Okta Customer Support System Breach: Lessons in Supply Chain Risks and Cybersecurity
How successful are you in ensuring your cybersecurity in the digital environment? Personal and corporate data security has become more critical in today’s digital world.
In an age where technology is rapidly advancing, recent incidents have highlighted how cloud-based Identity Access Management (IAM) technologies and third-party software and services can be both conveniences and potential cybersecurity risks. The cyber attacks in 2023 on significant companies like Uber, Boeing, and Okta and the vulnerability in the widely used MOVEit software demonstrate that cybersecurity is not just the responsibility of I.T. departments but of everyone.
The critical role of cloud-based identity verification and access management solutions in cybersecurity is undeniable. The importance of the risks associated with these systems is increasing daily. This article will comprehensively analyze a cybersecurity breach in Okta’s support services. Following the Okta incident, we began researching how Okta, a key player in supply chains, created a sort of cyber domino effect with this incident and how similar attacks could be faced in the future.
The latest developments in the cybersecurity world, the risks they pose for individuals and organizations, and the continued hacking of critical institutions in supply chains have driven us to write this article and define the risk. Our Threat Research team’s article aims to inform readers, raise awareness about these critical security issues, and minimize risks.
What is Identity and Access Management (IAM)? Why Companies Use IAM?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a fundamental component of cybersecurity in managing an organization’s access. IAM provides users and institutions secure data and resource access through authorization and authentication. This system increases efficiency while reducing security risks. Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), essential components of I.A.M., assist users in secure and easy access to systems. SSO allows access to multiple systems using a single authentication. At the same time, MFA aims to enhance security by using various security factors for authentication.
What is Single Sign-On (SSO)?
Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication process that enables users to access systems using a single set of credentials. SSO improves user experience by simplifying password management and reducing login procedures. For example, an employee with access to multiple servers can access all systems using just one username and password without storing and remembering different account information for each server.
Technically, the SSO connection process typically involves the following steps:
- The user attempts to access a service protected by the SSO system.
- The user is requested to authenticate.
- The user enters their credentials into the central authentication server.
- If the authentication is successful, the server generates an authentication token.
- This token is used during the user’s access to other applications and services, eliminating the need for separate logins for each application.
Benefits of SSO:
- Single sign-on provides users with easy and quick access to multiple systems.
- It requires the management of only one password instead of multiple passwords.
- It reduces the time users spend accessing various services.
Risks of SSO:
- If the SSO system is targeted, the theft of a user account can jeopardize the security of multiple systems associated with that account.
- Attackers who breach internal network systems by exploiting security vulnerabilities can quickly gain broader access using SSO systems.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires users to verify their identity using two or more independent authentication factors (knowledge, possession, and inherence). MFA significantly enhances account security by providing additional protection against unauthorized access.
MFA allows users to authenticate their identity using multiple factors, typically including:
- Knowledge Factor: Something the user knows, usually a password or P.I.N.
- Possession Factor: Something the user has, such as a security token or an authenticator app on a smartphone.
- Inherence Factor: Biometric characteristics of the user, like a fingerprint or facial recognition.
In the MFA process, the user first enters a knowledge factor (e.g., their password) and then completes the authentication with either a possession (SMS code, verification through a mobile app) or an inherence factor (biometric verification). This multi-layered approach increases security and makes unauthorized access more difficult.
Benefits of MFA:
- Multiple authentication factors significantly enhance account security.
- MFA provides effective protection against automated cyber-attacks and phishing attempts.
- It offers an additional layer of security against weak or stolen passwords.
Risks of MFA:
- Although MFA is an effective method for increasing security, it can be vulnerable to social engineering attacks in some situations. For example, MFA systems that rely on user verification can be bypassed through requests made to IT departments via social engineering, or the additional layer of protection can be compromised if a code sent to the user’s email is intercepted. Therefore, the implementation of MFA is crucial. Solutions like passwordless authentication, which we will discuss later in the article, are recommended to enhance security, and stronger protection against social engineering attacks is necessary.
We will analyze the critical role of cloud-based IAM solutions in ensuring cybersecurity by examining some cyber incidents caused by IAM solutions and similar third-party applications below.
Supply Chain Attacks in 2023
Before examining the Okta cybersecurity breach, which is the subject of our research paper, let’s look at some recent supply chain issues impacting cybersecurity incidents.
Uber Data Leak
The data breach at Uber was caused by a third-party service company named Teqtivity. Teqtivity provided asset management and tracking services to Uber. This leak occurred due to hacking a backup server of Teqtivity on Amazon Web Services (AWS). Threat actors obtained information belonging to Uber from this server. The server contained the personal information of Uber employees and data related to various I.T. devices. Teqtivity provided a system for Uber’s asset management and tracking services.
