Top 12 Takeaways from Verizon 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report
Verizon’s highly anticipated 16th annual data breach investigation report was released on June 6, 2023. This report, including useful information, deserves to be one of the most anticipated and valued ones from the cybersecurity industry because it is based on data analysis and real-world incidents.
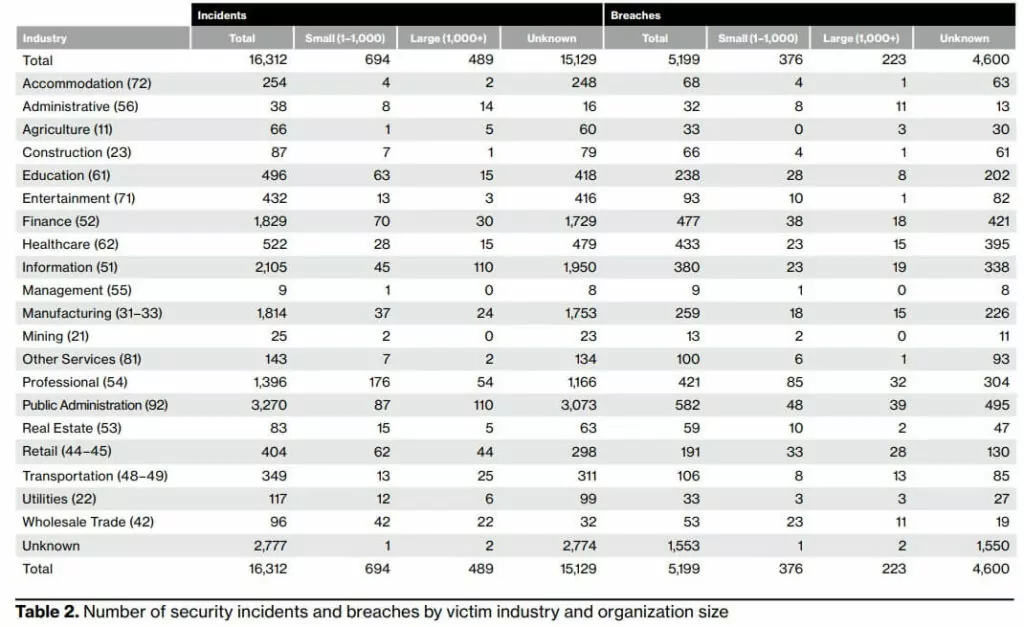
The 2023 report is created by collecting, aggregating, anonymizing, and analyzing data from 16,312 incidents that occurred between November 1, 2021, and October 31, 2022, for a total of 5,199 global data breaches. This data is distributed across 10 major industries plus the mid-market. Rather than broad statistics, it takes a deep dive into the “how” and “why” of incidents and breaches and helps organizations understand what they can do to protect themselves by referencing the Center for Internet Security (CIS) Critical Security Checks. Here are what we have selected and interpreted from the findings of this important report under the 12 prominent takeaways.
1. Social engineering remains an effective and lucrative way for cybercriminals.
BEC (Business Email Compromise) attacks have almost doubled in the entire incident dataset, representing more than 50% of the incidents in the social engineering method. Combined with the frequency of these attacks, the median amount stolen from these attacks has also risen to $50,000 in the last few years. BEC attacks can also be organized from within, e.g.; the attacker uses a compromised employee’s email account to target their own organization by impersonating the user. Another method is that actors can target partners using access to an employee’s email account so that they can impersonate the user and request payment updates to include the attacker’s bank account. Using the dark web monitoring service, you can gain a line of defense against potential threats.
