
The “Evil” of Everything – Part I: EvilProxy Rises AitM

In today’s digital era, detecting a burgeoning type of cyberattack, known as Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) attacks, is becoming increasingly challenging. As cyber threat actors continually refine their techniques, organizations find themselves vulnerable, often ill-equipped to detect and counteract these sophisticated intrusions.
The rapid technological advancements and the deepening integration of digital solutions in our daily lives have inadvertently expanded the attack surface for these adversaries. Of course, we should not forget the harmful use of educational tools developed “for educational purposes only” by threat actors. This research paper is the first part of a two-part series. In this part, we will delve into the intricacies of EvilProxy, one of the tools that epitomize the advanced methodologies employed by these threat actors. The second part, which explores EvilQR and Evilginx, can be accessed through the link provided at the end of this article.
The contemporary digital landscape is characterized by an intricate web of interconnected systems spanning organizational infrastructures and personal domains. As businesses accelerate their digital transformation journeys and individuals become more reliant on online platforms, the avenues for cybercriminal exploitation grow exponentially. This paper aims to shed light on the sophisticated attack campaigns orchestrated by these cyber adversaries, primarily focusing on EvilProxy. At the same time, the subsequent part will cover EvilQR and Evilginx and their role in targeting unsuspecting individuals and enterprises.
It is imperative to understand that cybersecurity is not a mere afterthought in this age but an essential pillar supporting the digital ecosystem. The intertwining of the digital domain with critical sectors, from finance to healthcare, underscores the potentially catastrophic consequences of successful cyber breaches. By demystifying the operations and functionalities of tools wielded by threat actors, we can pave the way for enhanced defensive strategies.
This research endeavors to dissect the operational mechanics of these malicious tools, offering insights into their capabilities, modus operandi, and potential weak points. By understanding the intricacies of attacks facilitated by tools like Evilginx, EvilProxy, and EvilQR, we can better anticipate and counteract the strategies employed by cyber adversaries.
Moreover, this investigative journey will enrich our understanding of the ever-evolving cyber threat landscape, equipping cybersecurity experts, businesses, and the general populace with the knowledge to safeguard their digital assets.
In exploring the cyber threat realm, it is paramount to acknowledge that informed awareness is our most formidable defense. By understanding the underlying mechanisms of these cyberattacks, we are better positioned to fortify our digital future against the malicious endeavors of threat actors. This research represents a commitment to understanding, countering, and ultimately neutralizing the threats posed by tools like Evilginx, EvilProxy, and EvilQR in our interconnected digital world.
EvilProxy: A Deep Dive into the Rising Threat of Advanced Phishing Attacks
A new adversary has emerged in the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, causing ripples in the cybersecurity community: EvilProxy. This tool, designed to bypass Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), has been linked to a surge in Business Email Compromise (BEC) cases, emphasizing the need for organizations to re-evaluate their security postures.
EvilProxy is another phishing tool and a paradigm shift in cyberattack methodologies. Bypassing most forms of MFA undermines the foundation upon which many organizations have built their cybersecurity defenses. The tool operates as an Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) attack framework, available for purchase on the dark web, making it accessible to a wide range of threat actors.

At its core, EvilProxy crafts targeted phishing emails containing links to custom phishing websites, mimicking legitimate sign-in pages like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365. When users interact with these pages, their traffic is proxied to genuine login sites, allowing attackers to intercept credentials and valid session cookies and effectively hijack the MFA process. This interception grants them continuous access to services like Microsoft Exchange Online without re-authentication.
The sophistication of EvilProxy lies in its ability to use compromised accounts to send further phishing emails. This means recipients are more likely to trust and interact with these emails, as they appear to come from known contacts. Furthermore, the phishing landing pages crafted by EvilProxy are more convincing than ever, making it challenging for even the most vigilant users to discern their malicious nature.
While the primary goal of most EvilProxy attacks has been payment fraud, the tool’s versatility suggests that threat actors could pivot to other objectives, such as data exfiltration or initiating broader attacks on organizational networks.