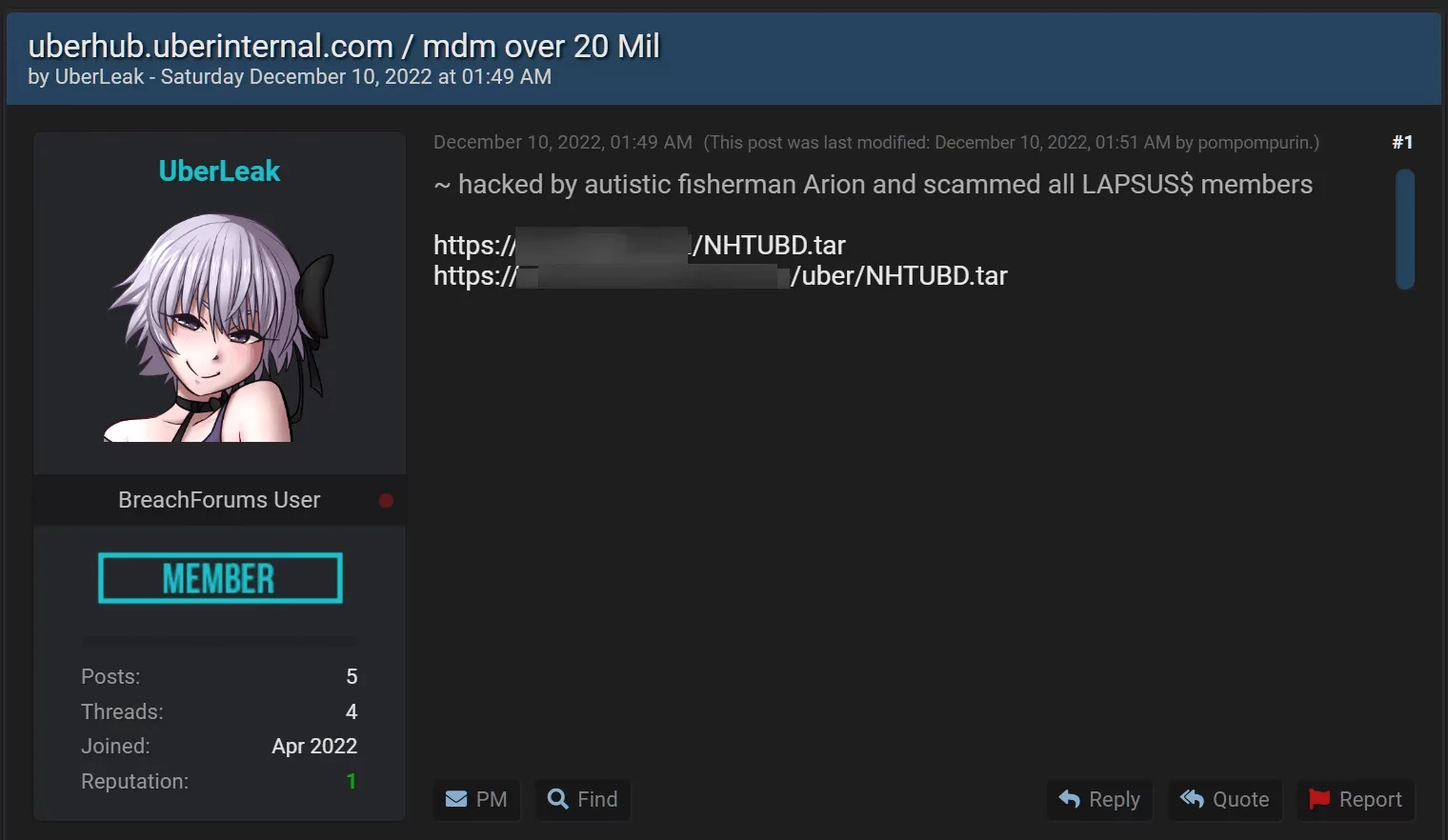
A dark web post sharing Uber’s sensitive data.
Leak Data:
It includes the personal identification and account information of approximately 77,000 Uber employees.
Size of Leaked Data:
The total size of the leaked data has not been specified. However, a forum post shared by threat actors stated that the leaked archive contained about 20 million Uber-related records. The exact size in gigabytes or terabytes is not known.
Scope of the Leak:
The leaked data includes user information (names, email addresses, details of workplace locations) and device information (serial numbers, brands, models, technical specifications). The information compromised in this leak is critical and could potentially be the source of many future data breaches.
Boeing Ransomware Cyber Incident
In 2023, Boeing became a target of the LockBit ransomware group. As a result of this attack, the attackers publicly released data belonging to Boeing.
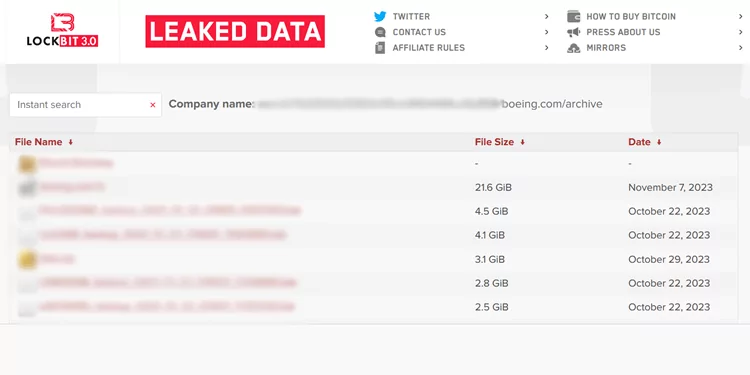
LockBit ransomware group’s leak site.
Boeing suffered a cyber attack by the LockBit ransomware group in 2023. This attack originated from a security vulnerability in Boeing’s Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway devices, known as “Citrix Bleed” (CVE-2023-4966). The attackers exploited this vulnerability to bypass password and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) systems and seize control of authorized user sessions (session hijacking). LockBit used this access to establish persistent access in Boeing’s parts and distribution business lines, steal data, move within the network, and potentially deploy ransomware. This security weakness made Boeing a target due to a vulnerability originating from Citrix NetScaler, a third-party application.
Here are some critical details about this incident:
Nature of the Attack:
LockBit 3.0 targeted Boeing and other organizations by exploiting a security flaw in Citrix’s software, commonly called “Citrix Bleed.” LockBit admitted to being behind the attack on Boeing and published about 50 GB of data they claimed to have stolen from Boeing’s systems. LockBit is estimated to have targeted up to 800 organizations alone in 2023.
Boeing’s Confirmation and Impact:
LockBit published screenshots of the data claimed to be stolen from Boeing. These data included Citrix logs, indicating that the breach might have been executed using the Citrix Bleed vulnerability. Boeing confirmed that certain parts and distribution operations encountered a cybersecurity incident.