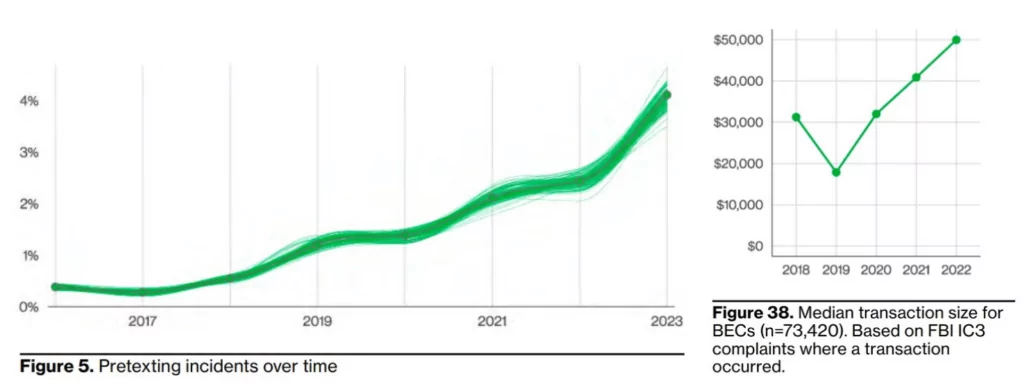
While social engineering attacks are carried out by phishing at a rate of 44%, the 3rd most common attack vector is using employee credentials interestingly. This brings to mind the info-stealer pests that have recently been widely sold and distributed on the dark web marketplace. You can go over SOCRadar’s comprehensive whitepaper related to info-stealer malware in this regard and gain a line of defense against potential threats by taking advantage of the dark web monitoring service.
2- Humans are still a significant factor, known and accepted as the weakest link, contributing to data breaches.
According to the Verizon report, 74% of all data breaches involve human elements. This includes not only social engineering but also user error, misuse of privilege, and stolen credentials.
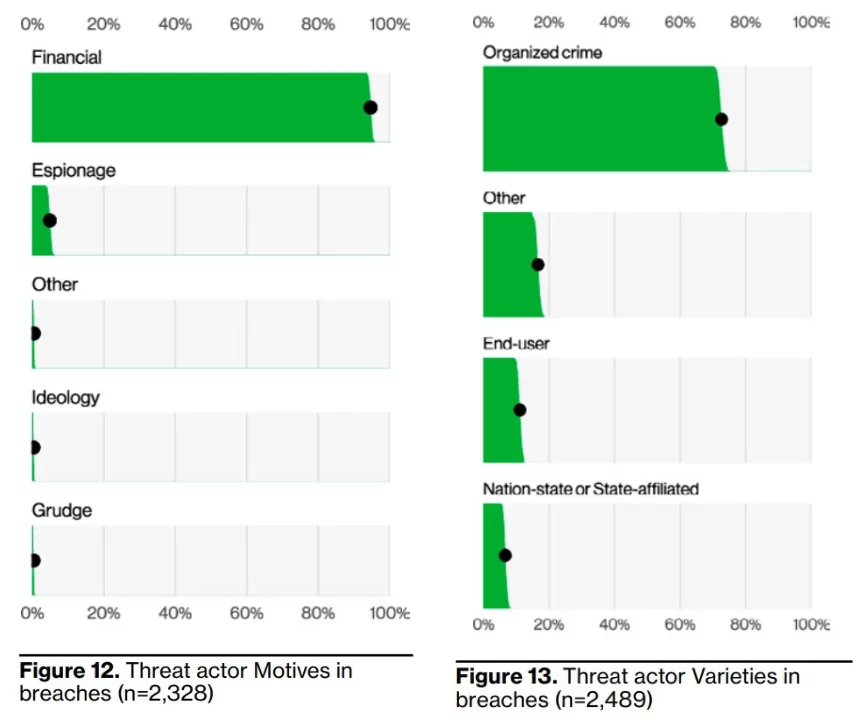
83% of data breaches involve external threat actors, and the primary motivation for attacks remains overwhelmingly financial in 95% of breaches. The top three ways attackers gain access to an organization are stolen credentials, phishing, and exploiting vulnerabilities.