While the proxy attack framework is not novel, with tools like Modlishka, Necrobrowser, and Evilginx having been in use since 2018, its user-friendliness sets EvilProxy apart. It offers comprehensive training, a user-friendly GUI, and a vast library of fake phishing websites. As MFA becomes more prevalent, the demand for such tools will rise.
Investigative Analysis of EvilProxy: Unveiling the Menace and Potential Ramifications
At the forefront of modern cybersecurity concerns lies the intricate web of malicious tools designed by threat actors to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise digital security. The SOCRadar Threat Research team, in its relentless pursuit of understanding and mitigating cyber threats, has focused its attention on the capabilities of the malevolent tool known as EvilProxy and the potential damages it can inflict on corporate entities and individual users. This comprehensive research endeavor, based on a thorough examination, aims to shed light on the insidious functionalities of EvilProxy and the extent of the threat posed by its utilization.
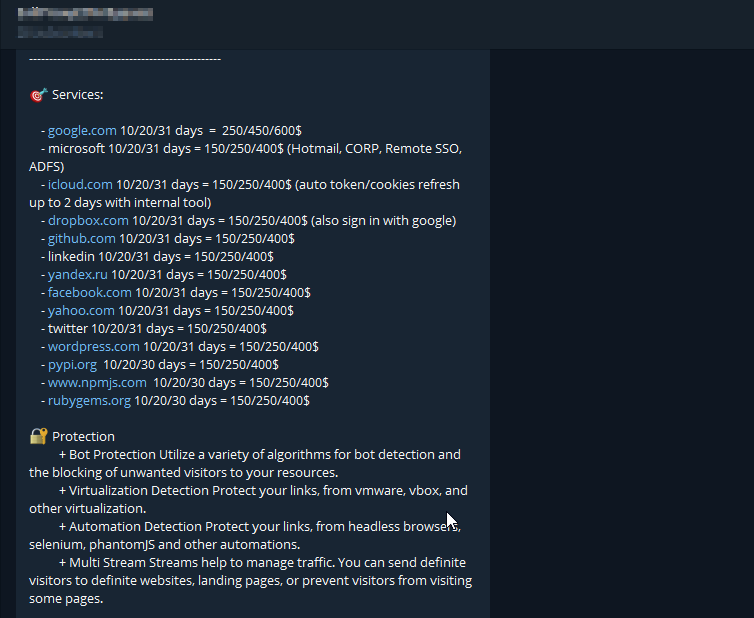
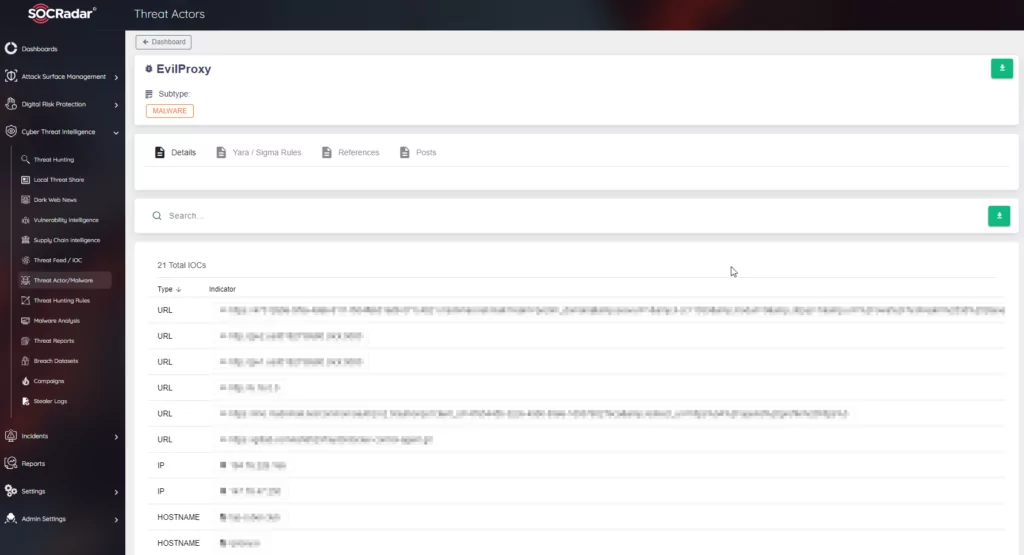
Our investigative journey commenced with a short reconnaissance of the accessible depths of the Dark Web, particularly on the Telegram platform. We acquired the EvilProxy tool through this expedition and meticulously analyzed its attributes. Notably, this study encompasses insights derived from interactions with the tool’s purveyors, discussions with various sellers on Telegram channels, and screenshots of pertinent forum conversations.