Financial Impact and Security Measures:
LockBit reportedly received ransom payments totaling up to 90 million dollars from organizations in the U.S.A. from 2020 to mid-2023. This underscores the significant financial impact created by LockBit since its inception in 2020. Following the analysis of data provided by Boeing, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued an alert in collaboration with the FBI and the Australian Cyber Security Centre. “Citrix Bleed allows threat actors linked to LockBit 3.0 to bypass password requirements and Multi-Factor Authentication (M.F.A.), thereby successfully seizing control of legitimate user sessions in Citrix NetScaler web application delivery control (ADC) and Gateway devices,” they stated.
Exploitation of the MOVEit Vulnerability
A security vulnerability in MOVEit Transfer software led to a widespread cyber attack affecting various organizations, including several U.S. government agencies.

The MOVEit incident was one of the most critical cyber attacks in 2023.
MOVEit is a file transfer software developed by Progress Software Corporation. This software was targeted in 2023 by a ransomware group named Cl0p. Cl0p exploited a vulnerability in the MOVEit software to infect organizations with ransomware and demand ransom. The effects of this attack can be summarized as follows:
- MOVEit is used by thousands of public and private sector organizations worldwide.
- In late May 2023, during hundreds of transfers conducted through MOVEit, threat actors stole a significant amount of data.
- The attacks affected a total of 2,659 organizations and 83,750,513 individuals.
- 78.4% of the affected organizations were based in the U.S.A., 13.8% in Canada, 1.4% in Germany, and 0.8% in the U.K.
- The most affected sectors were education (40%), healthcare (19.6%), and finance and professional services (12.7%).
- According to IBM data, the average cost of data breaches is 165 USD per record.
- Based on the number of affected individuals, the estimated cost of the MOVEit incident is approximately 13.8 billion USD.
- On May 31, Progress Software published a bulletin and patch for a security vulnerability identified as CVE-2023-34362, with a vulnerability score of 9.8/10.
- On June 9 and June 15, respectively, more patches were released for two critical security vulnerabilities identified as CVE-2023-35036 and CVE-2023-35708.
- The MOVEit incident highlights the importance of supply chain security and managing risks from third-party software providers.
Okta Hacking
In 2023, Okta’s customer support system was hacked due to an employee using their personal Google account on a company-managed laptop. This incident led to the theft of data from numerous Okta customers. Okta’s Chief Security Officer David Bradbury said an internal error was the “most likely path” for the attack’s execution. A threat actor gained unauthorized access to Okta’s customer support system between September and October 2023, reaching files belonging to 134 customers. These files contained session tokens, which were used for session hijacking attacks. Hackers utilized a service account stored in the system, which was granted permission to view and update customer support cases. The username and password for this account were saved in the employee’s personal Google account. Bradbury mentioned that these credentials were likely exposed due to a breach of the employee’s personal Google account or personal device.
It was discovered that Okta’s customer support system in 2023 was breached using stolen credentials. A threat actor accessed customer support case files containing HTTP Archive (HAR) and conducted multiple attacks using these files.
What Are HAR Files Used For?
- HAR files provide detailed information about the loading and interactions of a web page, assisting in diagnosing problems.
- They can identify slow-loading elements and areas needing optimization.
- Used to detect errors in web applications.
- It can aid in identifying security breaches or suspicious activities.
How To Obtain a HAR File?
- Open developer tools in the web browser where you want to record activities (for Chrome, press F12).
- Switch to the ‘Network’ tab.
- Start recording interactions by refreshing the web page.
- After recording the activities, download the H.A.R. file to your computer.
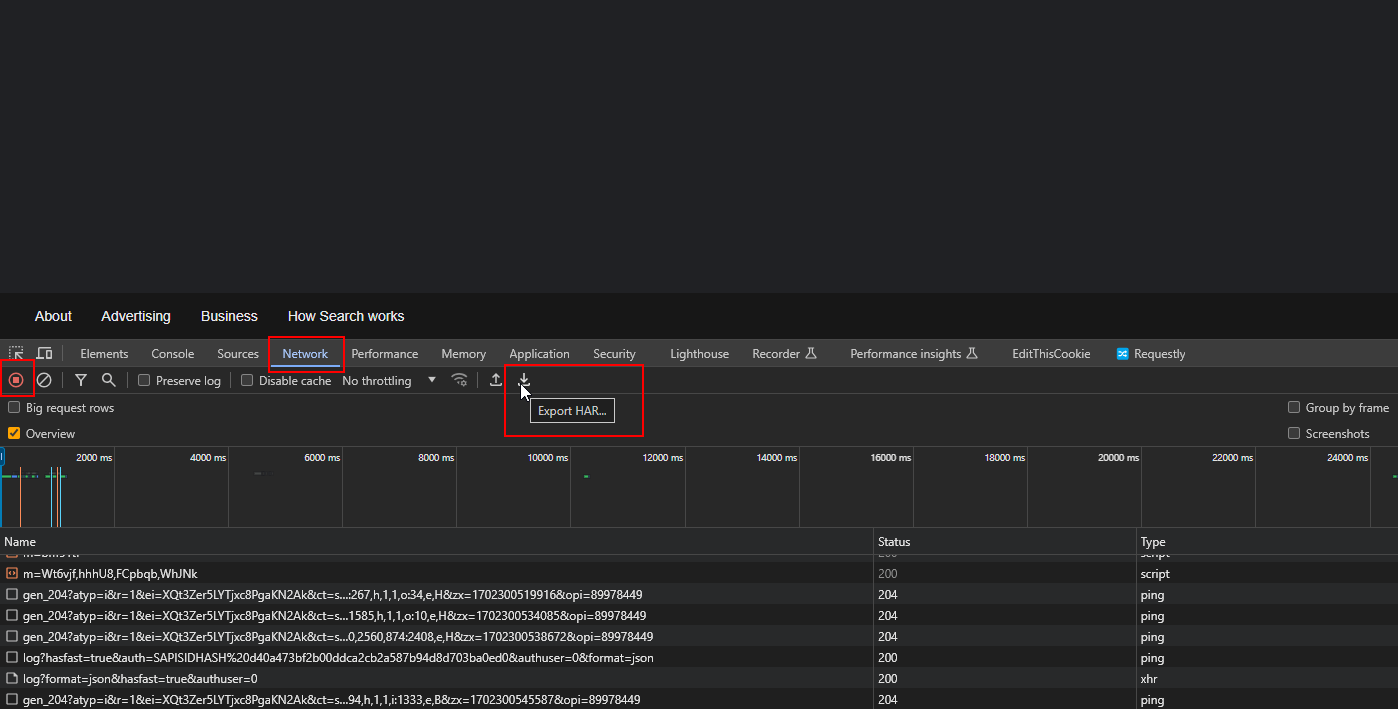
Downloading a HAR file.