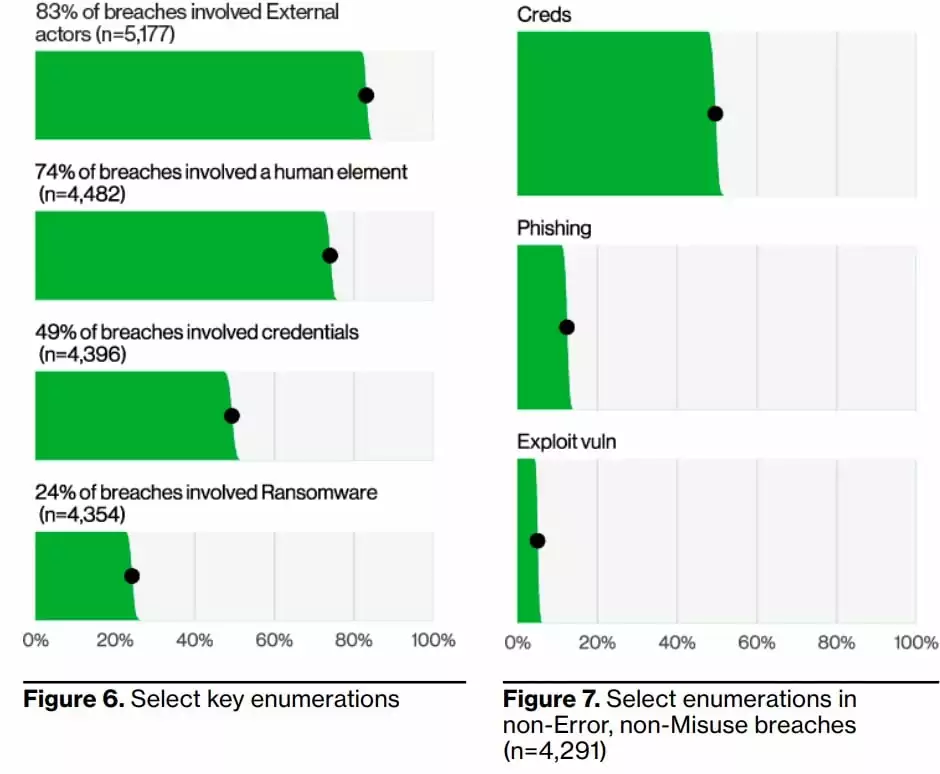
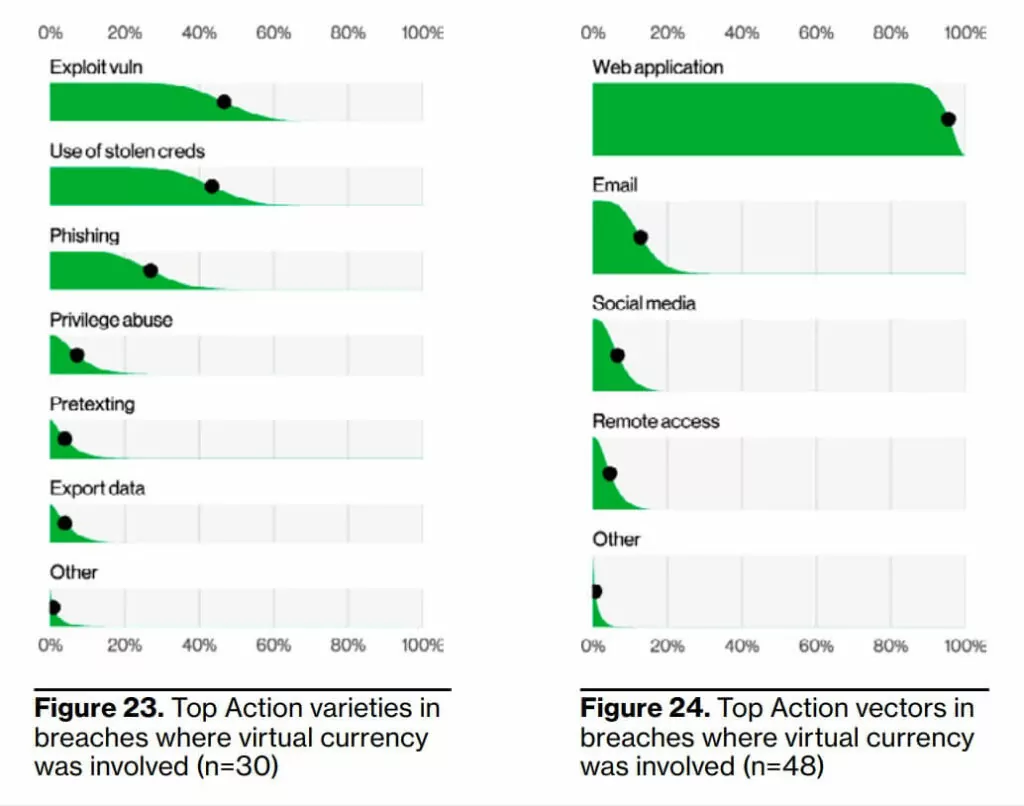
The images below show the answer to which actions cause data breaches the most. The following visuals describe the top action types (what happens in more detail, left image) and vectors (how these actions occur, right image) in data breach incidents. What is worrying is that ransomware, present in 15.5% of all cyber incidents, also ranks second in those resulting data.