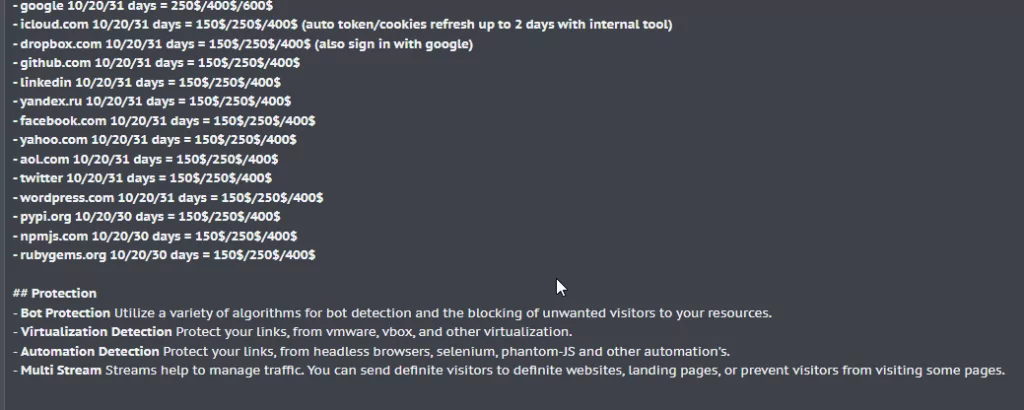
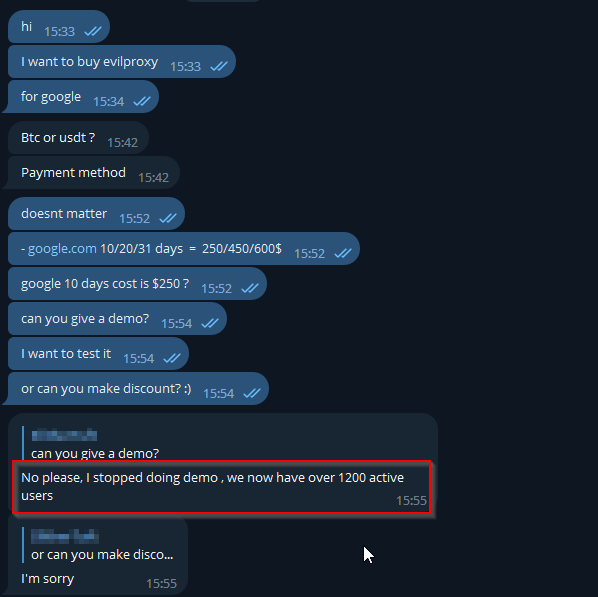
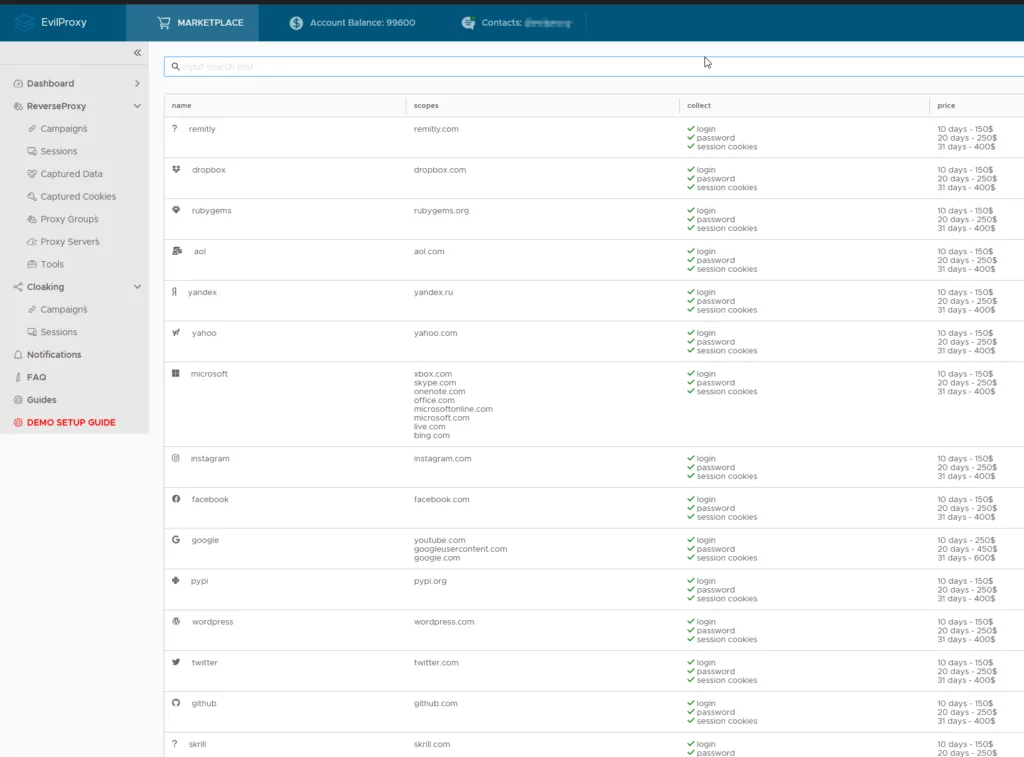
In our exploration, it was evident that EvilProxy had established a conspicuous presence in specific Telegram channels, offering ready-to-use packages that included templates mimicking the authentication processes of 21 prominent banks. Notably, these packages were often structured on a subscription basis, categorized as Bronze, Silver, and Gold, with weekly or monthly options. A particular focus of our study was the distinct separation of individuals handling the forum and