Companies like BeyondTrust, specializing in Privileged Access Management (PAM), and Cloudflare, offering various solutions such as Content Delivery Network (CDN), DDoS attack protection, secure access services, and DNS services, revealed that Okta was slow in becoming aware of and responding to the breach. BeyondTrust detected suspicious activity earlier and warned Okta but received a slow response. Despite quickly directing internal reactions without impacting the customer, Cloudflare also criticized Okta’s disclosure process. The full extent and timeline of the breach remain unclear.

The Okta incident was a cautioning attack that pointed out the magnitude of supply chain risks.
Scope of the Breach:
Two months before the network breach, information of all users utilizing Okta’s customer support system was stolen. This included the names, email addresses, and web access records within Okta’s customers’ saved HTTP Archive files using the customer support system.
Nature of the Breach:
Attackers accessed files Okta customers uploaded during their most recent support incidents. These files typically contained HTTP Archive (HAR) files, which can include session tokens and cookies. Hackers used this information to impersonate legitimate users.
Impact on Customers and Companies:
Okta has over 18,000 customers, and the breach affected about 1%. One significant affected company was 1Password, a password management company that uses Okta to manage applications for employees. However, 1Password confirmed after a comprehensive review that user data was not accessed.
Financial Impact:
The breach caused an over 2 billion USD decline in Okta’s market value. It reduced the company’s stock value by more than 11%.
Cybersecurity Risks:
Although there’s no direct evidence of the stolen information being actively misused, the nature of the stolen data increases the risks of phishing and social engineering.
Our research aims to pre-analyze potential future cybersecurity incidents by investigating central IAM services like Okta within stealer logs. We will examine the risks organizations face with exposed corporate SSO account information found.
Why do Threat Actors Target IAM Products like Okta?
There could be several key reasons why threat actors continuously target Identity and Access Management (IAM) providers like Okta:
- IAM solutions are platforms that manage identity and access control. This means they tend to have user access to numerous applications and services. If a threat actor breaches a system like Okta, they can gain access to a multitude of systems and data.
- IAM providers offer critical cybersecurity services like Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (M.F.A.). Breaching these systems could enable users to log in across various applications and circumvent identity verification controls.
- A successful cyber attack on an IAM solution can impact the product and other businesses and institutions that use the IAM service. Such domino effects can create significant impacts for cybercriminals.
- A successful attack against a large, recognized service provider can mean prestige gains for threat actors, enhancing their reputation within cybercrime communities.
The global market for SSO, an essential component of IAM, was estimated at 3.1 billion USD in 2022 and is projected to grow at 13.3% during the 2022-2030 analysis period, reaching a revised size of 8.4 billion USD by 2030. This growth is enticing not only for S.S.O. companies but also for threat actors.
One of the primary reasons services like Okta are continuously targeted is their critical positioning in accessing networks and the sensitive information of numerous organizations. Such services become attractive targets for state-sponsored groups, financially motivated cybercriminals, and hacktivist groups.
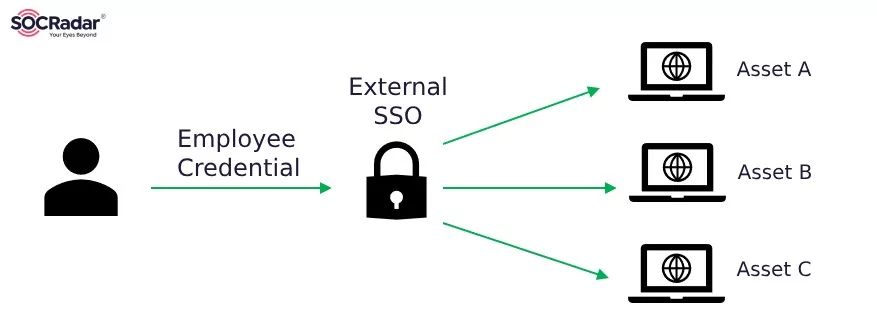
How Single Sign-On works.
Supply chain attacks aim to bypass the robust security defenses made by the targeted organizations by targeting their suppliers and vendors instead, creating unexpected impacts.
According to Gartner research, over 50% of help desk tickets are related to password issues. Attackers know that help desk employees often face many password and MFA requests, sometimes leading to laxity in verification processes.
Let’s recall the hacking incident at MGM Resorts. Threat actors identified MGM’s official account on LinkedIn. Then, they used social engineering on the help desk to impersonate the authorized person, requesting the removal of MFA during account access. The help desk, without requiring additional verification due to the urgency and frequency of such requests, disabled MFA verification over the phone (with the threat actor) and granted access to the account. This incident is a recent example of the vulnerability of SSO and MFA to social engineering attacks, as mentioned at the beginning of this article.
You can visit the following address for details on the M.G.M. hacking incident and social engineering methods.
What are IAM Products Similar to Okta?