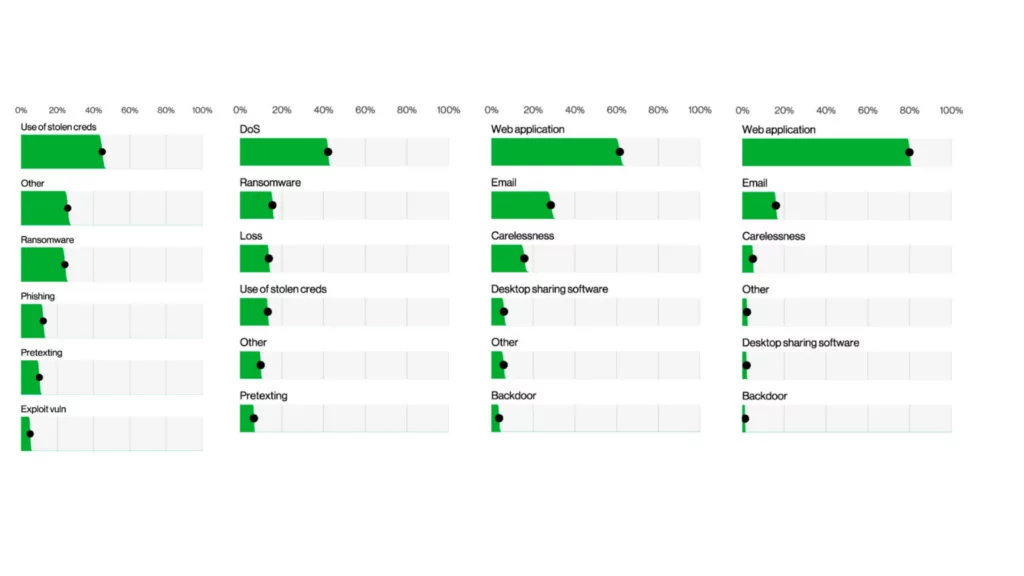
3- Ransomware is the most critical action in data breaches and cyberattacks.
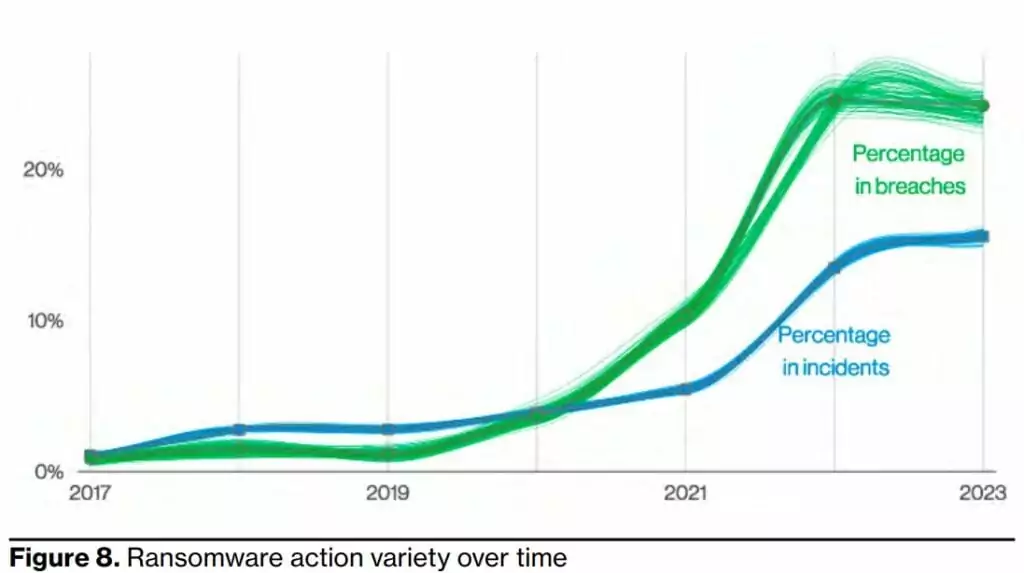
According to the Verizon 2023 DBIR report, ransomware continues to be a major threat and spread to organizations of all sizes and industries, with 24% of data breaches despite being statistically steady at 24% compared to last year. Moreover, more than 62% of all incidents today involve ransomware that organized crime actors committed, and 59% of all incidents had a financial motive, so unfortunately, there is still a growing trend.