the Telegram presence, indicative of a robust operation with claimed membership exceeding 1000 users.
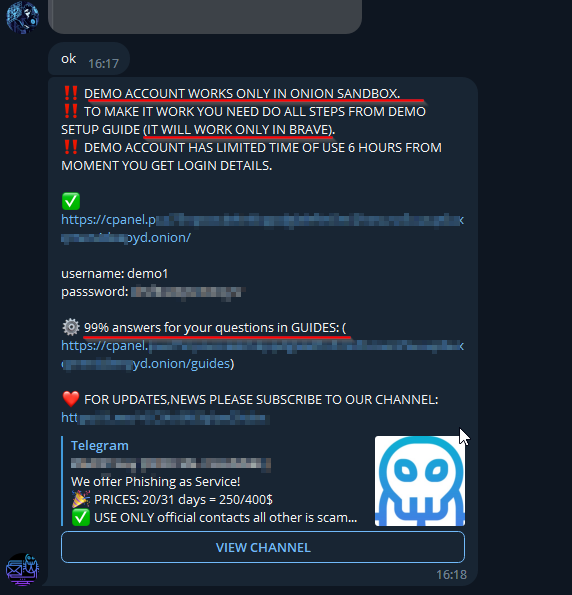
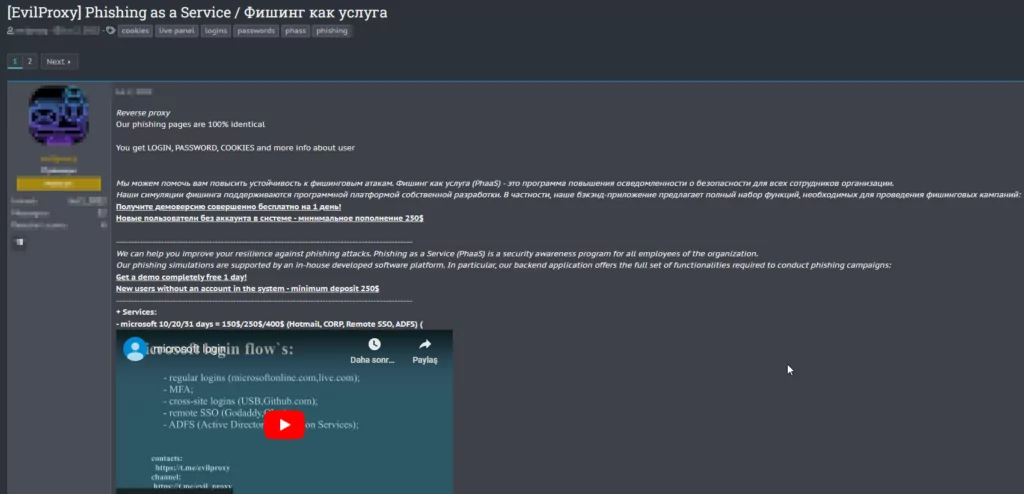
After successfully persuading another seller to provide a demo account, we were granted access to a test portal that exclusively functioned within the confines of the TOR network. The demo account demonstrated the utilization of EvilProxy and included instructional videos guiding users through the process. This detailed documentation allowed the easy setup of phishing services by deploying preconfigured templates