SSO products fall under the Access Management subcategory of Identity and Access Management solutions. Generally, access management products provide services to organizations in account management and access.

Other SSO solutions found via Google search.
When you search for “SSO Solutions” on Google, the products shown in the image above appear. To research external and popular SSO products, we can base our analysis on the Gartner list. Gartner, recognized as an authority on industry trends and IT strategies, looks at the most popular Access Management solutions in 2023 at this address.
This research examines account information of organizations using central solutions known as external and offering SSO solutions. Hence, a random selection from the solutions in the Gartner report has been made. IAM products from the Gartner list – Okta, OneLogin, JumpCloud, Ping Identity Corporation, ForgeRock, and Auth0 – have been selected for this research.
The scope of the research includes analyzing data leaked and shared by stealer malware in the last month.
What is Stealer Malware?
Stealer malware are programs typically designed to covertly steal personal and sensitive data from users. These types of malware infiltrate users’ devices unnoticed, collecting passwords, financial information, identity details, and other important data. Stealer malware spreads through email attachments, fake software updates, or malicious websites. It transmits the data to remote servers for cybercriminals to access. These malicious programs pose a threat to the security of both individuals and organizations. They are frequently used for purposes such as financial fraud or identity theft.
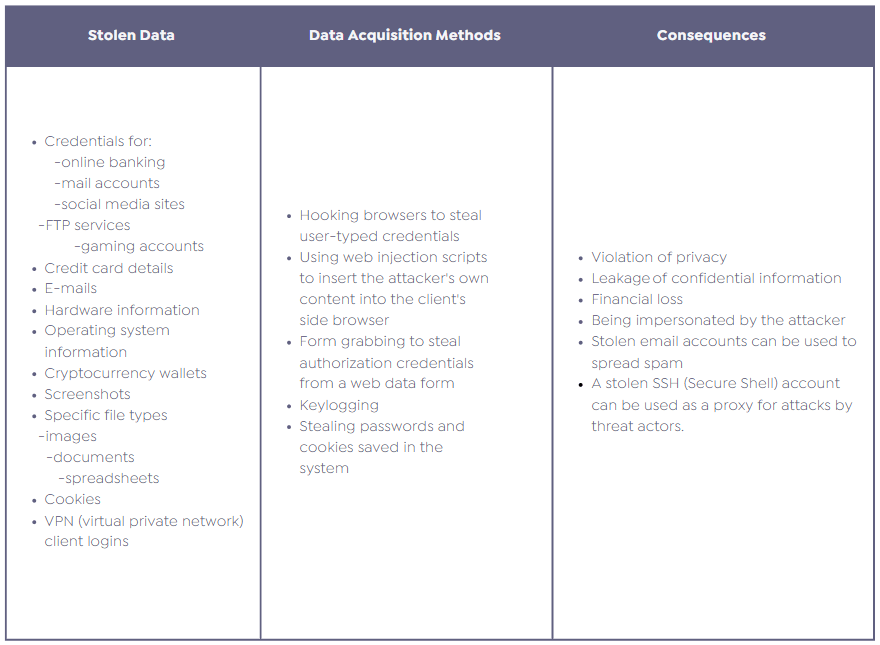
How Stealer Malware Leaks Could Affect Organizations?
For an organization, a data breach through stealer malware on an employee’s personal computer at a partner firm in the supply chain can have various impacts. The risk significantly increases, especially if this employee has access rights to the organization and stores these access details on their computer.
Examples of these risks include:
- Threat actors can capture these details if the employee possesses information that provides access to the organization’s systems. This could allow cyber attackers to access the organization’s internal systems, networks, or sensitive databases.
- Confidential or sensitive information about the organization could be leaked through the supply chain partner. This situation can lead to important information such as customer details, financial records, or intellectual property falling into the hands of malicious individuals.
- A security breach can damage the organization’s reputation and customer trust. This can lead to loss of customers and trust issues in business relationships.
- If the breach violates legal regulations related to personal data protection, the organization could face legal sanctions and fines.
- Rectifying the security breach, compensating for potential damages, and implementing additional security measures to prevent future attacks will require extra cost and time for the organization.
Therefore, organizations should pay attention to supply chain security and ensure their suppliers meet security standards. They must also be careful about securely storing and sharing access information.
SOCRadar aims to prevent such risks by analyzing data leaked by stealer malware.
(Source: SOCRadar)
Analysis of IAM Products in the Stealer Database
SOCRadar feeds its platform with data leaked by stealer malware, sending near real-time notifications to its customers in case of findings. For our research on IAM solutions, we examined data within SOCRadar from the past month, focusing on analyses within stealer logs. The data was researched using keywords like ‘okta.com.’