94% of ransomware incidents are performed through system intrusion. While ransomware has only increased slightly this year, it is so pervasive that it may always be a threat we must protect against; in 91% of our industries, ransomware is one of their top three actions.
Furthermore, the overall cost of recovering from ransomware has increased even if the ransom amounts are lower. This fact may indicate that the overall company size of ransomware victims tends to decrease. Even though the amounts demanded money by threat actors are smaller (because they want to extort some amount of money even by negotiation), organizations’ additional costs in a possible IT infrastructure problem may increase their total loss.
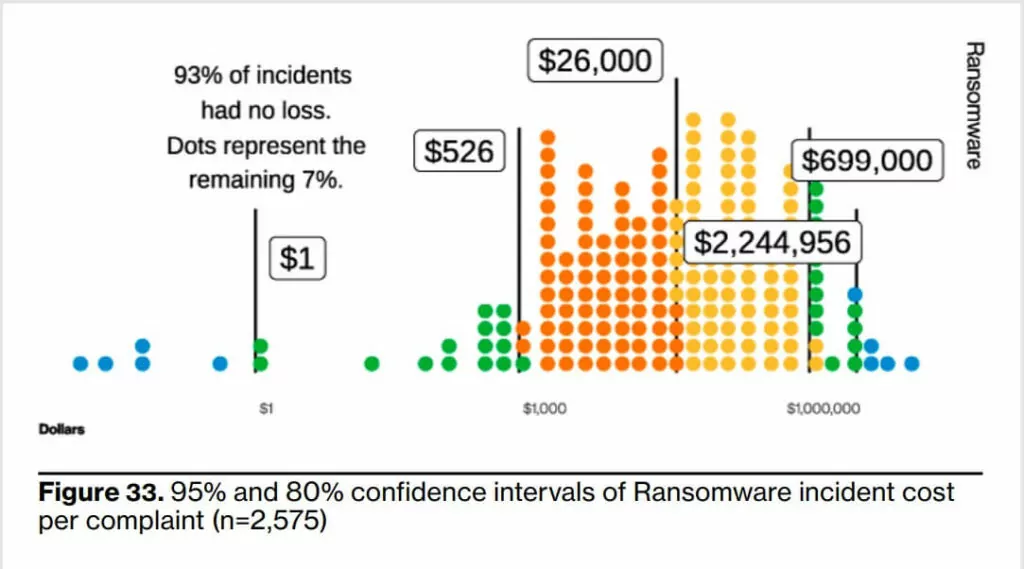
DBIR report concluded that according to the 2023 data on incidents resulting in loss, the median more than doubled from the most recently calculated 2021 data, reaching USD 26,000, and the 95% loss range increased to between $1M and $2.25M, towards a dangerous upper limit for a small business.
4- Insider threats, yes, but mostly externals role play.
External actors (the vast majority of which are organized criminals) are responsible for a considerable percentage (83%) of breaches, while internal actors are involved in 19%. This up to 20% may include not only intentional damage caused by internal actors but also actions involving user error actions.
At this point, it is worth reminding some research that insider threats have become increasingly prominent in recent years. Taken together with an increase in external data breaches in the Verizon report, we can claim that only the rate is low, but it does not mean negligible. On the contrary, considering the aim of external actors to somehow bypass the authentication and authorization phases easily, it is critical to identify insider threats with reliable intelligence information (e.g., collaboration and offers of money to disgruntled employees).
It’s hard to face the fact that some of our employees also cause data breaches for malicious reasons. The most common internal actor breach that is not accidental is the abuse of privilege. Employees may misuse the access they are given to do their job to steal data. They are more likely to do so for their own financial gain.
