Cybersecurity Predictions: What Trends Will Be Prevalent in 2024?
The evolving digital environment and expanding attack surface demand vigilant adaptation to stay one step ahead of adversaries. Recognizing when to shift priorities and understanding specific dangers to cybersecurity is not just critical for organizational budgets; it is the cornerstone of a robust security strategy, and will continue to be in 2024 and in the foreseeable future.
In our exploration at the end of 2022, we delved into the prevailing trends shaping the cybersecurity landscape, projecting their continuity into 2023 while anticipating certain shifts. Key focal points included the influence of AI support, the impact of global events, and the ever-expanding attack surface. Referencing our previous insights in the blog post “Ten Things Will Change Cybersecurity in 2023,” we set the stage for what we are about to unveil in 2024.
Now, in the early days of 2024, a landscape teeming with cybersecurity threats awaits us, as always. But what are the specific threats? Fortinet researchers have meticulously compiled a report on cyber threat predictions for 2024, drawing insights from the cyber landscape of 2023. Let’s outline interesting key points from the researchers’ report, and from our previous predictions, and explore the expected cybersecurity trends that will shape the year ahead.
The Threat of Generative AI, and Easier Access to Attacker Tools and Services

The Threat of Generative AI, and Easier Access to Attacker Tools and Services
Executing successful cyberattacks has evolved into a streamlined process due to the flourishing Cybercrime-as-a-Service (CaaS) market and the ascent of generative AI. The convenience provided by these developments has given threat actors more opportunities, prompting them to adopt a much simpler approach to cybercrime, leveraging the capabilities at their disposal.
The predicted surge in vulnerabilities and increased pre-attack activities among adversaries have propelled the expansion of the CaaS market. Comprising of many as-a-service threats such as RaaS and MaaS, CaaS simplifies the execution of attacks, often offering user-friendly interfaces and even assisting with victims’ payments to the affiliates.
You can discover how some of these CaaS models work in our blog posts, “What Is Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)?” and “What is Malware as a service (MaaS)?”.
Simultaneously, the weaponization of AI heightens threats, enabling attackers to refine every stage of an attack efficiently. AI’s malicious applications include generative profiling for scraping PII, AI-supported attacks, password spraying, poisoning attacks, thwarting phishing algorithms, deepfake creation for social engineering, and AI-generated malware.
The convergence of AI technologies raises the stakes in the ongoing battle between cybersecurity defenders and threat actors. AI’s versatility, initially adopted for constructive purposes, has become a double-edged sword in the hands of threat actors. As AI continues to trend across various domains, from personal assistants to business applications, threat actors also leverage its power to their advantage.
Armed with CaaS and AI, threat actors will persist in using proven tactics while embracing emerging trends in 2024.
Insider Threats and Possible Emergence of Recruitment-as-a-Service
As enterprises fortify their defenses against external threats, attackers are adapting by shifting their focus to internal tactics, reconnaissance, and weaponization.
Observing this trend, researchers predict an evolution toward attackers recruiting from within organizations.
Leveraging generative AI to clone voices and tricking targets into executing commands, disclosing passwords, or sharing sensitive data, attackers could propel the emergence of Recruitment-as-a-Service. This evolving trend enables attackers to gain more access and information, enhancing their ability to profile targets.
Laundering-as-a-Service, Mixers, and Beyond
Threat actors delved into Laundering-as-a-Service (LaaS) to conceal their ill-gotten gains. Fortinet emphasizes that the shutdown of ChipMixer in March 2023 underscored the risks associated with such services. While new crypto mixers and tumblers emerged, the KillNet threat group also entered the scene with a crypto exchange and mixer services.
However, as efforts to dismantle Bitcoin mixers continue, their popularity is declining, prompting hacker groups to prefer traditional money laundering schemes – like transferring the funds over mules or online frauds – over tumblers.
This shift reflects the adaptability and constant evolution of cybercriminals’ tactics.
Anticipated Surge in APT Activities, and Shifting Targets and Tactics

Anticipated Surge in APT Activities, and Shifting Targets and Tactics
The collaboration between threat actors and Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) groups has intensified, evident in the heightened APT activity observed. Fortinet emphasized that in the first half of 2023, 41 out of 138 MITRE-tracked APT groups were active, including notable names like Turla, StrongPity, Winnti, OceanLotus, and WildNeutron.