for widely-used services such as Google, Microsoft, and Dropbox. The alarming ease with which a phishing campaign could be orchestrated, even without advanced technical skills, was a grave concern we uncovered.
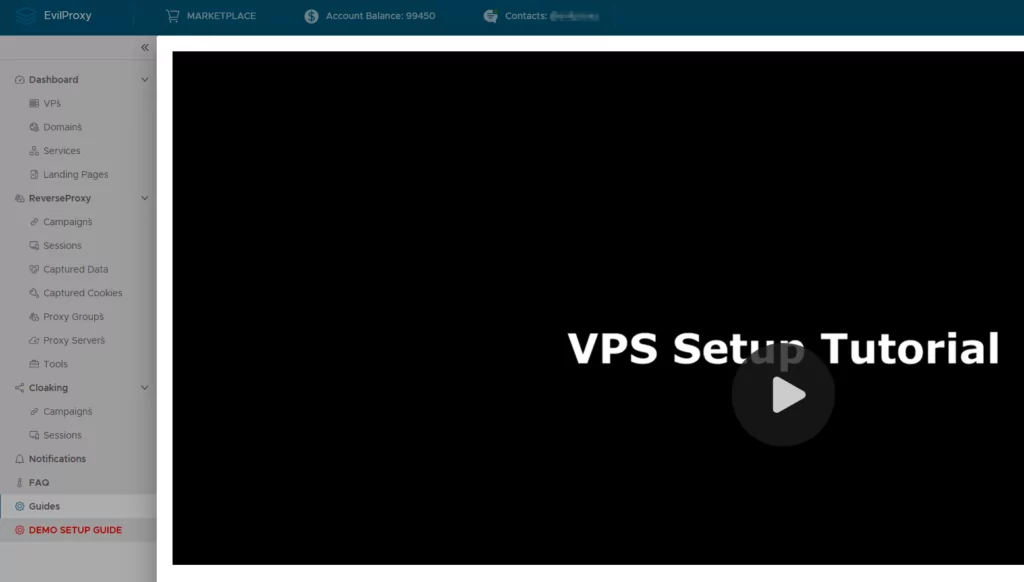
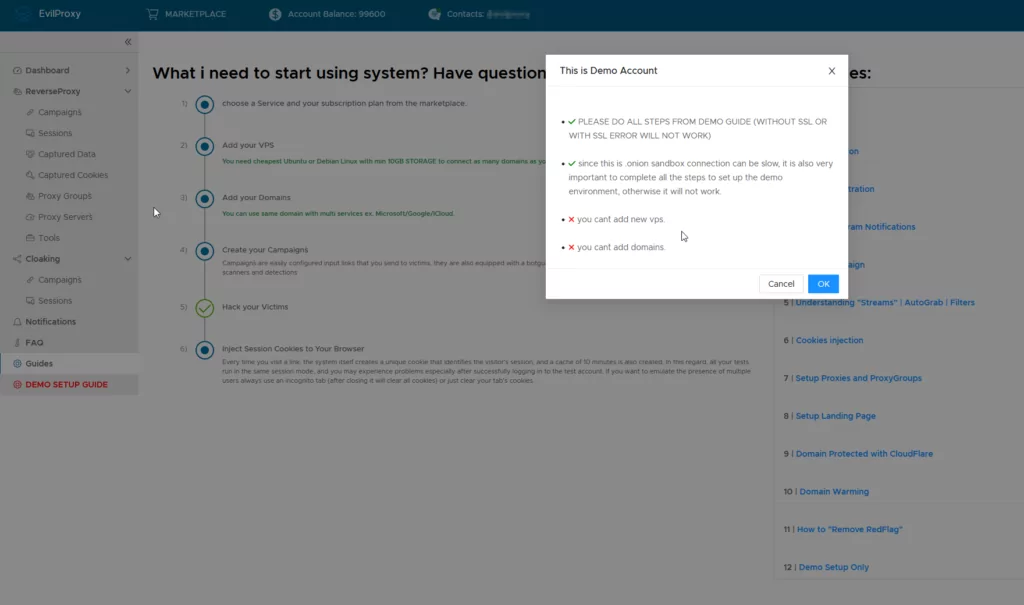
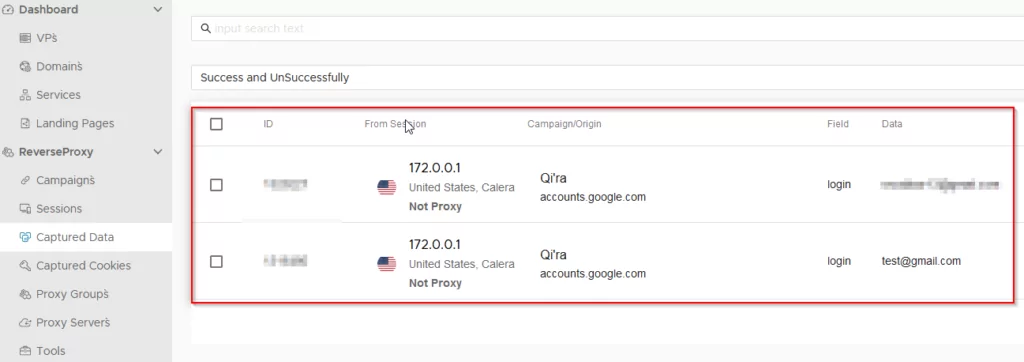
Despite the sophistication of the tool, our interactions with the sellers exposed certain limitations. Technical issues, such as the tool’s inability to effectively function with every template due to certificate-related obstacles, remained unaddressed despite our attempts to seek solutions. Furthermore, while some deployed services presented errors, we verified that user credentials were indeed being compromised.
A particularly disconcerting feature of EvilProxy’s capabilities was its ability to copy stolen cookie information to an automatic clipboard, readily pasted into the browser developer console. This seemingly straightforward copy-paste maneuver granted attackers access to a user’s session, bypassing multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems. This revelation underscored the criticality of MFA in contemporary cybersecurity strategies.