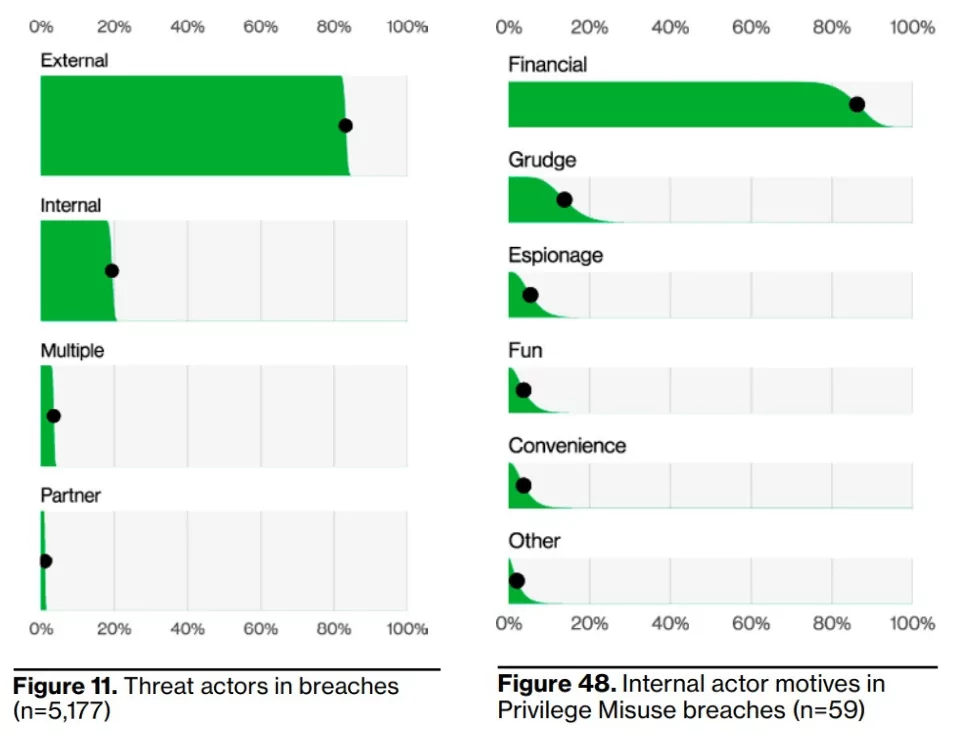
5- Financial motives still drive the vast majority of data breaches.
A massive 94.6% representation of data breaches increased year-on-year. If we look inwards to see which external actors are working the hardest, the best performer is organized crime. However, there is one interesting finding: the variety of internal end users causing misuse and intentional or accidental errors occur more often than external state-sponsored attackers, which shows that we need to pay more attention to security management and cybersecurity awareness training.
6- Fewer servers and more user devices trend.
The figure below also shows the types of valuable assets affected by data breaches and the results. Even if the affected servers are in the first place, they have decreased slightly compared to previous years, and the affected user devices have also increased. After the human factor moved to 2nd place in this ranking, it kept the place for at least a few years.

7- The emerging threat of cyber attacks on cryptocurrencies.
There has been a fourfold increase in the number of breaches involving virtual currencies this year compared to last year. This is a far cry from the days of innocence that had been seen in isolated cases in 2020 and before.
8- The system intrusion pattern has been used in more sophisticated attacks.
It appears that the system intrusion pattern was initially successful. This ranges from distributing ransomware to multi-step and sophisticated attacks.
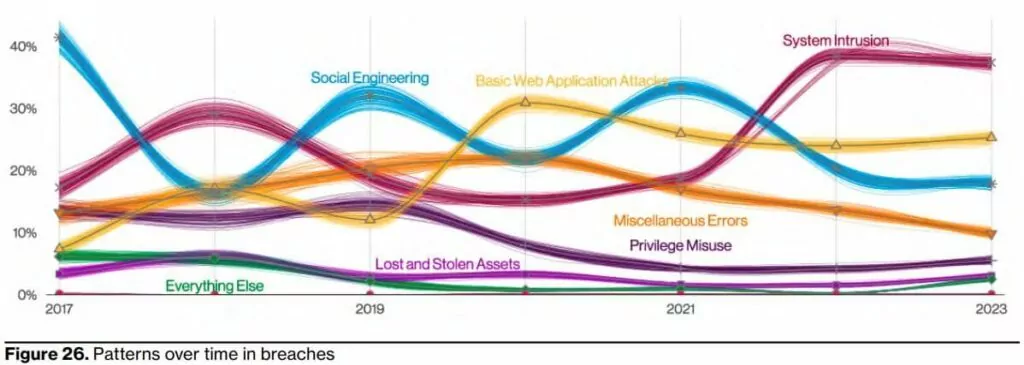
In terms of hacking, 9% of incidents involve the exploitation of vulnerabilities, and 8% involve the use of stolen credentials. Considering the incidents involving the exploitation of vulnerabilities, it was found that these vulnerabilities were largely exploited through web applications.