Looking ahead, a further surge in APT group activities is expected, surpassing the 138 identified by MITRE. Another notable trend on the horizon involves APT groups adopting stealthier and more innovative attack methods, exemplified by the growing popularity of techniques like HTML smuggling.
In addition, cybercrime groups are expected to diversify their targets, moving beyond traditional sectors like manufacturing to encompass healthcare, utilities, finance, oil and gas, and transportation. The shift towards extortion, over data encryption, will be accompanied by an increased reliance on supply chain attacks to disrupt critical services.
This evolution marks a dynamic landscape with heightened threats and changing tactics.
Access current reports on a variety of industries through SOCRadar Labs’ Industry Threat Landscape Report page. These reports include information about the prevalence of specific cyber threats targeting the industry, as well as details on ransomware and APT groups focusing on the sector, along with the top target countries.
Industry Threat Landscape Report on SOCRadar Labs
2/3 of MITRE TTPs Used Actively; Credential and Access Brokers Rise
As threat actors continue to adopt stealthier and more innovative attack methods, the report underscores their active utilization of around two-thirds of MITRE ATT&CK techniques; defense evasion and process injection emerge as prevalent tactics.
Stolen credentials persist as a prized asset for threat actors, leading researchers to predict the proliferation of Credential and Initial Access Brokerage services, mirroring the evolution of RaaS. This development is poised to make such services commercially accessible, extending beyond the confines of the dark web.
Recognizing the prevalence of Threats, Tactics, and Techniques (TTPs) in the current landscape is significant for effective organizational defense.
For comprehensive insights into known threat actors, groups, and malware details, the SOCRadar platform offers a wealth of information, including associated groups, known vulnerabilities, Indicators of Compromise (IoCs), and mentions of the latest activities. Additionally, the AI Insights feature provides concise reports on each threat actor, encompassing their prevalent TTPs and recommended mitigation strategies.
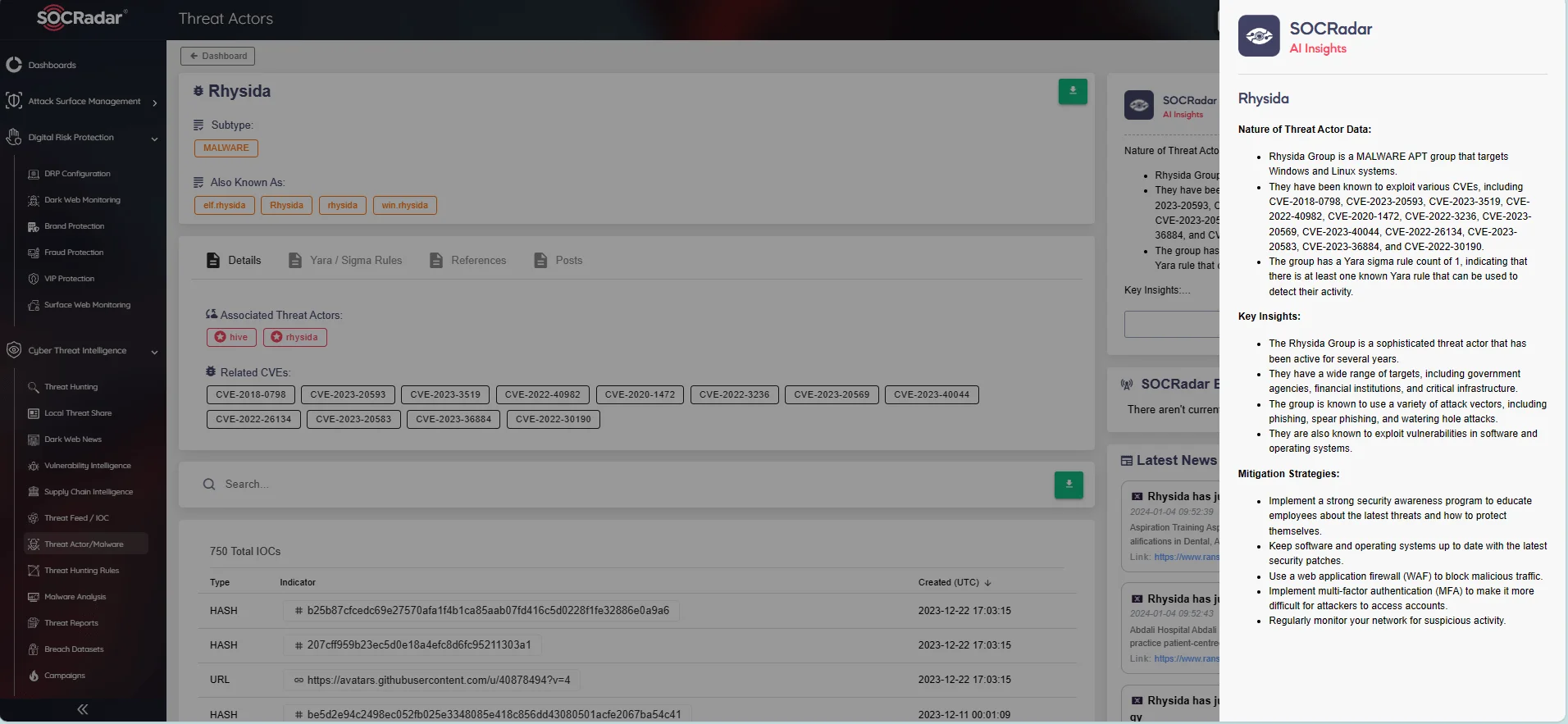
SOCRadar Threat Actor/Malware page – Rhysida Ransomware
The Unrelenting Surge of Ransomware: How Are Threat Actors Changing Their Methods?

The Unrelenting Surge of Ransomware: How Are Threat Actors Changing Their Methods?
