What is Stealer as a Service?
By SOCRadar Research
Stealer as a service is a marketing approach in which threat actors offer to sell or lease access to information-stealer tools designed to steal sensitive data from victims’ devices. This model enables anyone to deploy info-stealer malware regardless of technical ability or resources. Therefore, the “Stealer as a Service” model has a wide spectrum of users, from nation-state groups such as APT 37 and APT 29 or the Lapsus$ group, known for high-profile attacks, to amateurs with low technical skills.
“Stealer as a Service,” like all other legitimate or criminal ‘as a service’ models, is a professional business model. While branding their services, threat actors provide malicious software and run an extortion and payment system with customer support and guidance.
Overview of the Stealer as a Service
On dark web forums, many info-stealers are advertised as ‘Stealer as a Service’ (or Malware as a Service). The functionalities of the info-stealing malware may vary. Some are exclusively concerned with data collecting, but others offer remote functionality that allows the threat actor to drop and run additional malware into the compromised device.

On dark web forums, there are also advertisements for purchasing customized stealer malware that will answer the specific needs of threat actors.

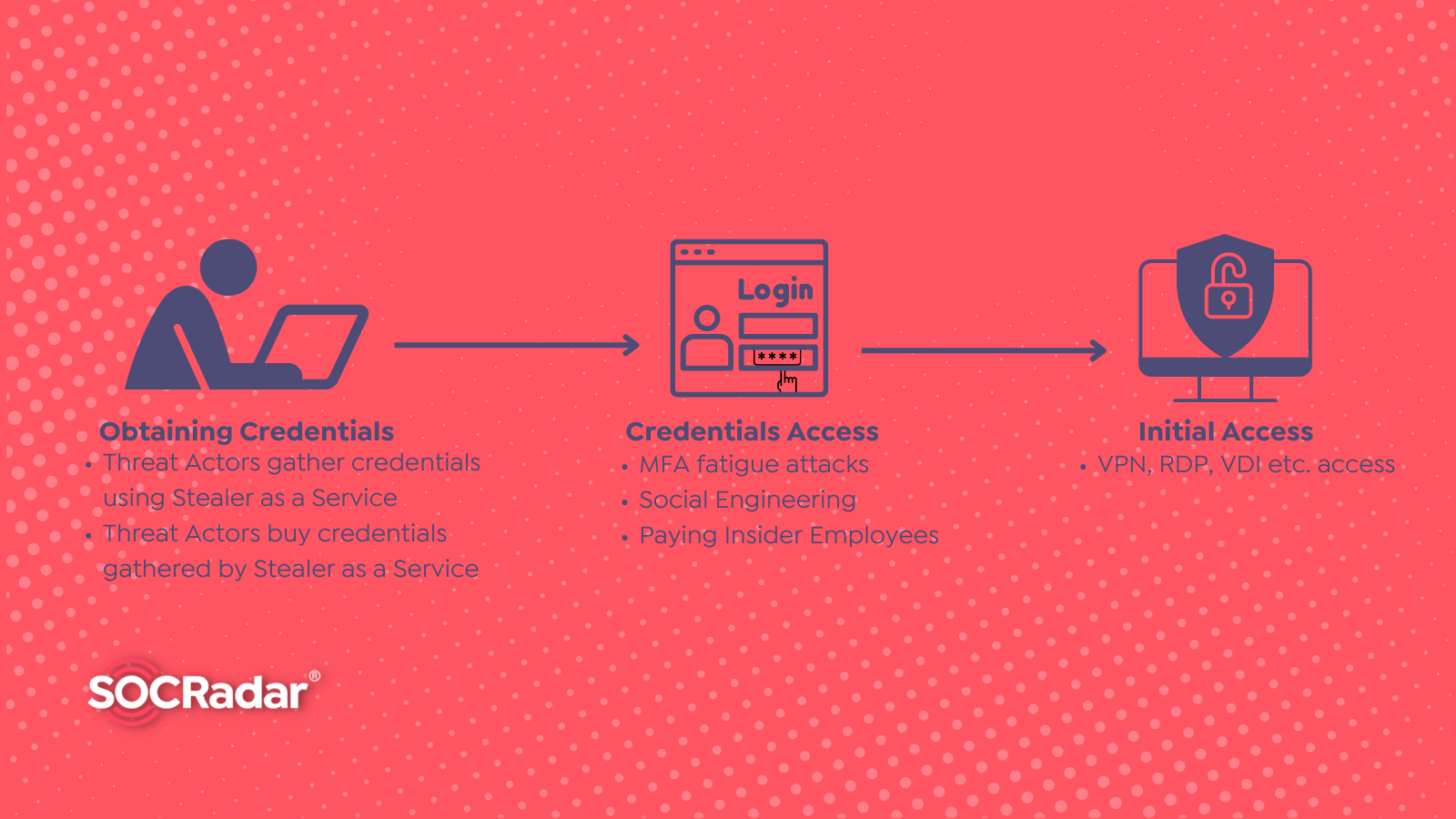
Threat actors can gather various types of data with several different methods from infected devices by utilizing stealer as a service. Many undesirable situations may occur when these data are compromised. This diversity can be summarized in its most general form as follows.