Here, it is worth mentioning that ASM products, as Gartner recommended, can be a helpful solution. EASM (Extended Attack Surface Management) is useful in identifying unknown assets and providing information about the vulnerabilities of the organization’s systems, cloud services, and applications that are exposed and visible on the internet and, therefore, can be exploited by an attacker/adversary. This security visibility-enhancing technology can also be extended to the organization’s subsidiaries or third parties.
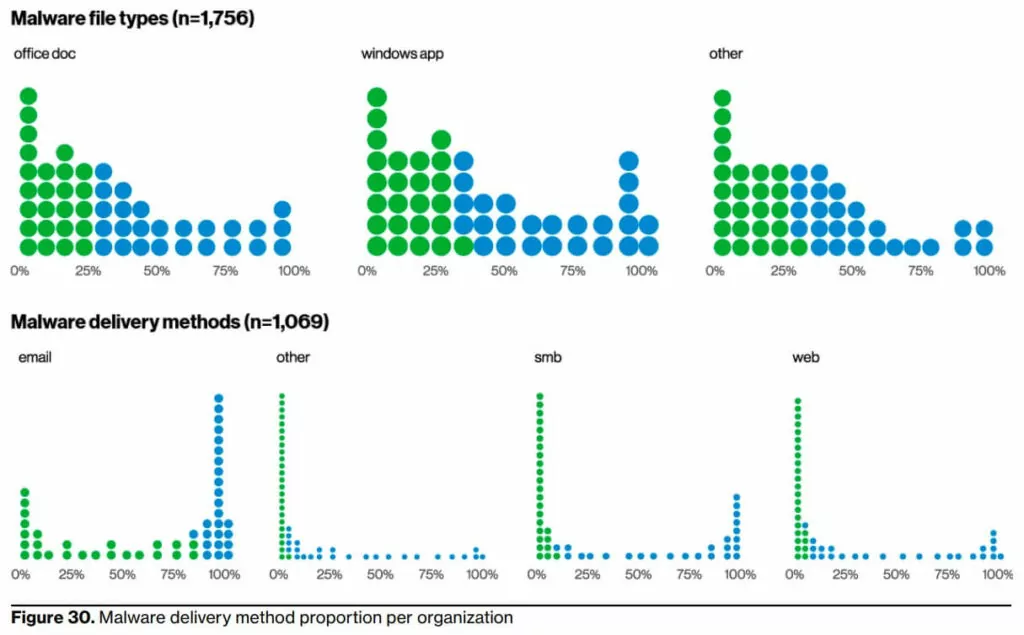
9- Malicious software still and persistently love the email path and Microsoft Office documents.
DBIR Report shows that they are primarily distributed via email and often come in the form of Microsoft Office documents (see Figure 30). This makes sense when you consider that many of these documents can now execute code on the client system, which is extremely useful in an attack. Admittedly, there are many cases where we do not know the exact entry path used by the attacker. However,these ways of exploiting vulnerabilities, using stolen credentials and phishing, are very similar to previous years’ findings.
10- Cyber attackers grow their DDoS capacity by building a giant botnet.
Verizon 2023 DBIR discovers an important point highlighting the increase in the median and percentiles above the median of DDoS attacks in bits per second (see Figure 45). The median increased by a massive 57%, from 1.4 gigabytes per second (Gbps) last year to 2.2 Gbps. Now, the 97.5 percentile has grown by 25%, from 99 Gbps to 124 Gbps. As bandwidth and CPU processing costs become more accessible and available, it is expected that the trend is hard to break in the growing competition between cyber attackers and DDoS mitigation providers.