In a relentless surge, ransomware exhibits a 13-fold increase in mid-2023, challenging organizations, despite perceived readiness. Fortinet’s survey reveals that while 78% of organizations felt prepared for ransomware attacks, half still fell victim.
Another observed trend is that, as attackers intensify using advanced strains, the focus shifts from encryption to Denial-of-Service (DoS) and extortion.
While a closer look into the evolution of ransomware and extortion methods is available on our blog post “Evolution of Ransomware: So Far and Hereafter”, we would like to highlight two emerging methods:
Fake Extortion Tactics: Some ransomware actors, steering away from traditional extortion tactics, resort to tricking victims into believing they have lost corporate data. Creating a false sense of urgency, they attempt to extort payments. Fake extortion is not a new method, but with the shift away from encryption, its prevalence may rise.
Regulatory Pressure for Extortion: Certain ransomware groups leverage regulatory pressure as an extortion method. For instance, ALPHV (BlackCat) filed an SEC complaint against a targeted company, while RansomedVC exploited Europe’s GDPR laws, threatening companies with data exposure and potential fines.
On a different front, as high-value targets diminish, a foreseen shift involves threat actors’ possibility of targeting cyber insurers. With insurers imposing tighter restrictions, they become potential, yet untapped, targets for future attacks, considering the ransomware actors’ reliance on ransom payouts.
Another noteworthy ransomware trend surfaces wherein multiple adversaries converge on the same victims in quick succession. This has resulted in the deployment of various ransomware variants, including AvosLocker, Diamond, Hive, Karakurt, LockBit, Quantum, and Royal. The recurrence of such attacks prompted a warning from the FBI in September 2023.
Attackers Increasingly Seek Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
As organizations extend their digital presence, threat actors seize enhanced opportunities to exploit software vulnerabilities. In 2023, a surge in zero-day discoveries was observed. It can be exemplified by incidents like Cl0p Ransomware group’s MOVEit Transfer hack, which is known to have affected at least 60 million individuals.
Explore the aftermath of the MOVEit Transfer hack through our blog posts, “Top 10 Facts About MOVEit Breach” and “Attackers Exploit Critical Zero-Day Vulnerability in MOVEit Transfer.”
Compounding the risk, it takes a mere 14 days, on average, for an exploit to be available in the wild after a vulnerability’s public disclosure.