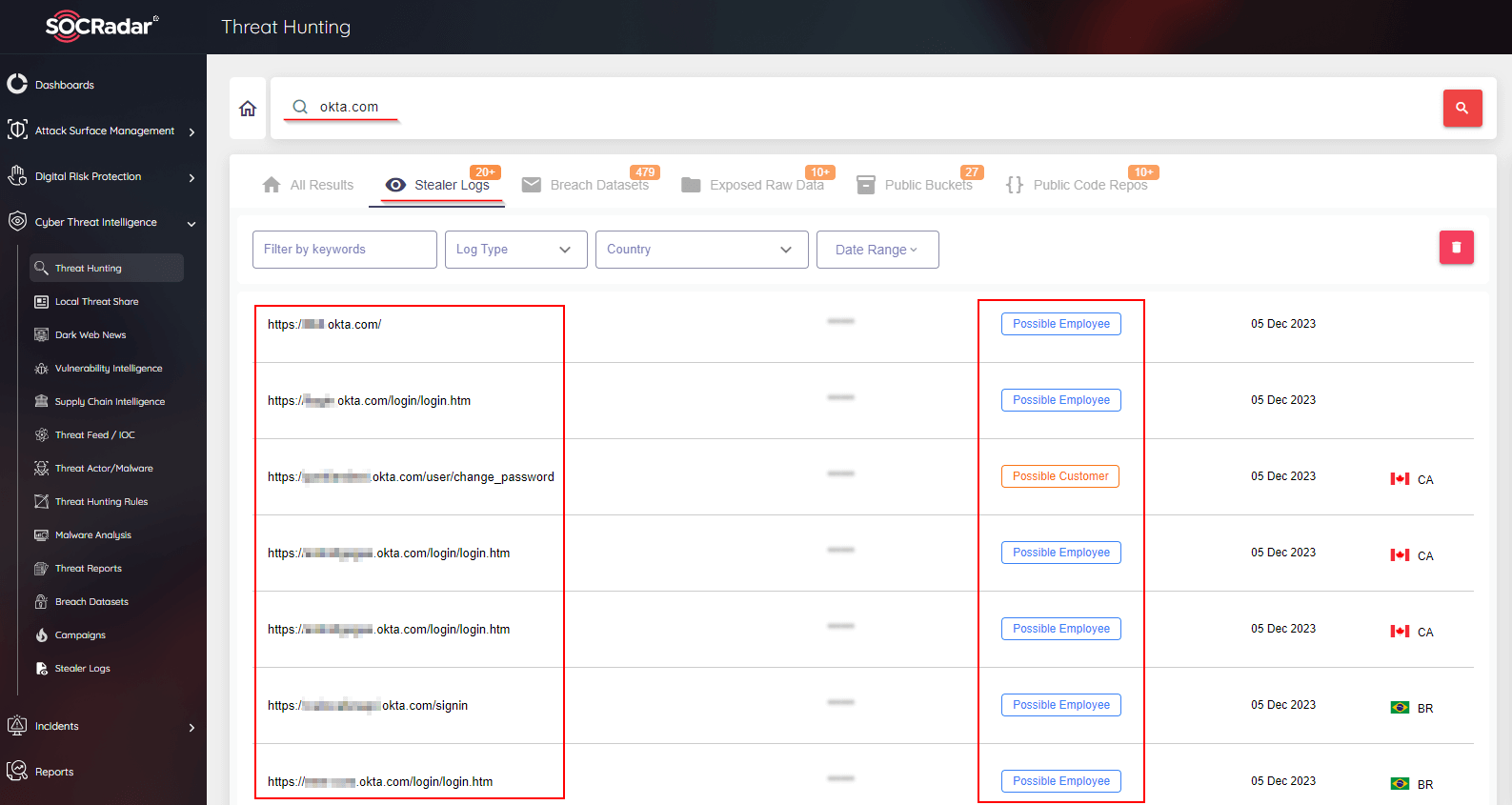
SOCRadar Threat Hunting module
The findings from the research are as follows.
In one month of stealer malware leaks, conducting a keyword search using IAM providers’ addresses revealed:
- A total of 50,000 username and password pairs were leaked by stealer malware.
- Only 16.02% of these passwords were unique, indicating a high rate of password repetition and posing a serious security risk.
- 1.43% of the account information belonged to corporate accounts, suggesting many companies could be at risk of hacking in a short period.
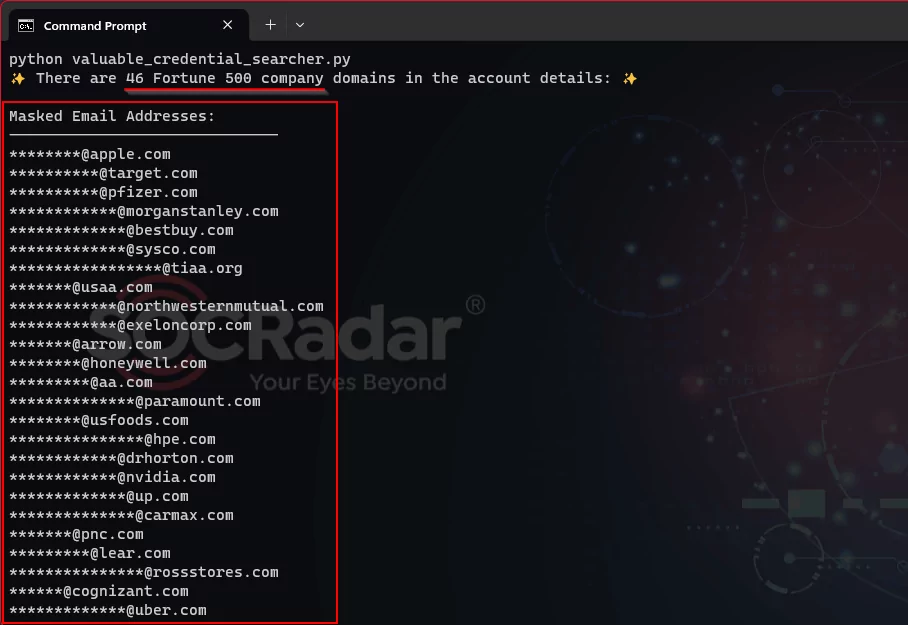
- Among these corporate account details, 46 organizations from the Fortune 500 list were identified. The presence of so many Fortune-listed companies underscores the magnitude of the risk.
