Introducing Radar Pages: Major Cyber Attacks
Cybersecurity has grown in importance as a geopolitical factor. Cyberattacks target public and private systems each day, and the variety of attacks has grown quickly.
Cybercriminals are primarily driven by financial gain; they are looking for information they can use in identity fraud or for the chance to extort their targets’ IT systems.
By 2025, cybercrime is predicted to cost the world $10.5 trillion.
Cyberattacks can have wide-ranging effects, regardless of their financial or political motivations. The consequences of a breach may be disastrous.
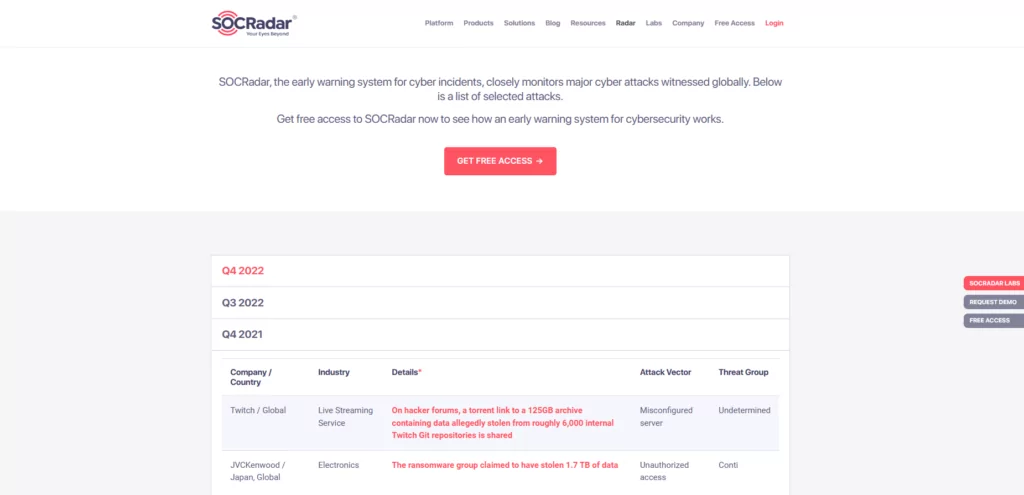
Improved cybersecurity requires tracking evolving and growing cyberattacks. SOCRadar, the early warning system for cyber incidents, closely monitors major cyberattacks that are seen worldwide. Our Major Cyber Attacks radar page is updated monthly with the most significant cyberattacks for each quarter of the year.
How to Utilize the Radar Pages?
You can find the “Major Cyber Attacks” under our platform’s “Radar” title. The page lists all selected major cyberattacks that occur throughout the year, divided by quarters.
On the list, you can find information such as the targeted industry, the initial attack vector, and the responsible threat actor, as well as a short description of the incident.
The information on this list can be used as intelligence to prevent further damage to any other organization that resides in the cyber world. It is very simple to achieve this by incorporating other SOCRadar tools into your security routine.
Via the list, you can be aware of the new major threats that have impacted the cyber ecosystem and implement proper security measures accordingly. To visit the Radar page, click here.
Access SOCRadar free to learn more about how a cybersecurity early warning system works.
A Review of Major Cyber Attacks in Q4 2022
Various types of cyberattacks caused serious problems in the fourth quarter of 2022. Cases include attacks on retailers in different industries, hacking of cryptocurrency platforms, and a variety of other attack methods to expose, sell, or ransom sensitive data.
Here are some of the major cyberattacks that occurred in Q4 2022:
Ransomware Gang Breaches Medibank’s System
Australian health insurance provider Medibank reported unusual activity in its system in October after it was targeted by a group that might be affiliated with the REvil (Sodinokibi) ransomware gang. Medibank was able to stop the attack, but the attackers were able to steal 9.7 million customers’ personal information during the breach.
The ransomware group demanded $10 million by releasing samples. After refusing to pay the ransom, Medibank faced a data leak.