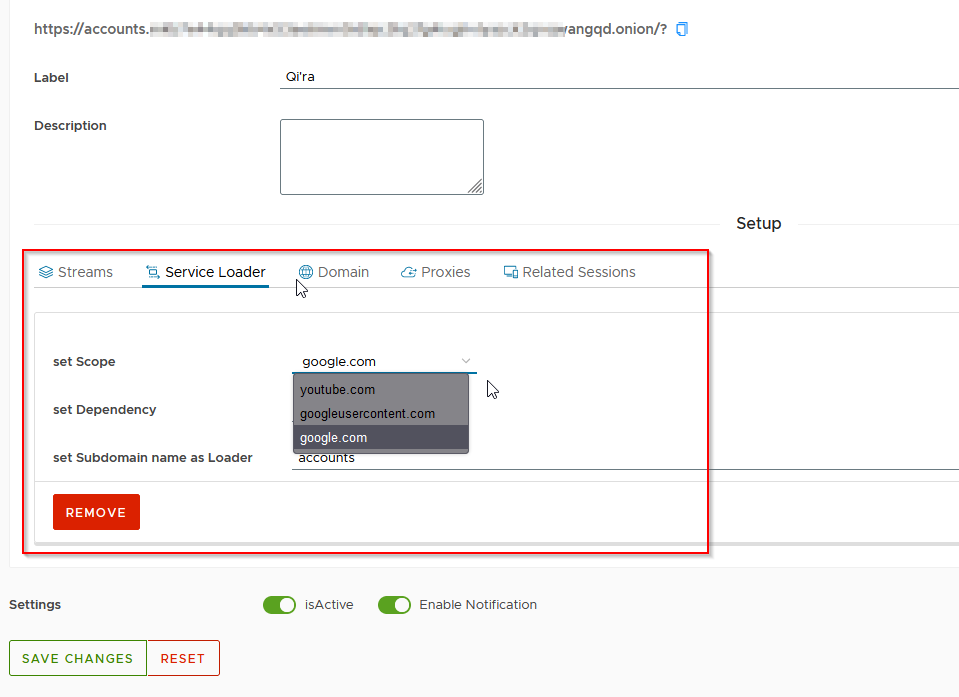
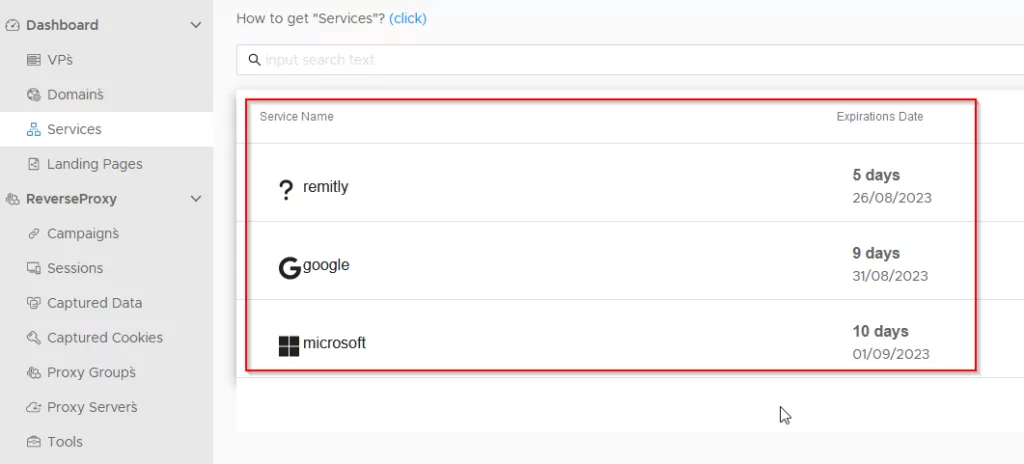
EvilProxy’s ability to replicate legitimate services under different domains creates a highly deceptive facade, posing substantial risks to end users. Recognizing this threat, SOCRadar is committed to proactive monitoring, raising awareness among our clients, and promptly notifying them in the event of potential threats. By relentlessly pursuing comprehensive threat intelligence, we empower organizations and individuals alike to fortify their defenses against the evolving landscape of cyber adversaries.
The portal also has a tool that creates an HTML page that redirects to the page you want with a single click. This tool works with obfuscated JavaScript code, making it difficult to detect. In this way, the attack surface is also enlarged.
