prevent the exploitation of compromised credentials. By employing these strategies and leveraging SOCRadar Extended Threat Intelligence’s capabilities, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of credential-based attacks and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture. Staying vigilant and responsive to potential threats is key to maintaining the integrity and security of your digital environment.