MyDeal Data Breach Affected 2.2M Customers
The Australian retail marketplace MyDeal, a subsidiary of Woolworths, was the victim of a data breach incident. MyDeal detailed that a hacker accessed their CRM system by using stolen credentials and stole 2.2 million customers’ data, which they later put on sale.
The threat actor evidenced screenshots of the company’s Confluence server and an AWS SSO prompt. Threat actors exposed the email addresses of 1.2 million customers, as well as additional information about the remaining 1 million customers.
Hacker Claims to Have Stolen 400M Twitter Users’ Data
A threat actor on the dark web claimed to have 400 million Twitter user data after scraping the site using a vulnerability. The cybercriminal shared sample data of 37 people, allegedly celebrities, and an additional link to 1,000 other users’ data.
The threat actor urged Elon Musk to buy the data exclusively in order to avoid GDPR fines. The sample data leak included email addresses, names, usernames, follower counts, account creation dates, and phone numbers.
Hive Ransomware Attacked Tata Power
Tata Power disclosed a cyberattack on its IT infrastructure on October 14. The company’s critical systems remained operational, and additional security measures, such as employee access restrictions, were implemented.
The Hive ransomware gang claimed responsibility and began releasing stolen data on their dark web forum. The information leaked included bank account information, statements, employee remuneration, passport information, power grid diagrams, and battery details.
Deribit Crypto Exchange Lost $28M in a Hack
Deribit cryptocurrency exchange reported in November that its hot wallet was compromised and stopped accepting withdrawals for a while after a $28 million loss in the hack.
According to Deribit’s chief commercial officer, Strijers, client assets were unaffected. Deribit’s reserves covered losses, so client funds were also safe.
Gain Further Threat Intelligence with SOCRadar
The information SOCRadar provides on the Major Cyber Attacks Radar page can enable organizations to take action if any of the mentioned targets are associated with them.
You can stay informed about the most recent compromised businesses by using the SOCRadar Supply Chain Intelligence tab. You can also add vendors to the WatchList. The module ultimately helps prevent incidents that may occur due to a third-party.
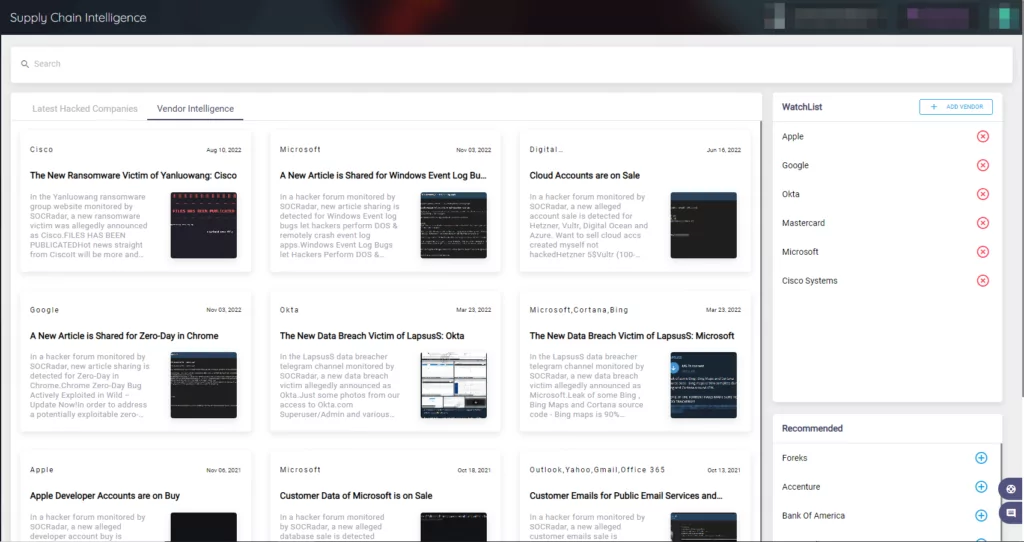
SOCRadar monitors threat actors’ activities and identifies the trends among them, allowing you to manage your security posture effectively and avoid their attempts. On our platform, you can search for every threat actor listed on the Radar page and find detailed information about their tactics and indicators of compromise (IOCs).