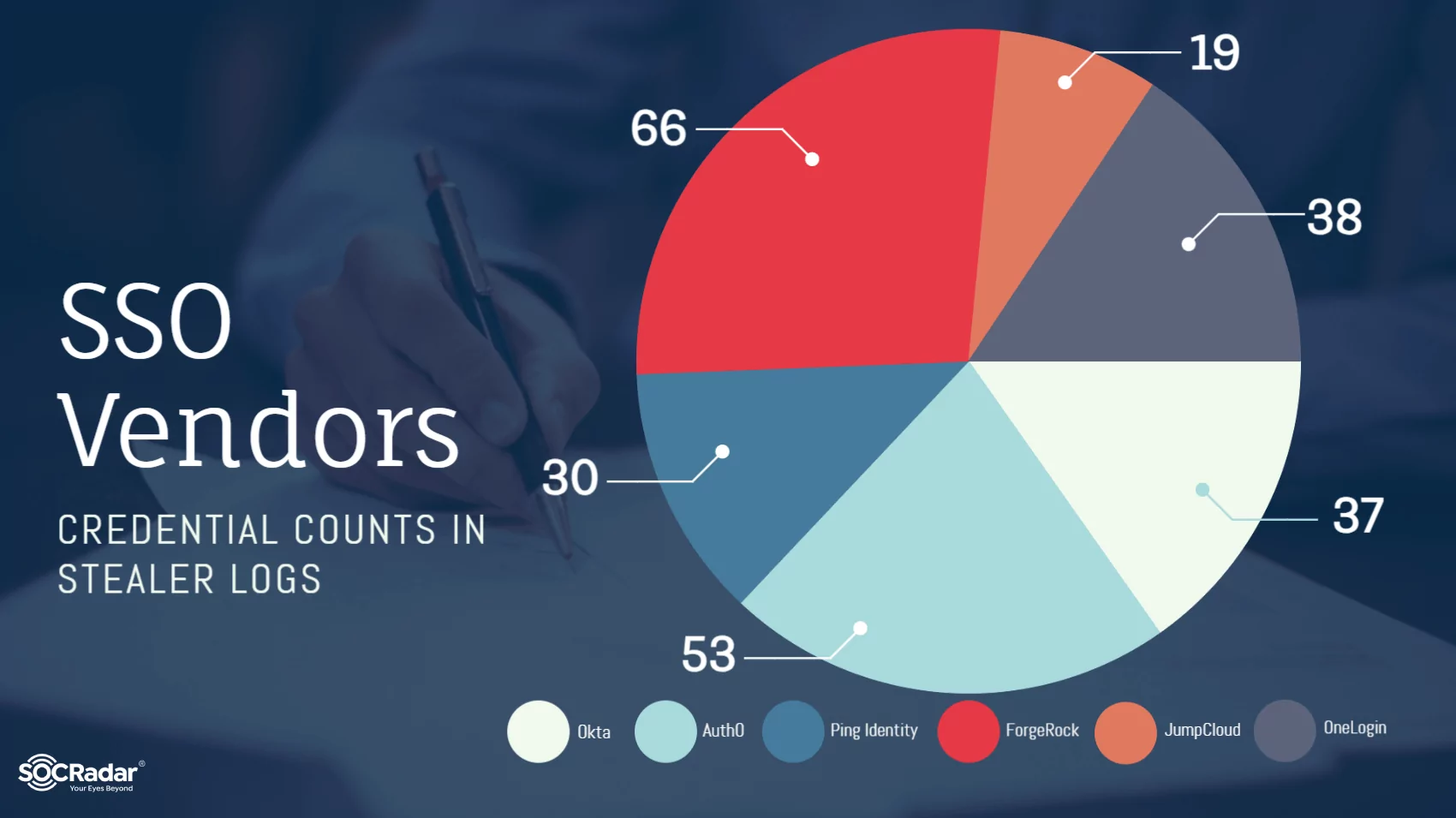
- In the examined data, ‘auth0.com‘ was found 53 times, ‘okta.com‘ 37 times, ‘onelogin.com‘ 38 times, ‘jumpcloud.com‘ 19 times, and ‘pingidentity.com‘ 30 times. This highlights the necessity for continuous security reviews and strengthening of S.S.O. systems.
Be Aware of Your Cyber Security Risks with SOCRadar Solutions
Organizations should consider the following points for measures against Stealer malware and similar cyber threats and how SOCRadar can assist.
Organizations may use third-party solutions for efficient and continuous access management. However, these solutions increase the security vulnerabilities that need to be managed. With SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence, you can track current vulnerabilities related to all products you are associated with.
Hacking of organizations providing third-party solutions can pose a significant risk for corporations. Organizations can use the SOCRadar platform to monitor suppliers exposed to such risks for a prompt response.
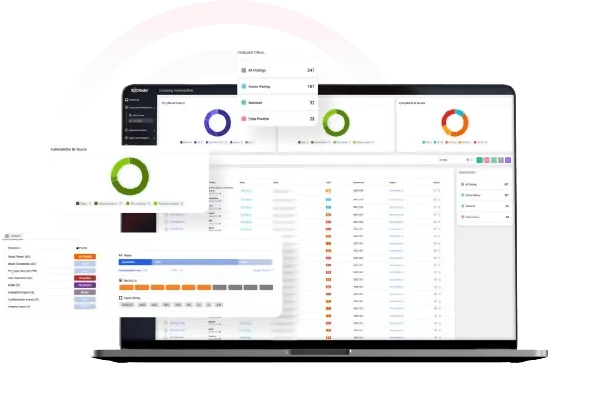
SOCRadar Company Vulnerabilities module.
Threat Actors Can Launch Cyber Attacks Using Stolen Account Information
SOCRadar monitors stolen account information on the dark web and social media, sending near real-time notifications to its customers. This enables organizations to identify security vulnerabilities and take proactive measures against potential cyber incidents.
Organizations should consider both internal and external risks. SOCRadar can assist in monitoring the organization’s online presence and managing supply chain risks. SOCRadar’s leakage monitoring services scan all data shared in public platforms (like GitHub or Postman), alerting you when it finds data that could be considered sensitive and facilitating prompt action before it falls into the hands of threat actors.