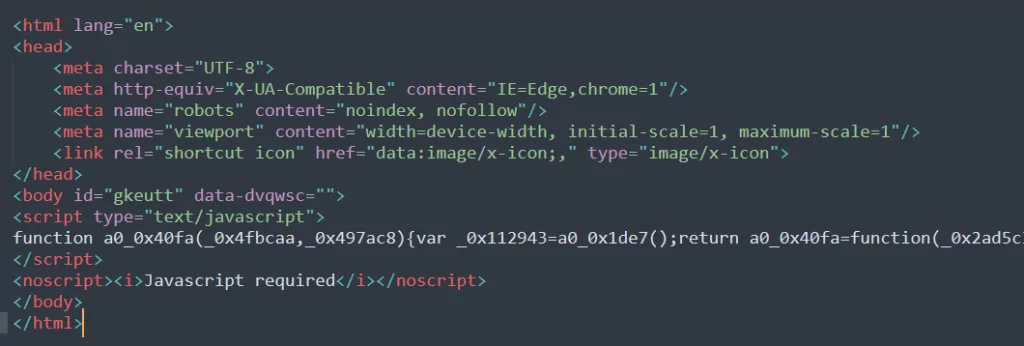
Defending against AiTM attacks requires a multi-faceted approach. Organizations should consider:
- Conditional Access Policies and Alternative MFA Methods: Implementing conditional access, configuring compliance to deny access to untrusted devices, and adopting password-less authentication methods can bolster defenses.
- Email Security Software: Advanced software solutions that scan incoming emails for malicious links, especially those associated with EvilProxy campaigns, are crucial.
- Phishing Awareness Campaigns: Regular training and awareness campaigns can empower employees to recognize and report phishing attempts.
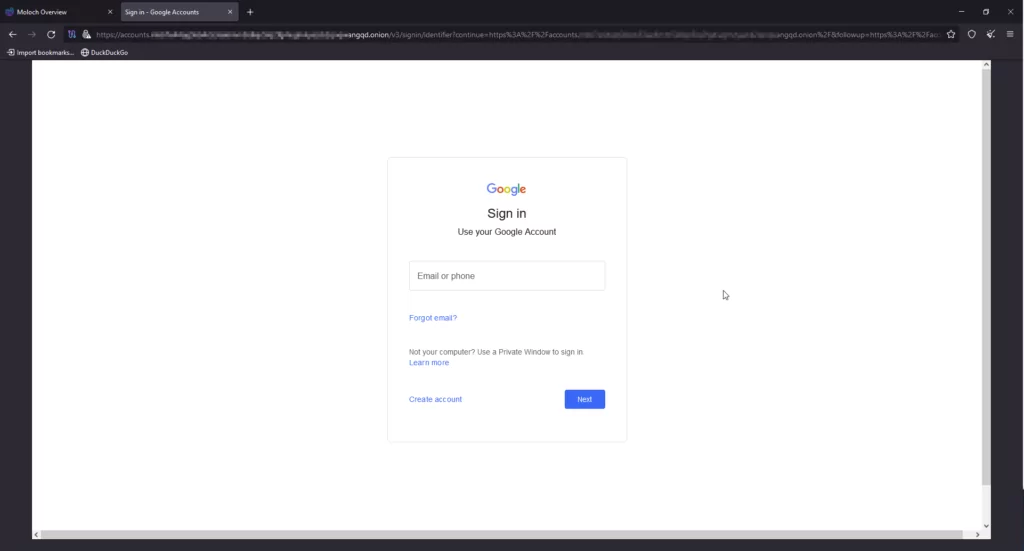
In the unfortunate event of a successful EvilProxy attack, immediate actions include enforcing password resets for compromised accounts and revoking user sessions across platforms. A thorough forensic investigation is also imperative to understand the scope of the breach and prevent future intrusions.
Stay Ahead of Cyber Threats with SOCRadar XTI
To proactively defend against threats like EvilProxy, organizations can leverage SOCRadar Extended Threat Intelligence. Our teams actively investigate emerging threats, enriching the platform with data to aid clients. By providing real-time insights and indicators of compromise, we ensure that our clients remain a step ahead of cyber adversaries.
In conclusion, while tools like EvilProxy pose significant challenges, organizations can safeguard their digital assets and maintain trust in their digital interactions with the right intelligence, awareness, and defensive measures. For a comprehensive understanding of the evolving landscape of AiTM attacks and the tools involved, we invite you to explore the second part of this research series.
You can access the second part, which delves into Evilginx and EvilQR, by clicking here.



