Access vulnerability details, lifecycle information, and more through SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence. This feature also allows you to stay informed about available exploits, understand a vulnerability’s popularity with the specialized SOCRadar Vulnerability Risk Score (SVRS), and obtain quick AI insights for each vulnerability.
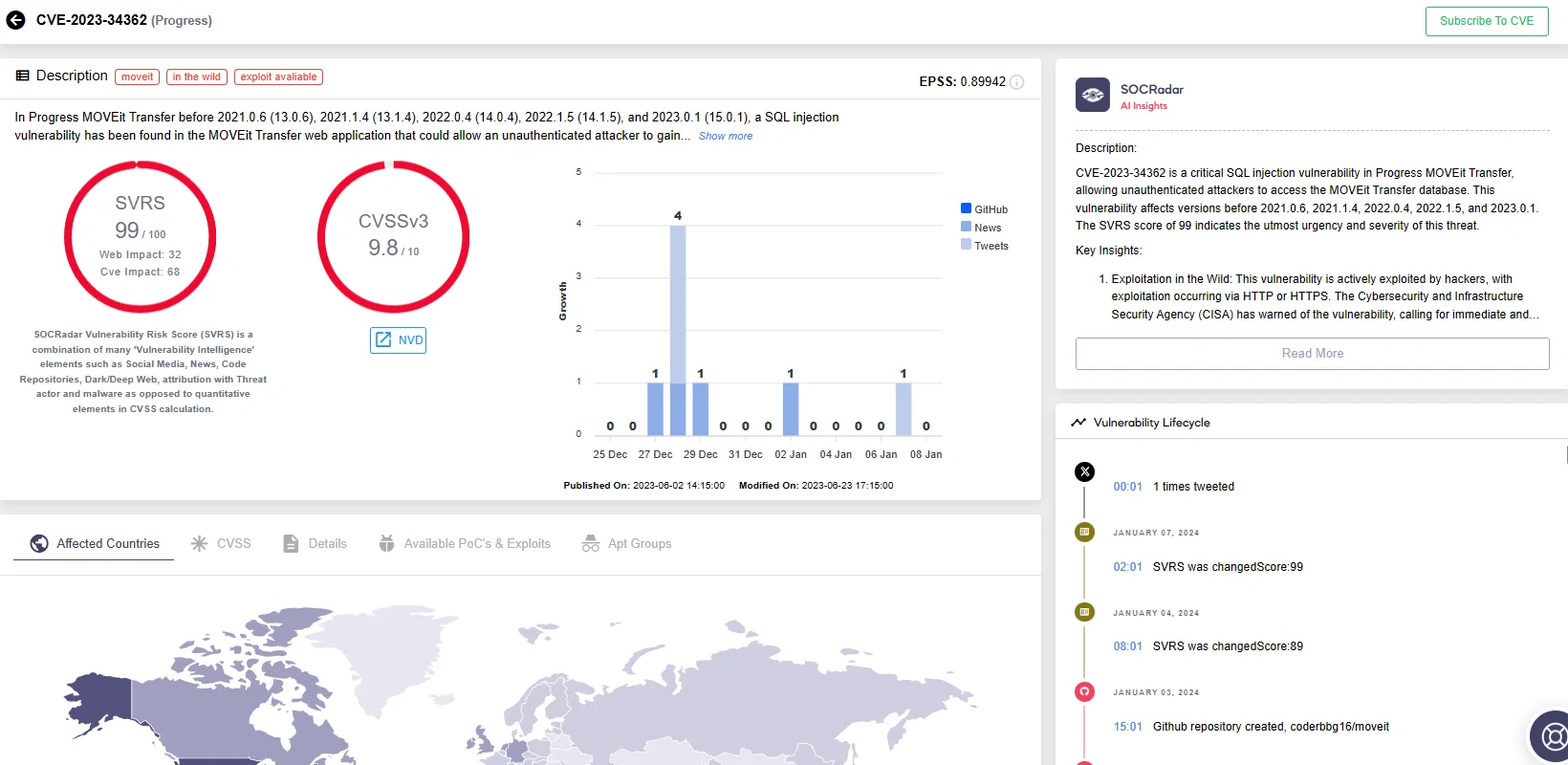
MOVEit Transfer vulnerability (CVE-2023-34362) on SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence
In anticipation of a continued rise in zero-day attacks, researchers foresee the emergence of zero-day broker services. This shift will empower threat actors to scale efforts and coordinate broader campaigns, exploiting vulnerable products and the multitude of expected CVE discoveries.