11- The public administration industry is on the radar of more threat actors.
According to the Verizon Report, this year, 16% of public administration breaches showed evidence of multiple actors’ actions and working together with collaboration. There have been no multi-actor breaches in the public administration industry in the last two years and only 2% in the 2020 report.
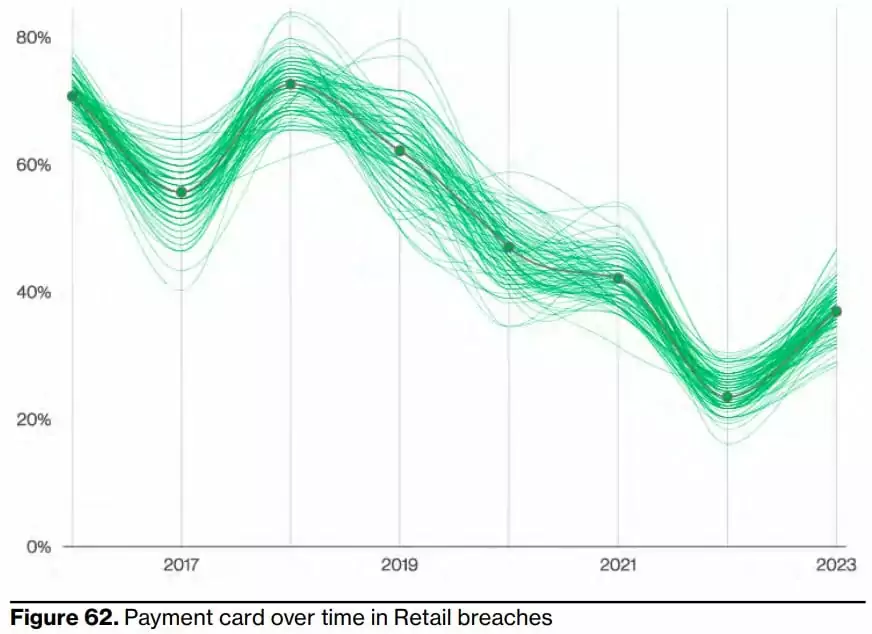
12- Stolen payment card details are on the rise again.
Given the function of the retail industry, it’s no surprise that payment card data is one of the most commonly breached data types, accounting for 37% of breaches this year. However, you can easily observe that while there has been a significant increase in stolen payment card data compared to last year, it has been on a downward trend since its peak in 2018. While stealing card data is a tried-and-true way to make money, sometimes, as in the case of ransomware, the threat actor wants a faster payday. Therefore, the report suggests that being the target of a ransomware attack has been shown to skew the data in this industry.
Conclusion
The Verizon 2023 DBIR contains important headlines that deserve to be highlighted and discussed throughout the year as before. Data breaches seriously threaten the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data organizations must protect. It not only causes a loss of reputation and prestige but also puts organizations in difficulty in the face of regulations and compliance processes. One of the reasons for that is cybersecurity measures are not taken professionally at the state-of-the-art level in parallel with digitalization. So, board members need to put security concerns on the table. Especially considering the BEC attacks can also be increased by compromising the accounts of C-level executives within the organization, SOCRadar VIP Protection can be a useful solution.
Stolen credentials are commonly used for “initial access” to bypass cyber defense lines, even as MFA becomes widespread. Such information can be sold cheaply on dark web markets and sometimes distributed free of charge. As a result, it becomes easy for those without technical competence to get involved in cyber-attacks. It is critical that you obtain actionable intelligence information and alerts via SOCRadar Digital Risk Protection on dark web channels on time.
Ransomware is the main agenda item this year, as in previous years. The easy and profitable way that ransomware gangs distribute this type of malware using the RaaS model has a considerable impact on this trend. Legal and technical hardening against ransomware attacks, which constantly appear with new actors and improve their methods, requires being proactive. The spiking popularity of cryptocurrencies led to continuing to be targeted by cyber attackers through extensions in browsers and applications on mobile phones. Finally, with the expansion of the botnets, DDoS attacks break records every year and continue to be the most crucial tool of cyber hacktivist groups like KillNet.