Following a successful attack, attackers can exploit stolen data in several ways. They can also sell the stolen data in underground forums and black markets.

Threat actors may use stolen data, especially credentials, in later criminal activities such as ransomware or other comprehensive attacks.

Stealer as a Service Distributing Methods
When deploying a stealer as a service model, a major challenge for threat actors is to lead the victim to download the stealer malware. Threat actors can distribute stealer malware through a variety of attack vectors. To deliver the malware to the victims, threat actors frequently use browser extensions, exploited websites, malicious attachments, and Google ads. Some of the most common methods of infection include:
- Infected legitimate app: Threat actors infect legitimate apps with malware. Stealer malware is often embedded in YouTube video reviews of popular games, mining software, or NFT (Non-Fungible Token) files on private forums, cheats for popular video games, social media giveaways, and lottery URLs.
- Spam: Threat actors generally send stealers via email, often impersonating trusted organizations. The stealer can be attached to the email directly, or the recipients can be tempted to click on a malicious URL.
- Compromised system: Stealer malware is sometimes distributed remotely after threat actors gain access to the target system.
- Malicious advertising: Victims are redirected to a fake site to download malware by clicking on the malicious ads. In some cases, simply viewing the malicious ads can be enough to initiate the download of a stealer.
- Cracked software: Combining stealer malware with cracked software is a distribution method commonly preferred by threat actors.
Additionally, threat actors can exploit features of popular messaging apps like Discord and Telegram. In Discord and Telegram, underlying elements called bots are used to play games, share data, manage channels, or design any other automated task.
Cybercriminals use Telegram messaging apps for command and control (C&C) by utilizing the bot capabilities on the Telegram platform. Stealer malware can send automatic messages via the Telegram application.
Threat actors can use the Discord program to transmit data via automatic messaging capabilities known as webhooks. Furthermore, some attackers actively host malware payloads on Discord’s content delivery network (CDN).

Popular Stealers as a Service
Information collected by info-stealer malware has recently been used in high-profile attacks such as Uber and Rockstar Games. These attacks reveal that stealers not only target individual users but also the newer versions of stealers are increasingly being utilized to target businesses and large organizations.
RedLine Stealer, active since 2020, is one of the most popular stealer as a service models. RedLine was first distributed with Covid-19 phishing emails. RedLine is mainly spread by phishing emails, malicious advertising, cracked software, cheats for popular games, and malicious software disguised as installation packages such as Telegram and Discord.

Many threat actors like APT29, APT32, APT37, Lapsus$, MuddyWater, and KillNet use RedLine Stealer.


Vidar, another notable stealer, has been actively used since 2018. It is distributed through malicious advertising, spam emails, phishing websites, and cracked software.



SOCRadar Dark Web Research Team constantly seeks new stealer as service malware on underground platforms. The most notable new stealer malware for 2022 Q2 was Rhadamanthys and LummaC.


SOCRadar research team prepared a detailed malware analysis report for LummaC2 Stealer.

The research summary, which analyzes well-known and newly released stealers, is presented below.

Although stealer malware is relatively small, it is quite effective and can steal significant amounts of data. Stealing sensitive information can be highly profitable because it can be sold on the black market for a high price and utilized for further high-profile attacks. Moreover, the Stealer as a Service system is a user-friendly(!) stealer with easy-to-access and easy-to-use capabilities. In this context, threat actors can be motivated to create and deploy stealer malware to make a profit. So, the popularity of the Stealer as a Service concept is expected to increase in 2023.
Organizations should train their staff on social engineering attacks and online account security. Furthermore, they should ensure that the staff is fully aware of fundamental cyber security measures such as using antivirus, avoiding downloading software from suspicious sites, not saving passwords in browsers, and deleting browser cookies regularly.
One of the most effective defenses against Stealer as a Service malware is having 360-degree visibility over the attack surface and real-time intelligence from all digital assets.
An extended threat intelligence solution is required to have threat intelligence on the dark web and surface web about the latest tactics, techniques, and procedures related to the Stealer as a Service malware and the threat actors who use them and to take proactive measures against threats and risks.



