Researchers advise proactive measures, urging organizations to enhance Software Development Life-Cycle (SDLC) methodologies, ensuring products are secure by design.
Additionally, to fortify against potential vulnerabilities, organizations can harness advanced tools like SOCRadar’s comprehensive Attack Surface Management (ASM) solution. ASM provides businesses with a holistic view of their external attack surface, aiding in the identification of potential entry points for adversaries.
Targeting Major Events and Tailored Cyberattacks in 2024
In 2024, tailored cyberattacks are set to exploit major events, such as the US elections and the Paris 2024 games, leveraging generative AI to manipulate individuals and disseminate disinformation.
According to Fortinet, the increasing integration of technology in event management renders these systems potential targets for threat actors.
A hack announcement for Paris 2024 Olympics website
Explore our detailed blog post on cybersecurity threats surrounding the Paris 2024 Olympics, “Possible Cyber Threats in the 2024 Olympics,” revealing specific dangers and threat actor intentions.
You can uncover potential Dark Web threats targeting you, your employees, customers, or your organization through SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring. You can also stay updated on hacker trends and targets with Dark Web News, offering a comprehensive overview of the latest incidents and occurrences.
Beyond major events, governments with limited resources face heightened cyber threats. Malicious actors may employ ML and AI to regionalize attacks in 2024, translating communications into local languages using large-language models.
Expanding Attack Surfaces with the Advent of 5G Technology

Expanding Attack Surfaces with the Advent of 5G Technology
As forecasted in our 2023 predictions, the emergence of 5G technology has significantly impacted the cybersecurity landscape, providing threat actors with increased opportunities to launch attacks on a broader scale and at faster speeds.
The report highlights a continuous surge in both the sophistication and frequency of cyberattacks targeting unconventional devices, including Operational Technology (OT) systems, over the past decade. Fortinet’s predictions regarding the rise of Edge-Access Trojans have manifested in real-world scenarios. The introduction of 5G by Lynk Global, coupled with direct-to-device connectivity and the growing congestion in low earth orbit satellites, has expanded the connectivity of devices that were previously offline.
This widened attack surface creates abundant opportunities for threat actors, particularly in critical sectors such as oil and gas, transportation, public safety, and healthcare; expect an increase in the activities of threat actors within these sectors in 2024.
Conclusion, Cybersecurity in 2024 and Beyond
As we navigate the intricate landscape of cybersecurity in 2024, several looming threats demand our unwavering attention. The proliferation of Generative AI, serving as a double-edged sword, empowers both defenders and attackers alike. The dark side, however, manifests in AI-driven cyberattacks.
The Cybercrime-as-a-Service (CaaS) market’s exponential growth opens an extensive menu of malicious capabilities for threat actors, allowing them to execute attacks with alarming ease.
Ransomware, continues its relentless surge, with threat actors constantly evolving their tactics. The focus has largely shifted from data encryption to Denial-of-Service (DoS) and extortion, and the landscape has also given rise to fake extortion schemes and attempts to exploit regulatory pressures.
Zero-day vulnerabilities, a persistent menace, pose an elevated risk, exacerbated by unreported zero days. Anticipating the rise of zero-day broker services, organizations must bolster their security postures.
Tailored attacks leveraging major events, coupled with resource-constrained governments facing increased cyber threats, paint a landscape where cybercriminals exploit opportunities with precision. The ever-expanding attack surface fueled by 5G technology presents a new frontier for compromise, with critical industries becoming prime targets.
As we confront the challenges of 2024, a proactive stance backed by robust cybersecurity tools becomes the linchpin in securing our digital future. In this dynamic cyber battleground, knowledge is the most crucial. Organizations can stay ahead of the curve by harnessing the capabilities of Cyber Threat Intelligence platforms such as SOCRadar. From data leaks and phishing threats to supply chain compromises and vulnerabilities in unmanaged assets, the platform offers a vigilant eye on the evolving threat landscape, providing timely alerts to fortify digital ramparts.