Organizations should adopt the zero-trust security model based on the principle of not automatically trusting any source. This requires continuous verification and monitoring of internal and external resources. With SOCRadar’s extensive IOC feed list, you can conduct pre-analysis and threat intelligence integration at every layer of your organization. SOCRadar Extended Threat Intelligence works integrally with most known log management solutions.
Security vulnerabilities in all your externally exposed services and systems can put your organization at risk. SOCRadar helps in detecting and analyzing such vulnerabilities through regular scanning services. With SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM), stay one step ahead of threat actors.
FIDO2 Authentication Specification
So, how does FIDO2 affect the general user experience with real-life examples? More importantly, how can you implement this in your daily life as an average user?
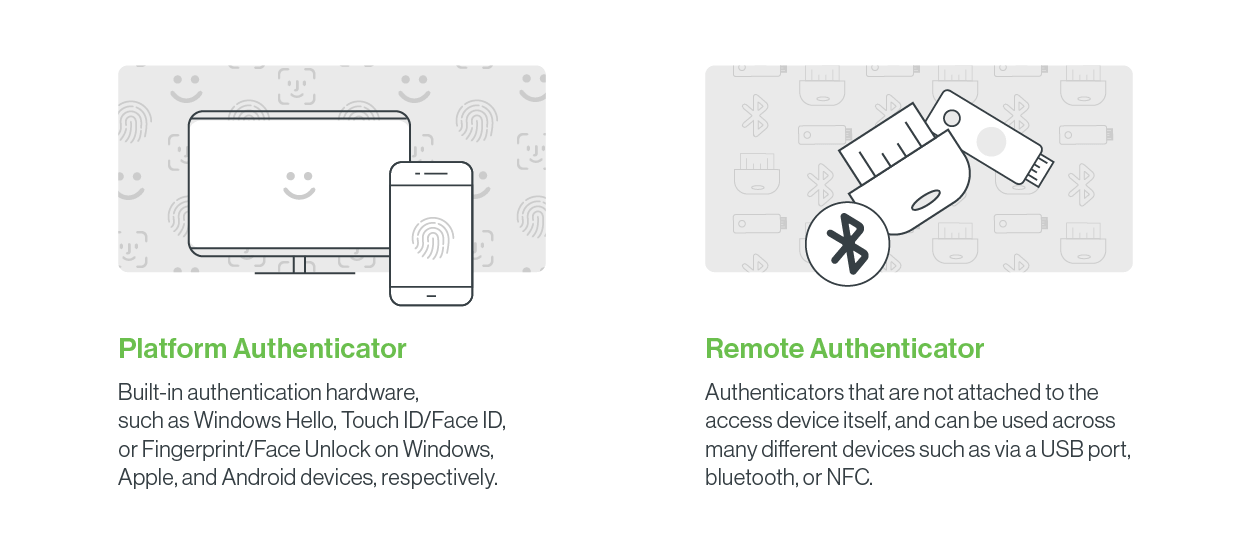
With FIDO2, users may simply authenticate to internet services in desktop and mobile contexts by utilizing common devices.
Let’s take a closer look at how you can implement FIDO2 passwordless entry in different ways:
Platform authenticators: Platform authenticators are integrated with employees’ smartphones, tablets, or laptops with built-in cryptographic hardware elements and biometric capabilities. For example, a platform authenticator can be an Android smartphone, a Windows device using Windows Hello, or an Apple device with Touch ID or Face ID features.
Remote Authenticators: authentication relies on a unique physical USB, NFC, or Bluetooth security key that enables you to log into services by inserting your key into your device’s USB port or pressing a button on the authenticator.
Security Recommendations for SSO and MFA
In the modern cybersecurity landscape, combining SSO solutions with MFA and passwordless methods is recommended to create a strong defense line. This approach makes the authentication process both secure and user-friendly.
Passwordless solutions, such as biometric data and FIDO2-based security keys, can be used for user authentication. These methods provide an extra layer of security, especially against password leaks and phishing attacks.
Following the cybersecurity incident at Okta, officials said that all customers should strongly consider using MFA, at least for administrative access. They also suggest making identity verifiers (such as Okta Verify FastPass, FIDO2 WebAuthn, or PIV/CAC Smart Cards), which offer additional security against phishing, mandatory for accessing all administrative applications for administrator users.
Okta recommends limiting session durations to 12 hours and inactivity periods to 15 minutes, in accordance with the cybersecurity risk management tool, NIST.
Okta advises its customers to be vigilant against phishing and social engineering attempts targeting their employees, particularly IT Help Desks and related service providers.
Reevaluate your IT Help Desk staff identity verification processes. Pay special attention to appropriate checks before performing high-risk operations like password or MFA resets on privileged accounts, such as visual verification.
Conclusion
The breach of Okta’s customer support system, which resulted in the theft of HAR (HTTP Archive) files, offers significant lessons in cybersecurity. This breach demonstrates how sensitive data and system access can be jeopardized. As emphasized by Okta officials, the incident highlights the importance of organizations continually reviewing their internal security protocols and employee behaviors.
In this breach, an employee using a personal Google account on a company-managed computer enabled hackers to access the customer support system and steal HAR files containing sensitive information. This situation underscores the need for companies to provide more training to their employees on secure internet usage and data sharing. Additionally, the importance of separating personal and work accounts, secure password management, and using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) are again brought to the forefront.
On the other hand, the incident illustrates the critical need for organizations to have the capability to detect cybersecurity threats early and respond quickly. It took time for Okta to detect and respond to this breach, increasing potential risks and damages. This underscores the importance of enhancing security practices such as continuous monitoring, rapid response, and post-incident analysis.
In conclusion, this incident demonstrates that cybersecurity is not limited to technological tools and security systems but also involves employee awareness, training, and organizational policies as critical components of the equation. Organizations should develop a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy considering technological security measures and human factors.
SOCRadar helps your organization and those in your supply chain with risk monitoring, ensuring you are always one step ahead.